Ophthalmic nerve
| Nerve: Ophthalmic nerve | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Oblique section through the cavernous sinus. | |
 | |
| Nerves of the orbit, and the ciliary ganglion. Side view. | |
| Latin | n. ophthalmicus |
| Gray's | p.887 |
| From | trigeminal nerve |
| MeSH | Ophthalmic+Nerve |
The ophthalmic nerve (V1) is one of the three branches of the trigeminal nerve, the fifth cranial nerve. The ophthalmic nerve carries only sensory fibers.[1]
Branches
Path
The ophthalmic nerve supplies branches to the cornea, ciliary body, and iris; to the lacrimal gland and conjunctiva; to the part of the mucous membrane of the nasal cavity; and to the skin of the eyelids, eyebrow, forehead and nose.
It is the smallest of the three divisions of the trigeminal, and arises from the upper part of the trigeminal ganglion as a short, flattened band, about 2.5 cm. long, which passes forward along the lateral wall of the cavernous sinus, below the oculomotor and trochlear nerves; just before entering the orbit, through the superior orbital fissure, it divides into three branches, lacrimal, frontal, and nasociliary.
The frontal branch passes through the orbit superiorly, then reenters the frontal bone briefly before exiting above the orbit through the supraorbital foramen and the supratrochlear notch to provide sensory innervation for the skin of the forehead and scalp. The lacrimal nerve passes through the orbit superiorly to innervate the lacrimal gland. The nasociliary branch gives off several sensory branches to the orbit and then continues out through the anterior ethmoidal foramen, where it enters the nasal cavity and provides innervation for much of the anterior nasal mucosa. It also gives off a branch which exits through the nasal bones to form the external nasal branch.
The ophthalmic nerve is joined by filaments from the cavernous plexus of the sympathetic, and communicates with the oculomotor, trochlear, and abducent nerves; it gives off a recurrent (meningeal) filament which passes between the layers of the tentorium.
Additional images
-
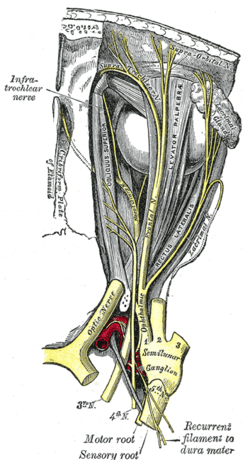
Nerves of the orbit. Seen from above.
-

Dermatome distribution of the trigeminal nerve
-

Pathways in the ciliary ganglion.
-

Ophthalmic nerve
-
Ophthalmic nerve
-
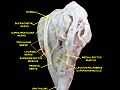
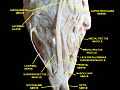
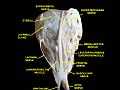
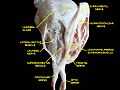
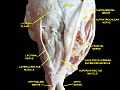
Extrinsic eye muscle. Nerves of orbita. Deep dissection.
-
Extrinsic eye muscle. Nerves of orbita. Deep dissection.
-
Extrinsic eye muscle. Nerves of orbita. Deep dissection.
-
Extrinsic eye muscle. Nerves of orbita. Deep dissection.
-
Extrinsic eye muscle. Nerves of orbita. Deep dissection.
This article incorporates text from a public domain edition of Gray's Anatomy.
References
External links
- MedEd at Loyola GrossAnatomy/h_n/cn/cn1/cnb1.htm
- eye_33 at the University of Michigan Health System
- cranialnerves at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University) (V)
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||