Otsu's method


In computer vision and image processing, Otsu's method is used to automatically perform clustering-based image thresholding,[1] or, the reduction of a graylevel image to a binary image. The algorithm assumes that the image to be thresholded contains two classes of pixels or bi-modal histogram (e.g. foreground and background) then calculates the optimum threshold separating those two classes so that their combined spread (intra-class variance) is minimal.[2] The extension of the original method to multi-level thresholding is referred to as the Multi Otsu method.[3] Otsu's method is named after Nobuyuki Otsu (大津展之 Ōtsu Nobuyuki).
Method
In Otsu's method we exhaustively search for the threshold that minimizes the intra-class variance (the variance within the class), defined as a weighted sum of variances of the two classes:
Weights 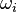 are the probabilities of the two classes separated
by a threshold
are the probabilities of the two classes separated
by a threshold 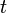 and
and  variances of these classes.
variances of these classes.
Otsu shows that minimizing the intra-class variance is the same as maximizing inter-class variance:[2]
which is expressed in terms of class probabilities 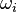 and
class means
and
class means 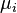 .
.
The class probability 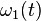 is computed from the histogram as
is computed from the histogram as 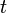 :
:
while the class mean  is:
is:
where 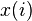 is the value at the center of the
is the value at the center of the  th histogram bin.
Similarly, you can compute
th histogram bin.
Similarly, you can compute  and
and 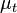 on the right-hand side
of the histogram for bins greater than
on the right-hand side
of the histogram for bins greater than 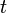 .
.
The class probabilities and class means can be computed iteratively. This idea yields an effective algorithm.
Algorithm
- Compute histogram and probabilities of each intensity level
- Set up initial
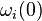 and
and 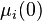
- Step through all possible thresholds
 maximum intensity
maximum intensity
- Update
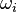 and
and 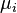
- Compute

- Update
- Desired threshold corresponds to the maximum

- You can compute two maxima (and two corresponding thresholds).
 is the greater max and
is the greater max and 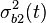 is the greater or equal maximum
is the greater or equal maximum - Desired threshold =
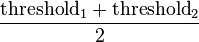
JavaScript implementation
NB: Argument 'total' is the number of pixels in the image. Argument 'histogram' is a 256-element histogram of a greyscale image with 256 different grey-levels (typical for 8-bit images).
function otsu(histogram, total) { var sum = 0; for (var i = 1; i < 256; ++i) sum += i * histogram[i]; var sumB = 0; var wB = 0; var wF = 0; var mB; var mF; var max = 0.0; var between = 0.0; var threshold1 = 0.0; var threshold2 = 0.0; for (var i = 0; i < 256; ++i) { wB += histogram[i]; if (wB == 0) continue; wF = total - wB; if (wF == 0) break; sumB += i * histogram[i]; mB = sumB / wB; mF = (sum - sumB) / wF; between = wB * wF * Math.pow(mB - mF, 2); if ( between >= max ) { threshold1 = i; if ( between > max ) { threshold2 = i; } max = between; } } return ( threshold1 + threshold2 ) / 2.0; }
References
- ↑ M. Sezgin and B. Sankur (2004). "Survey over image thresholding techniques and quantitative performance evaluation". Journal of Electronic Imaging 13 (1): 146–165. doi:10.1117/1.1631315.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Nobuyuki Otsu (1979). "A threshold selection method from gray-level histograms". IEEE Trans. Sys., Man., Cyber. 9 (1): 62–66. doi:10.1109/TSMC.1979.4310076.
- ↑ Ping-Sung Liao and Tse-Sheng Chen and Pau-Choo Chung (2001). "A Fast Algorithm for Multilevel Thresholding". J. Inf. Sci. Eng. 17 (5): 713–727.
External links
- Lecture notes on thresholding - covers the Otsu method.
- A plugin for ImageJ using,/.,/,.?>?, Otsu's method to do the threshold.
- A full explanation of Otsu's method with a worked example and Java implementation.
- Implementation of Otsu's method in ITK
- Otsu Thresholding in C# A straightforward C# implementation with explanation.
- Ostu's method using MATLAB
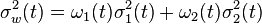
![\sigma _{b}^{2}(t)=\sigma ^{2}-\sigma _{w}^{2}(t)=\omega _{1}(t)\omega _{2}(t)\left[\mu _{1}(t)-\mu _{2}(t)\right]^{2}](/2014-wikipedia_en_all_02_2014/I/media/8/9/4/8/894892ba54d00a159aaebfb515c6643d.png)
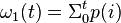
![\mu _{1}(t)=\left[\Sigma _{0}^{t}p(i)\,x(i)\right]/\omega _{1}](/2014-wikipedia_en_all_02_2014/I/media/5/8/0/8/5808e003ae2e65d8b7de35bbf571d18a.png)