Operation Blackcock
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
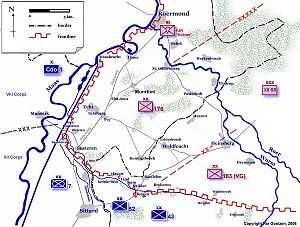
Operation Blackcock was World War II operation to clear German troops from the Roer Triangle, formed by the towns of Roermond and Sittard in the Netherlands and Heinsberg in Germany. It was conducted by the British Second Army between 14-26 January 1945. The objective was to drive the German 15th Army back across the Rivers Rur and Wurm and move the frontline further into Germany. The operation was carried out under the command of XII Corps by three divisions: the 7th Armoured Division (better known as the "Desert Rats"), the 52nd (Lowland) and the 43rd (Wessex) ("Wessex Wyverns") Infantry Divisions. The operation, named after the Scottish black male grouse, is relatively unknown despite the sometimes fierce battles that were fought for each and every village and hamlet within the Roer Triangle.
Dispositions along the Roer Front
By the end of 1944, the frontline in Dutch Limburg had stabilized along several natural barriers. By far the most difficult barrier to cross was the River Maas running along the Dutch - Belgian border. The next barrier was the River Rur, running from the German Eifel area through Heinsberg towards Roermond, where it joins the Maas. From Heinsberg, southwards the famous Siegfried Line or 'West Wall' was formed along the banks of the Rur. Dutch South-Limburg was already liberated in September by the Ninth United States Army, but the area above the Sittard - Geilenkirchen line was still in German hands. Here the front had settled along the "Saefeller Beek", a small creek forming another seemingly immense obstacle. These obstacles formed a triangular area, indeed; it was referred to as the Roermond Triangle, which protruded like a small bulge into the frontline. As a result of the German offensive - Operation Herbstnebel - in the Ardennes (also known as the Battle of the Bulge). The Allies had to withdraw resources to stop the German advance in the American First Army's sector. Therefore the British Second Army's XII Corps, had taken over the task of guarding the frontline north of Sittard for the US Army. The Maas front was guarded by the British VIII Corps.
The British XII Corps was facing the German XII SS Corps, commanded by Günther Blumentritt, which had two infantry divisions present along the frontline between Geilenkirchen and Roermond. In the Roermond area these divisions were strengthened by the Fallschirmjäger-Regiment Hübner.
Concept of the Operation
The clearing of the Roer Triangle was planned along three axes. The left axis, formed by the 7th Armoured Division, was aimed at capturing the bridge across the Roer in Sint Odiliënberg (51°8′55.9″N 6°0′12.6″E / 51.148861°N 6.003500°E). For the 7th, the operation would start with bridging the creeks south of Susteren. The centre axis, formed by the 52nd Lowland Division, was aimed at the capture of Heinsberg. In order to do this, a break-through at the German defence line was to be undertaken near Hongen in order to open the road between Sittard and Heinsberg for moving troops. The right axis, formed by the 43rd Wessex Division, was aimed at clearing the area south-east of Dremmen. This axis would use the break in the German defence line that was to be created by the Lowland Division.
VC Actions

The Victoria Cross was awarded twice, both posthumously, for actions during Operation Blackcock. It (the VC), is the highest award for valour that can be awarded to members of the British and Commonwealth armed forces of any rank in any service and civilians under military command. It is only awarded for bravery "in the face of the enemy". Fusilier Dennis Donnini of the 4/5 Royal Scots Fusiliers, 52nd Lowland Division, received the VC after his heroic actions in the village of Stein in Selfkant on 18 January. Fusilier Donnini is buried at the Sittard War Cemetery (Netherlands). The second VC was awarded to Lance Corporal Henry Eric Harden of the Royal Army Medical Corps (RAMC), a medical orderly attached to 45 Commando, for his heroic action during the bitter fighting at the Dutch villages of Brachterbeek and Linne on 23 January. Lance Corporal Harden is buried at Nederweert War Cemetery (Netherlands).
Hübner's defeat at Sint Joost

The Battle for the Dutch village of Sint Joost was a turning point in Operation Blackcock. After four days of fighting, the Germans were well aware that the armoured division that was facing them relied heavily on the roads to manoeuvre their vehicles, especially due to poor winter conditions. The small village of Sint Joost was on the route of the 7th Armoured Division’s drive north towards Montfort. On 20 January, in cold and misty weather, infantry and cavalry units of the Desert Rats launched a first attack on the (assumed) two German companies of the 2nd Battalion Fallschirmjäger Regiment Hübner in Sint Joost. It would take four attacks to clear the village, the final assault taking place on Sunday, 21 January. In total, sixty Fallschirmjäger were taken prisoner. The 9th Durham Light Infantry and 1st Rifle Brigade had suffered heavy losses in Sint Joost. The DLI suffered 33 casualties, of which eight were killed in action. The Rifle Brigade counted 34 casualties, of which three men from I Company were killed in action. More than one hundred German soldiers died, most of them lying in the houses. Those paratroopers who were not killed only dared to leave the cellars under safe cover of the civilians, afraid that they would be shot by the victors. Hübner had lost one company and a second had been nearly destroyed.
The Bombing Raids on Montfort
Between Friday evening 19 January and Tuesday 23 January the Dutch village of Montfort was shelled or bombed on seven occasions, and was hit by more than 100 bombs. Most of these fell in the centre of the village. Nearly all of the 250 houses were damaged. Some houses were no more than ruins, and entire families were killed. During these raids the Germans took shelter in the cellars among the civilians, and in the wooded areas just outside the village. The bombing raids that struck Montfort on the 21st and 22nd were carried out by the Royal Canadian Air Force (RCAF) 2nd Tactical Air Force - No. 83 Group - 143 Wing. This Wing consisted of 438, 439 and 440 Squadron, based at Eindhoven. The squadrons were equipped with the Hawker Typhoon 1B fighter bomber. 143 Wing lost six aircraft during Operation Blackcock, two of which crashed in Montfort. When Montfort was finally liberated by the "Desert Rats" on 24 January, the civilians were in a deep state of shock. The air raids on Montfort had cost the lives of 186 civilians, most of them buried under their destroyed homes.

Aftermath
Operation Blackcock was a success for the Allies since all the objectives of the operation were met. The German divisions were thrown out of the Roer Triangle with the exception of the area immediately south of Roermond. Here Hübner's paratroopers stayed in control for the time being. The British Division that fought the toughest battles during the operation was without doubt the 52nd Lowland which counted 752 casualties. Of these 101 were killed. 258 soldiers were transported from the front because of sickness, mostly as a direct result of the adverse weather conditions and the extreme cold. The 7th Armoured Division counted just over 400 casualties. The Desert Rats losses in vehicles was rather light, with only 20 tanks knocked out by the enemy and a further 23 broken down due to mechanical problems. Of the knocked-out tanks 10 were damaged beyond repair. The number of German casualties is unknown, it can be estimated to be approximately 2,000. During the operation 490 prisoners were taken by the Desert Rats, amongst them were six officers. The Lowland Division took more than 1,200 prisoners, the Wessex Division took some 400 soldiers captive.
Once Operation Blackcock was completed, the plans for the capture of the Rhineland could commence. Operation Veritable, by the First Canadian Army, was launched on 8 February and was aimed at breaking through the German defences in the Klever Reichswald, some 60 km (37 mi) north of the Roer Triangle. Operation Grenade, the southern part of the pincer movement, by the US Ninth Army was launched on 23 February. General William Hood Simpson's US Ninth Army crossed the river Roer south of Heinsberg in the early hours of 23 February 1945. Twelve hours later Simpson had 16 battalions on the east bank, together with seven heavy bridges, and a number of light assault bridges. American losses were light on the first day; 700 prisoners were taken. A task force was formed by Ninth Army's XVI Corps which rushed towards Venlo to meet-up with the British in the north. On 1 March Roermond was captured by the reconnaissance troop of the US 35th Infantry Division (the "Santa Fe" Division) without a single shot being fired.