Oxazolidine
| Oxazolidine | ||
|---|---|---|
 | ||
| IUPAC name oxazolidine | ||
| Other names 1,3-oxazolidine | ||
| Identifiers | ||
| CAS number | 504-76-7 | |
| Jmol-3D images | Image 1 | |
| ||
| Properties | ||
| Molecular formula | C3H7NO | |
| Molar mass | 73.0938 g/mol | |
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | ||
| Infobox references | ||
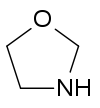
An Oxazolidine is a five-membered ring compound consisting of three carbons, a nitrogen, and an oxygen. The oxygen and NH are the 1 and 3 positions, respectively. In oxazolidine derivatives, there is always a carbon between the oxygen and the nitrogen (or it would be an isoxazolidine).[1][2] All of the carbons in oxazolidines are reduced (compare to oxazole and oxazoline). Some of their derivatives, the oxazolidinediones, are used as anticonvulsants.
Bisoxazolidines
Bisoxazolidines are chemical compounds that contain two oxazolidine rings, they are used as performance modifiers in polyurethane coatings and paints. The rings hydrolyze in the presence of moisture to give amine and hydroxyl groups, these can then react with diisocyanates to form a coating.[3] The use of a bisoxazolidine in a polyurethane systems can prevent the unwanted reaction between isocyanate and moisture resulting in coating defects, a result of carbon dioxide release. This moisture triggered curing route is preferential to moisture cure.
The choice of linker between the two oxazolidine rings has a large impact on the performance when used to cure isocyanates. A rigid linker group increases a polyurethanes toughness. A flexible linker group imparts flexibility and increases elongation of a coating. These differences are the reason why bisoxazolidines are used to enhance the performance of polyurethane systems.
Isoxazolidines
In an isoxazolidine nitrogen and oxygen occupy positions 1 and 2 in the ring:
It is the saturated relative of Isoxazole.
See also
- Imidazole, an analog with the oxygen replaced by a nitrogen.
- Thiazole, an analog with the oxygen replaced by a sulfur.
- Benzoxazole, where the oxazole is fused to another aromatic ring.
- Pyrrole, an analog without the oxygen atom.
- Furan, an analog without the nitrogen atom.
- Oxazoline, which has only one double bond reduced.
- Oxazolidinedione, which has two in-cycle keto groups (a carbamate and a lactam).
- Oxazolidinone, which has an in-cycle carbamate.
References
- ↑ "SID 3881507 -- PubChem Substance Summary". The PubChem Project. United States National Center for Biotechnology Information. Retrieved 13 December 2005.
- ↑ Dr Neil G Carter OXAZOLIDINE DILUENTS: REACTING FOR THE ENVIRONMENT Industrial Copolymers Limited
- ↑ Emission control chembytes e-zine 2001.
