Optic canal
| Optic foramen | |
|---|---|
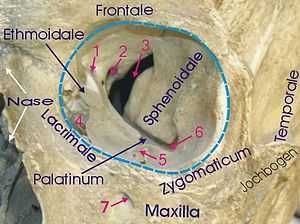 | |
| 1: Foramen ethmoidale 2: Canalis opticus 3: Fissura orbitalis superior 4: Fossa sacci lacrimalis 5: Sulcus infraorbitalis 6: Fissura orbitalis inferior 7: Foramen infraorbitale | |
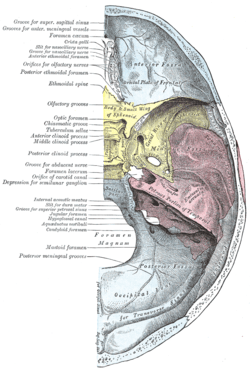 | |
| Base of the skull. Upper surface. (On the left, "Optic foramen" is the 12th label from the top. | |
| Latin | canalis opticus, foramen opticum ossis sphenoidalis |
| Gray's | p.147 |
The optic foramen is the opening to the optic canal.
The superior surface of the sphenoid bone is bounded behind by a ridge, which forms the anterior border of a narrow, transverse groove, the chiasmatic groove (optic groove), above and behind which lies the optic chiasma; the groove ends on either side in the optic foramen, which transmits the optic nerve and ophthalmic artery (with accompanying sympathetic nerve fibres) into the orbital cavity.
The left and right optic canals are 25mm apart posteriorly and 30mm apart anteriorly. They are funnel-shaped (narrowest anteriorly).
Additional images
-

The seven bones which articulate to form the orbit.
-

Sphenoid bone. Upper surface.
-

Medial wall of left orbit.
-

Dissection showing origins of right ocular muscles, and nerves entering by the superior orbital fissure.
-

Optic canal
See also
- Foramina of skull
External links
- 29:os-0501 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center
- eye_6 at the University of Michigan Health System - (look for #3)
- Anatomy at PSU skel/internal2 (look for #10)
This article incorporates text from a public domain edition of Gray's Anatomy.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||