Oxypurinol
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
| Oxypurinol | |
|---|---|
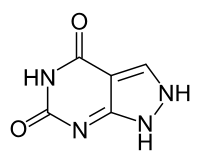 | |
| 1,2-Dihydropyrazolo[4,3-e]pyrimidine-4,6-dione | |
| Systematic name 1H,2H,4H,5H,6H-pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidine-4,6-dione | |
| Other names 1H,2H,5H-pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidine-4,6-dione | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | 2465-59-0 |
| PubChem | 4644 |
| ChemSpider | 4483 |
| UNII | G97OZE5068 |
| EC number | 219-570-9 |
| KEGG | C07599 |
| MeSH | Oxypurinol |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:28315 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL859 |
| Beilstein Reference | 139956 |
| Jmol-3D images | Image 1 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| Molecular formula | C5H4N4O2 |
| Molar mass | 152.11086 |
| Appearance | white crystals |
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |
| Infobox references | |
Oxypurinol is an inhibitor of xanthine oxidase. It is an active metabolite of allopurinol and it is cleared renally. In cases of renal disease, this metabolite will accumulate to toxic levels. Its function as an inhibitor of xanthine oxidase allows it to help inhibit gout production.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike; additional terms may apply for the media files.