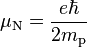Nuclear magneton
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
The nuclear magneton (symbol μN), is a physical constant of magnetic moment, defined in SI units by:
and in Gaussian CGS units by:
where:
- e is the elementary charge,
- ħ is the reduced Planck constant,
- mp is the proton rest mass, and
- c is the speed of light
In SI units, its value is approximately:
In Gaussian CGS units, its value can be given in convenient units as
The nuclear magneton is the natural unit for expressing magnetic dipole moments of heavy particles such as nucleons and atomic nuclei. On the contrary, the dipole moment of the electron, which is much higher as a consequence of much higher charge-to-mass ratio, is usually expressed in corresponding units of the Bohr magneton.
See also
- Proton magnetic moment
- Neutron magnetic moment
- Bohr magneton
External links
- Nuclear magneton, value from CODATA
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike; additional terms may apply for the media files.