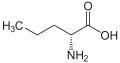
Norvaline
| Norvaline | ||
|---|---|---|
 |
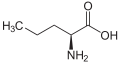 | |
| IUPAC name 2-Aminopentanoic acid | ||
| Other names 2-Aminopentyric acid; α-Aminopentanoic acid; Propylglycine | ||
| Identifiers | ||
| CAS number | 6600-40-4 | |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL55612 | |
| Jmol-3D images | Image 1 | |
| ||
| ||
| Properties | ||
| Molecular formula | C5H11NO2 | |
| Molar mass | 117.15 g mol−1 | |
| Acidity (pKa) | 2.36 (carboxyl), 9.76 (amino)[1] | |
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | ||
| Infobox references | ||
Norvaline is an amino acid with the chemical formula C5H11NO2. It is a constitutional isomer with valine. This amino acid is often made synthetically.[2]
Background
Norvaline is a non-proteinogenic branched-chain amino acid. It has previously been reported to be a natural component of an antifungal peptide of Bacillus subtilis. Norvaline and other modified branched chain amino acids have received attention in recent studies, as they appear to be incorporated in some recombinant proteins found in E. coli.[3]
Norvaline is known to promote tissue regeneration and muscle growth, and to become a precursor in the penicillin biosynthetic pathway.[4][5]
Norvaline and norleucine (1 hydrocarbon group longer) both possess the nor- prefix for historical reason, despite current conventional usage of the prefix to denote a missing hydrocarbon group (under which they would theoretically be called "dihomoalanine" and "trihomoalanine").
References
- ↑ Dawson, R.M.C., et al., Data for Biochemical Research, Oxford, Clarendon Press, 1959.
- ↑ Merriam-Webster Retrieved 4 September 2010
- ↑ microbialcellfactories.com Retrieved 4 September 2010
- ↑ reference.md Retrieved 4 September 2010
- ↑ Kisumi; Sugiura, Chibata (Aug 1976). "Biosynthesis of norvaline, norleucine, and homoisoleucine in Serratia marcescens.". J. Biochem. 80 (2): 333–9. PMID 794063.