Pacific Coast Railway
| Pacific Coast Railway | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Locale | California |
| Dates of operation | 1882–1941 |
| Track gauge | 3 ft (914 mm) |
| Length | 76 miles (122 km)[1] |
| Headquarters | San Luis Obispo |
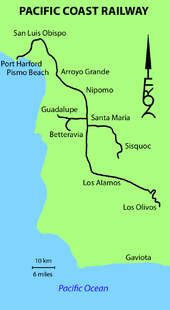
The Pacific Coast Railway is a defunct 3 ft (914 mm) narrow gauge railway in the Central Coast of California. The original 10 mile (16 km) link from San Luis Obispo to Avila Beach and Port Harford was later built southward to Santa Maria and Los Olivos, with branches to Sisquoc and Guadalupe.
Origins
Pacific Coast Steamship Company offered transport to Los Angeles and San Francisco in 1873 from a wharf at Port Harford serving communities of the Santa Maria Valley. A horse-powered, 2 ft 6 in (762 mm) gauge tramway transported passengers and freight between Port Harford and a wagon road at Avila Beach. In 1876, the steamship company replaced the tram with the 3 ft (914 mm) narrow gauge steam-powered San Luis Obispo & Santa Maria Valley Railroad to San Luis Obispo. Operations began with ten boxcars and one coach pulled by a 2-4-2 and a 4-4-0 built by Baldwin Locomotive Works. San Luis Obispo rail yard warehouses became a commercial center for inbound merchandise and outgoing shipments of hay, grain, dairy products, sheep and cattle. The rail line was extended from San Luis Obispo to Arroyo Grande in 1881 and to Santa Maria in 1882. Grant Locomotive Works built another 4-4-0 and two 2-6-0 locomotives to pull a fleet of new flatcars.[1]
Reorganization
Oregon Improvement Company obtained controlling interest in the Pacific Coast Steamship Company in late 1882, reorganized the railroad as the Pacific Coast Railway, and extended the line to Los Alamos. The next project was to replace the heavy grade of the original tramway alignment with a deep rock cut and long fill. The line was then extended to Los Olivos in 1887. A fire in 1892 destroyed the San Luis Obispo car shops, grain warehouse, loaded freight cars, half of the railroad's passenger cars and all the cabooses while heavily damaging the station and freight warehouse. Operations were profitable enough to promptly repair the damage. Passenger traffic though Port Harford declined when Southern Pacific reached San Luis Obispo from San Francisco in 1894. Southern Pacific freight rates were high enough to keep most Santa Maria Valley freight on the steamboats; but the loss of passenger traffic put the Oregon Improvement Company into receivership. The reorganized railroad built a 4 miles (6.4 km) branch line in 1899 from Santa Maria to a new Union Sugar Company beet refinery in Betteravia.[1]
Boom Years
The increased agricultural business was shortly overshadowed by discovery of oil in the Santa Maria Valley. By 1902 the railroad had converted its engines to burn oil and was strapping tanks from standard gauge cars onto their flatcars at the rate of ten per month. The railway's three 2-6-0 locomotives were inadequate to move all the oil to storage tanks near San Luis Bay. Five new Baldwin 2-8-0s were delivered by 1906 as the freight car fleet expanded to two hundred cars. The Betteravia branch was electrified in 1906 and extended to Guadalupe in 1909. Another electrified branch was built in 1910 to serve an oil refinery near Sisquoc.[1] Three center-cab electric locomotives worked the branches with a center-door interurban car built by Cincinnati Car Company in 1912.[2]
Decline
The 4 ft 8 1⁄2 in (1,435 mm) standard gauge Santa Maria Valley Railroad was built parallel to the electrified branch of the narrow gauge. Santa Maria Valley agriculture slowly shifted from sugar beets to produce which could be loaded directly onto Southern Pacific refrigerator cars. The sugar beet factory closed in 1927, and electric operations ended in 1928, although steam locomotives still worked the branches occasionally. Profits peaked in 1921 and declined as automobiles became more common, but the railroad saw a brief increase in business hauling gravel for construction of U.S. Route 101 in 1928 and '29. The gravel business required purchase of two 2-8-0s from the recently standard-gauged Nevada–California–Oregon Railway to replace Pacific Coast 2-8-0s dismantled for parts to keep the other engines running. Service to Los Olivos was reduced to a twice-weekly mixed train by 1930 and ended in 1933. A used Plymouth Locomotive Works gasoline switcher was purchased in 1936. The line beyond Los Alamos was dismantled in 1936, and the branch lines were dismantled in 1937. In 1938 locomotive number 106 was destroyed in a grade crossing collision with a gasoline truck, and the last three coaches and a baggage car were sold to the White Pass and Yukon Route. A single combine car numbered 106 was the last piece of passenger equipment. The United States Navy bought the boxcars for use at Naval Station Pearl Harbor when operations ended in 1941; and locomotive number 111 went to the Oahu Railway and Land Company. Bell Oil Company briefly used the railway north of Santa Maria until the line was dismantled in 1942. Most of the remaining equipment was cut up for scrap by 1948, but caboose number 2 has been preserved at the California State Railroad Museum.[1]
See also
- List of heritage railroads in the United States
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 Vail, Jim (1994). "Pacific Coast Rwy.". Railroad Model Craftsman (Carstens Publications) (April): 71–77.
- ↑ Demoro, Harre W. (1986). California's Electric Railways. Glendale, California: Interurban Press. p. 202. ISBN 0-916374-74-2.
Further reading
- Best, Gerald (1964). Ships and narrow gauge rails; the story of the Pacific Coast Company. Howell-North.
- Westcott, Kenneth & Johnson, Curtiss (1998). The Pacific Coast Railway: Central California's Premier Narrow Gauge. Benchmark Publications.
External links
- http://www.slorrm.com - San Luis Obispo Railroad Museum
- http://www.csrmf.org - California State Railroad Museum, which has restored PCRy caboose No. 2.