Orientin
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
| Orientin | ||
|---|---|---|
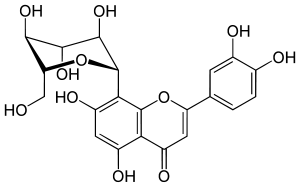 | ||
| IUPAC name 2-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-5,7-dihydroxy-8-[(2S,3R,4R,5S,6R)-3,4, 5-trihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-2-yl]chromen-4-one | ||
| Other names Lutexin, Luteolin-8-C-glucoside | ||
| Identifiers | ||
| CAS number | 28608-75-5 | |
| PubChem | 5281675 | |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:7781 | |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL239559 | |
| Jmol-3D images | Image 1 | |
| ||
| Properties | ||
| Molecular formula | C21H20O11 | |
| Molar mass | 448.38 g/mol | |
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | ||
| Infobox references | ||
Orientin is a flavone, a chemical flavonoid-like compound. It is the 8-C glucoside of luteolin.
Natural occurrences
Orientin is found in Adonis vernalis, in Anadenanthera colubrina and Anadenanthera peregrina, and in the Phyllostachys nigra bamboo leaves[1]
- in food
Orientin is also reported in the passion flower,[2] the Açaí palm and in millets.[3]
See also
Isoorientin (or homoorientin) is the luteolin-6-C-glucoside.
References
- ↑ Isolation and purification of four flavone C-glycosides from antioxidant of bamboo leaves by macroporous resin column chromatography and preparative high-performance liquid chromatography. Yu Zhang, Jingjing Jiao, Chengmei Liu, Xiaoqin Wu and Ying Zhang, Food Chemistry, 1 April 2008,, Volume 107, Issue 3, Pages 1326–1336, doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2007.09.037
- ↑ Separation by capillary electrophoresis of C-glycosylflavonoids in Passiflora sp. extracts. E. R. Pastene, G. Bocaz, I. Peric, M. Montes, V. Silva and E. Riffo, Bol. Soc. Chil. Quím., v.45 n.3 Concepción set. 2000, doi:10.4067/S0366-16442000000300017
- ↑ Sorghum and millet phenols and antioxydants, Linda Dykes, Lloyd W. Rooney, in Journal of Cereal Science, 2006, 44, pages 236-251, doi:10.1016/j.jcs.2006.06.007
External links
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike; additional terms may apply for the media files.