Numerical range
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
In the mathematical field of linear algebra and convex analysis, the numerical range or field of values of a complex n × n matrix A is the set
where x* denotes the Hermitian adjoint of the vector x.
In engineering, numerical ranges are used as a rough estimate of eigenvalues of A. Recently, generalizations of numerical range are used to study quantum computing.
A related concept is the numerical radius, which is the largest absolute values of the numbers in the numerical range, i.e.
r(A) is a norm.
Properties
- The numerical range is the range of the Rayleigh quotient.
- (Hausdorff–Toeplitz theorem) The numerical range is convex and compact.
-
 for all square matrix A and complex numbers α and β. Here I is the identity matrix.
for all square matrix A and complex numbers α and β. Here I is the identity matrix. -
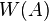 is a subset of the closed right half-plane if and only if
is a subset of the closed right half-plane if and only if 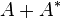 is positive semidefinite.
is positive semidefinite. - The numerical range
 is the only function on the set of square matrices that satisfies (2), (3) and (4).
is the only function on the set of square matrices that satisfies (2), (3) and (4). - (Sub-additive)
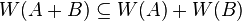 .
. -
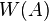 contains all the eigenvalues of A.
contains all the eigenvalues of A. - The numerical range of a 2×2 matrix is an elliptical disk.
-
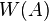 is a real line segment [α, β] if and only if A is a Hermitian matrix with its smallest and the largest eigenvalues being α and β
is a real line segment [α, β] if and only if A is a Hermitian matrix with its smallest and the largest eigenvalues being α and β - If A is a normal matrix then
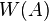 is the convex hull of its eigenvalues.
is the convex hull of its eigenvalues. - If α is a sharp point on the boundary of
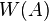 , then α is a normal eigenvalue of A.
, then α is a normal eigenvalue of A. -
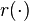 is a norm on the space of n×n matrices.
is a norm on the space of n×n matrices. -

Generalisations
- C - numerical range
- Higher rank numerical range
- Joint numerical range
- Product numerical range
See also
References
- Bibliography
- Choi, M.D.; Dribs, D.W.; Życzkowski (2006), "Quantum error correcting codes from the compression formalism", Rep. Math. Phys., 58, 2006.
- Dirr, G.; Helmkel, U.; Kleinsteuber, M.; Schulte-Herbrüggen, Th. (2006), "A new type of C-numerical range arising in quantum computing", Proc. Appl. Math. Mech. 6, 711–712 (2006).
- Bonsall, F.F.; Duncan, J. (1971), Numerical Ranges of Operators on Normed Spaces and of Elements of Normed Algebras, Cambridge University Press, ISBN 978-0-521-07988-4.
- Bonsall, F.F.; Duncan, J. (1971), Numerical Ranges II, Cambridge University Press, ISBN 978-0-521-20227-2 Check
|isbn=value (help). - Horn, Roger A.; Johnson, Charles R. (1991), Topics in Matrix Analysis, Cambridge University Press, ISBN 978-0-521-46713-1.
- Li, C.K. (1996), "A simple proof of the elliptical range theorem", Proc. Am. Math. Soc. 124, 1985.
- Keeler, Dennis S.; Rodman, Leiba; Spitkovsky, Ilya M. (1997), "The numerical range of
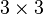 matrices", Linear Algebra Applications 252, 115.
matrices", Linear Algebra Applications 252, 115. - Roger A. Horn and Charles R. Johnson, Topics in Matrix Analysis, Chapter 1, Cambridge University Press, 1991. ISBN 0-521-30587-X (hardback), ISBN 0-521-46713-6 (paperback).
- "Functional Characterizations of the Field of Values and the Convex Hull of the Spectrum", Charles R. Johnson, Proceedings of the American Mathematical Society, 61(2):201-204, Dec 1976.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike; additional terms may apply for the media files.

