Operator (biology)
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
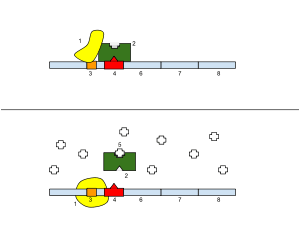
1: RNA Polymerase, 2: Repressor, 3: Promoter, 4: Operator, 5: Lactose, 6: lacZ, 7: lacY, 8: lacA.
Top: An operator is a segment of DNA that acts as an on/off switch for transcription. The gene is essentially turned off. There is no lactose to inhibit the repressor, so the repressor binds to the operator, which obstructs the RNA polymerase from binding to the promoter and making lactase.
Bottom: The gene is turned on. Lactose is inhibiting the repressor, allowing the RNA polymerase to bind with the promoter, and express the genes, which synthesize lactase. Eventually, the lactase will digest all of the lactose, until there is none to bind to the repressor. The repressor will then bind to the operator, stopping the manufacture of lactase.
In genetics, an operator is a segment of DNA to which a transcription factor protein binds. It is classically defined in the lac operon as a segment between the promoter and the genes of the operon. In the case of a repressor, the repressor protein physically obstructs the RNA polymerase from transcribing the genes. An inducer (protein) can displace a repressor (protein) from the operator site (DNA), which results in an uninhibited operon.
Also, an operator regulates "gene expression."
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike; additional terms may apply for the media files.