Vikings

The Vikings (from Old Norse víkingr) were seafaring north Germanic people who raided, traded, explored, and settled in wide areas of Europe, Asia, and the North Atlantic islands from the late 8th to the mid-11th centuries.[1] The Vikings employed wooden longships with wide, shallow-draft hulls, allowing navigation in rough seas or in shallow river waters. The ships could be landed on beaches, and their light weight enabled them to be hauled over portages. These versatile ships allowed the Vikings to travel as far east as Constantinople and the Volga River in Russia, as far west as Iceland, Greenland, and Newfoundland, and as far south as Nekor.[2] This period of Viking expansion, known as the Viking Age, constitutes an important element of the medieval history of Scandinavia, Great Britain, Ireland, Russia, and the rest of Europe.
Popular conceptions of the Vikings often differ from the complex picture that emerges from archaeology and written sources. A romanticised picture of Vikings as noble savages began to take root in the 18th century, and this developed and became widely propagated during the 19th-century Viking revival.[3] The received views of the Vikings as violent brutes or intrepid adventurers owe much to the modern Viking myth that had taken shape by the early 20th century. Current popular representations are typically highly clichéd, presenting the Vikings as familiar caricatures.[3]
Etymology

The Old Norse feminine noun víking refers to an expedition overseas. It occurs in Viking Age runic inscriptions and in later medieval writings in set expressions such as the phrasal verb fara í víking "to go on an expedition". In later texts, such as the Icelandic sagas, the phrase "to go on a viking" implies participation in raiding activity or piracy and not simply seaborne missions of trade and commerce. The derived Old Norse masculine noun víkingr appears in Viking Age skaldic poetry and on several rune stones found in Scandinavia, where it refers to a seaman or warrior who takes part in an expedition overseas. The word víking derives from the feminine vík, meaning "creek, inlet, small bay".[4]
The form also occurs as a personal name on some Swedish rune stones. There is little indication of any negative connotation in the term before the end of the Viking Age. Regardless of its possible origins, the word was used to indicate an activity and those who participated in it, and it did not belong to any ethnic or cultural group.[5]
In Old English, the word wicing appears first in the Anglo-Saxon poem, Widsith, which probably dates from the 9th century. In Old English, and in the history of the archbishops of Hamburg-Bremen written by Adam of Bremen in about 1070, the term is synonymous with pirate and a Scandinavian. As in the Old Norse usages, the term is not employed as a name for any people or culture in general. The word does not occur in any preserved Middle English texts.
In the modern Scandinavian languages, the word Viking usually refers specifically to those people who went on Viking expeditions.[6]
The word Viking was introduced into Modern English during the 18th-century Viking revival, at which point it acquired romanticised heroic overtones of "barbarian warrior" or noble savage. During the 20th century, the meaning of the term was expanded to refer not only to seaborne raiders from Scandinavia, but secondarily to any Scandinavian who lived during the period from the late 8th to the mid-11th centuries, or more loosely from about 700 to as late as about 1100. As an adjective, the word is used to refer to ideas, phenomena or artefacts connected with Scandinavians and their cultural life in these centuries, producing expressions like Viking age, Viking culture, Viking art, Viking religion, Viking ship, and so on. The people of medieval Scandinavia are also referred to as Norse, although this term properly applies only to the Old-Norse-speaking peoples of Scandinavia, and not to the Sami.
Other names
The Vikings were known as Ascomanni, ashmen, by the Germans,[7] Lochlanach (Norse) by the Gaels and Dene (Danes) by the Anglo-Saxons.
The Slavs, the Arabs and the Byzantines knew them as the Rus' or Rhōs, probably derived from various uses of rōþs-, i.e., "related to rowing" or derived from the area of Roslagen in east-central Sweden, where most of the Vikings who visited the Slavic lands came from. Archaeologists and historians of today believe that these Scandinavian settlements in the Slavic lands formed the names of the countries Russia and Belarus.[8] The modern day name for Sweden in several neighboring countries is possibly derived from rōþs-, Ruotsi in Finnish and Rootsi in Estonian.
The Slavs and the Byzantines also called them Varangians (ON: Væringjar, meaning sworn men from var- "pledge, faith," related to Old English wær "agreement, treaty, promise," Old High German wara "faithfulness"[9]). Scandinavian bodyguards of the Byzantine emperors were known as the Varangian Guard.
Sources
Literature

The most important primary sources on the Vikings are various sorts of contemporary evidence from Scandinavia and other regions where the Vikings were active.[10] Writing in Latin letters was introduced to Scandinavia with Christianity, so there are few native documentary sources from Scandinavia before the late 11th and early 12th centuries.[11] The Scandinavians did write inscriptions in runes, but these are usually very short and formulaic. Most contemporary documentary sources consist of texts written in Christian and Islamic communities outside of Scandinavia, often by authors who had been negatively affected by Viking activity. These texts reflect varying degrees of bias and reliability, but not more so than is usually the case in early medieval writings, and they remain very important.
Written evidence from after the Viking Age can also be important for understanding the Vikings, although it needs to be treated very cautiously. After the consolidation of the church and the assimilation of Scandinavia and its colonies into the mainstream of medieval Christian culture in the 11th and 12th centuries, native written sources begin to appear, in Latin and Old Norse. In the Viking colony of Iceland, an extraordinary vernacular literature blossomed in the 12th through 14th centuries, and many traditions connected with the Viking Age were written down for the first time in the Icelandic sagas. The reliability of these medieval prose narratives about the Scandinavian past is often doubtful, but some elements remain worthy of consideration, such as the great quantity of skaldic poetry attributed to court poets of the 10th and 11th centuries included in these writings. The linguistic evidence from medieval and later records and Old Norse place-names in Scandinavia and elsewhere also provides a vital source of information for the social history of Viking Age Scandinavia and the Viking settlements overseas.
A consequence of the available written sources, which may have coloured how we perceive the Viking Age as a historical period, is that we know a lot more of the activities in western Europe than those in the East. One reason for this is that the peoples living in northeastern Europe at the time were illiterate. Another reason is that the vast majority of Scandinavian written sources come from Iceland, a nation originally settled by Norwegian colonists. As a result there is much more material from the Viking Age concerning Norway than for instance Sweden, which, apart from Runic inscriptions, has almost no written sources from the early Middle Ages.
Runestones

The Viking peoples could read and write and used a non-standardized alphabet, called runor, built upon sound values. While there are few remains of runic writing on paper from the Viking era, thousands of stones with runic inscriptions have been found where Vikings lived. They are usually in memory of the dead, though not necessarily placed at graves. The use of runor survived into the 15th century, used in parallel with the Latin alphabet.
The majority of runic inscriptions from the Viking period are found in Sweden and date from the 11th century. The oldest Stone with runic inscriptions was found in Norway and dates to the 4th century, suggesting that runic inscriptions predate the Viking period. Many runestones in Scandinavia record the names of participants in Viking expeditions—such as the Kjula runestone, which tells of extensive warfare in Western Europe, and the Turinge Runestone, which tells of a warband in Eastern Europe. Other runestones mention men who died on Viking expeditions. Among them are around 25 Ingvar runestones in the Mälardalen district of Sweden, erected to commemorate members of a disastrous expedition into present-day Russia in the early 11th century. Runestones are important sources in the study of Norse society and early medieval Scandinavia, not only of the 'Viking' segment of the population.[12]


The Jelling stones, found in the Danish town of Jelling, date from between 960 and 985. The older, smaller stone was raised by King Gorm the Old, the last pagan king of Denmark, as a memorial honouring Queen Thyre.[13] The larger stone was raised by his son, Harald Bluetooth, to celebrate the conquest of Denmark and Norway and the conversion of the Danes to Christianity. It has three sides: One with an animal image, one with an image of the crucified Jesus Christ, and a third bearing the following inscription:
King Haraldr ordered this monument made in memory of Gormr, his father, and in memory of Thyrvé, his mother; that Haraldr who won for himself all of Denmark and Norway and made the Danes Christian..[14]
Runestones attest to voyages to locations such as Bath,[15] Greece,[16] Khwaresm,[17] Jerusalem,[18] Italy (as Langobardland),[19] London,[20] Serkland (i.e. the Muslim world),[21] England,[22] and various locations in Eastern Europe. Viking Age inscriptions have also been discovered on the Manx runestones on the Isle of Man.
Archaeology
Since the mid-20th century, archaeological sources have helped build a more complete and balanced picture of the lives of the Vikings.[23][24] The archaeological record is particularly rich and varied, providing knowledge of their rural and urban settlement, crafts and production, ships and military equipment, as well as their pagan and Christian religious artefacts and practices. Viking grave mounds are the primary source of evidence for circumstances in Scandinavia before the Viking Age, including entire ships used in the burial of nobles.[25] The items buried with the deceased give some indication as to what was considered important to possess in the afterlife.[26]
Burial sites
There are numerous burial sites associated with Vikings throughout Europe—in Sweden, Norway, Denmark, Germany and other North Germanic regions. Notable burial sites include:
- Gettlinge gravfält, Öland, Sweden, ship outline
- Jelling, Denmark, a World Heritage Site
- The cemeteries of Birka, Sweden, a World Heritage Site. The Hemlanden cemetery located here is the largest Viking Period cemetery in Scandinavia.[citation needed]

- Oseberg, Norway.
- Gokstad, Norway.
- Borrehaugene, Horten, Norway
- Valsgärde, Sweden.
- Gamla Uppsala, Sweden.
- Hulterstad gravfält, near the villages of Alby and Hulterstad, Öland, Sweden, ship outline of standing stones
- Trulben, by Hornbach, in Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany
- Port an Eilean Mhòir ship burial, Scotland.
- Scar boat burial, Orkney Islands, Scotland.
Ships

The discovery of two particular buried vessels at Gokstad and Oseberg in Norway provided information about Viking ships.[27] There were two distinct classes of Viking ships: the 'longship' (sometimes erroneously called drakkar, a corruption of "dragon" in Norse) and the 'knarr'. The longship, intended for warfare and exploration, was designed for speed and agility, and was equipped with oars to complement the sail as well as making it able to navigate independently of the wind. The longship had a long and narrow hull and shallow draft to facilitate landings and troop deployments in shallow water. The knarr was a dedicated merchant vessel designed to carry cargo. It was designed with a broader hull, deeper draft and limited number of oars (used primarily to maneuver in harbors and similar situations). One Viking innovation was the 'beitass', a spar mounted to the sail that allowed their ships to sail effectively against the wind.[28] It was common for Viking ships to tow or carry a smaller boat to transfer crews and cargo from the ship to shore. Longships were used extensively by the Leidang, the Scandinavian defence fleets. The term "Viking ships" has entered common usage, however, possibly because of its romantic associations (discussed below).
In Roskilde are the well-preserved remains of five ships, excavated from nearby Roskilde Fjord in the late 1960s. The ships were scuttled there in the 11th century to block a navigation channel, thus protecting the city, which was then the Danish capital, from seaborne assault. These five ships represent both the longship and the knarr. The remains of these ships can be found on display at the Viking Ship Museum in Roskilde.
Cuisine
Daily life of the Vikings in York, England, has been examined through archaeology. "We know from looking at undigested remains of plants from cesspits (latrine pits) at Coppergate that they certainly made bread from whole meal flour—probably both wheat and rye—but often it had seeds of cornfield weeds ground up in it. One of these, corncockle (Agrostemma), would have made the bread dark in colour, and as its seeds are poisonous, people who ate the bread contaminated with it might have become quite ill!"[29] Other items that have been discovered in the Viking diet included the seeds of carrots, parsnip, and brassicas. These were poor specimens and tend to show they came from white carrots and bitter tasting cabbages. Herbal seasonings were also found when the Coopergate cesspits were examined, and they included seeds of dill, coriander, and wild celery. Apple pits were a common find, from wild crab apples. Stones of small plums and cherries were also encountered.[29]
We also know from archeological remains that the Vikings in York ate mostly beef, mutton, and pork. Small amounts of horsemeat were eaten as well. Most of the beef and horse leg bones were found split lengthways, to get out the marrow. The mutton and swine were cut into leg and shoulder joints and chops. The frequent remains of pig skull and foot bones found on house floors indicate that brawn and trotters were also popular. Hens were kept for both their meat and eggs, and the bones of game birds such as the black grouse, golden plover, wild ducks, and geese have also been found.[30]
Experimental archaeology
On 1 July 2007, the reconstructed Viking ship Skuldelev 2, renamed Sea Stallion,[31] began a journey from Roskilde, Denmark to Dublin, Ireland. The remains of that ship and four others were discovered during a 1962 excavation in the Roskilde Fjord. Tree-ring analysis has shown the ship was built of oak in the vicinity of Dublin about 1042. Seventy multi-national crew members sailed the ship back to its home, and The Sea Stallion arrived outside Dublin's Custom House on 14 August 2007. The purpose of the voyage was to test and document the seaworthiness, speed, and maneuverability of the ship on the rough open sea and in coastal waters with treacherous currents. The crew tested how the long, narrow, flexible hull withstood the tough ocean waves. The expedition also provided valuable new information on Viking longships and society. The ship was built using Viking tools, materials, and much the same methods as the original ship.
Other vessels, often replicas of the Gokstad ship (full- or half-scale) or Skuldelev I have been built and tested as well. The Snorri (a Skuldelev I Knarr), for example, was sailed from Greenland to Newfoundland in 1998.[32] Viking-age reenactors have also undertaken experimental activities such as iron smelting and forging using Norse techniques.[33]
The Viking Age
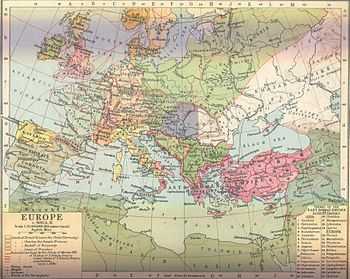
The period from the earliest recorded raids in the 790s until the Norman conquest of England in 1066 is commonly known as the Viking Age of Scandinavian history. Vikings used the Norwegian Sea[34] and Baltic Sea for sea routes to the south. The Normans were descended from Danish and Norwegian Vikings who were given feudal overlordship of areas in northern France—the Duchy of Normandy—in the 10th century.[citation needed] In that respect, descendants of the Vikings continued to have an influence in northern Europe. Likewise, King Harold Godwinson, the last Anglo-Saxon king of England, had Danish ancestors.
Geographically, a Viking Age may be assigned not only to Scandinavian lands (modern Denmark, Norway and Sweden), but also to territories under North Germanic dominance, mainly the Danelaw, including Scandinavian York, the administrative centre of the remains of the Kingdom of Northumbria,[35] parts of Mercia,[36] and East Anglia.[37] Viking navigators opened the road to new lands to the north, west and east, resulting in the foundation of independent settlements in the Shetland, Orkney, and Faroe Islands; Iceland; Greenland;[38] and L'Anse aux Meadows, a short-lived settlement in Newfoundland, circa 1000.[39] Many of these lands, specifically Greenland and Iceland, may have been originally discovered by sailors blown off course.[citation needed] They also may have been deliberately sought out, perhaps on the basis of the accounts of sailors who had seen land in the distance. The Greenland settlement eventually died out, possibly due to climate change.[40] Vikings also explored and settled in territories in Slavic-dominated areas of Eastern Europe, particularly the Kievan Rus. By 950 these settlements were largely Slavicised.

As early as 839, when Swedish emissaries are first known to have visited Byzantium, Scandinavians served as mercenaries in the service of the Byzantine Empire.[41] In the late 10th century, a new unit of the imperial bodyguard formed. Traditionally containing large numbers of Scandinavians, it was known as the Varangian Guard. The word Varangian may have originated in Old Norse, but in Slavic and Greek it could refer either to Scandinavians or Franks. The most eminent Scandinavian to serve in the Varangian Guard was Harald Hardrada, who subsequently established himself as king of Norway (1047–66).
Important trading ports during the period include Birka, Hedeby, Kaupang, Jorvik, Staraya Ladoga, Novgorod, and Kiev.
There is archaeological evidence that Vikings reached the city of Baghdad, the centre of the Islamic Empire.[42] The Norse regularly plied the Volga with their trade goods: furs, tusks, seal fat for boat sealant, and slaves. However, they were far less successful in establishing settlements in the Middle East, due to the more centralised Islamic power.[citation needed]
Generally speaking, the Norwegians expanded to the north and west to places such as Ireland, Scotland, Iceland, and Greenland; the Danes to England and France, settling in the Danelaw (northern/eastern England) and Normandy; and the Swedes to the east, founding the Kievan Rus, the original Russia. Among the Swedish runestones mentioning expeditions overseas, however, almost half tell of raids and travels to western Europe. Also, according to the Icelandic sagas, many Norwegian Vikings went to eastern Europe. These nations, although distinct, were similar in culture and language. The names of Scandinavian kings are known only for the later part of the Viking Age. Only after the end of the Viking Age did the separate kingdoms acquire distinct identities as nations, which went hand-in-hand with their Christianization. Thus the end of the Viking Age for the Scandinavians also marks the start of their relatively brief Middle Ages.
Viking expansion


The Vikings explored the northern islands and coasts of the North Atlantic, ventured south to North Africa and east to Russia, Constantinople, and the Middle East. They raided and pillaged, but also engaged in trade, settled wide-ranging colonies, and acted as mercenaries. Vikings under Leif Ericson, heir to Erik the Red, reached North America and set up short-lived settlements in present-day L'Anse aux Meadows, Newfoundland, and Labrador, Canada.
The motives driving the Viking expansion are a topic of much debate in Nordic history. One common theory posits that Charlemagne "used force and terror to Christianise all pagans", leading to baptism, conversion or death, and as a result Vikings and other pagans wanted revenge.[43][44][45][46][47] Professor Rudolf Simek states that "it is not a coincidence if the early Viking activity occurred during the reign of Charlemagne".[43][48] The penetration of Christianity into Scandinavia led to serious conflict dividing Norway for almost a century.[49]
Another explanation is that the Vikings exploited a moment of weakness in the surrounding regions. For instance, the Danish Vikings were aware of the internal divisions within the Carolingian empire, beginning in the 830s and resulting in schism.[citation needed] England suffered from internal divisions and was relatively easy prey given the proximity of many towns to the sea or to navigable rivers. Lack of organised naval opposition throughout Western Europe allowed Viking ships to travel freely, raiding or trading as opportunity permitted.
The decline in the profitability of old trade routes could also have played a role. Trade between western Europe and the rest of Eurasia suffered a severe blow when the Roman Empire fell in the 5th century.[50] The expansion of Islam in the 7th century had also affected trade with western Europe.[51] Trade on the Mediterranean was at its lowest level historically when the Vikings initiated their expansion.[citation needed] By opening new trade routes in Arabic and Frankish lands, the Vikings profited from international trade by expanding beyond their traditional boundaries.[citation needed]
The end of the Viking Age
During the Viking Age, Scandinavian men and women travelled to many parts of Europe and beyond, in a cultural diaspora that left its traces from Newfoundland to Byzantium. But this period of energetic activity also had a pronounced effect in the Scandinavian homelands, which were subject to a variety of new influences.[52] In the 300 years from the late 8th century, when contemporary chroniclers first commented on the appearance of Viking raiders, to the end of the 11th century, Scandinavia underwent profound cultural changes.

In the late 11th century, royal dynasties legitimised by the Catholic Church (which had had little influence in Scandinavia 300 years earlier) were asserting their power with increasing authority and ambition, and the three kingdoms of Denmark, Norway, and Sweden had taken shape. Towns appeared that functioned as secular and ecclesiastical administrative centres and market sites, and monetary economies began to emerge based on English and German models.[53] By this time the influx of Islamic silver from the East had been absent for more than a century, and the flow of English silver had come to an end in the mid-11th century.[54] Christianity had taken root in Denmark and Norway with the establishment of dioceses during the 11th century, and the new religion was beginning to organise and assert itself more effectively in Sweden. Foreign churchmen and native elites were energetic in furthering the interests of Christianity, which was now no longer operating simply on a missionary footing, and old ideologies and lifestyles were transforming. It was not until 1103, however, that the first archbishopric was founded in Scandinavia, at Lund, Scania, Denmark (as of then).
The assimilation of the nascent Scandinavian kingdoms into the cultural mainstream of European Christendom altered the aspirations of Scandinavian rulers and of those Scandinavians able to travel overseas and changed their relations with their neighbours. One of the primary sources of profit for the Vikings had been slave-taking. The medieval Church took the position that Christians should not own fellow Christians as slaves, so chattel slavery diminished as a practice throughout northern Europe. This took much of the economic incentive out of raiding, though sporadic slaving activity continued into the 11th century. Eventually, outright slavery was outlawed and replaced with serfdom at the bottom rung of medieval society. Scandinavian predation in Christian lands around the North and Irish Seas diminished markedly.
The kings of Norway continued to assert power in parts of northern Britain and Ireland, and raids continued into the 12th century, but the military ambitions of Scandinavian rulers were now directed toward new paths. In 1107, Sigurd I of Norway sailed for the eastern Mediterranean with a host of Norwegian crusaders to fight for the newly established Kingdom of Jerusalem, and the Danes and Swedes participated energetically in the Baltic Crusades of the 12th and 13th centuries.[55]
Weapons and warfare
Our knowledge about the arms and armour of the Viking age is based on relatively sparse archaeological finds, pictorial representation, and to some extent on the accounts in the Norse sagas and Norse laws recorded in the 13th century. According to custom, all free Norse men were required to own weapons and were permitted to carry them all the time. These arms were indicative of a Viking's social status: a wealthy Viking would have a complete ensemble of a helmet, shield, mail shirt, and sword. A typical bóndi (freeman) was more likely to fight with a spear and shield, and most also carried a seax as a utility knife and side-arm. Bows were used in the opening stages of land battles and at sea, but they tended to be considered less "honourable" than a melee weapon. Vikings were relatively unusual for the time in their use of axes as a main battle weapon. The Húscarls, the elite guard of King Cnut (and later of King Harold II) were armed with two-handed axes that could split shields or metal helmets with ease.
An ideology of warfare and violence motivated the Vikings, focused on the gods Porr and Odinn, the god of war and death.[56][57] In combat the Vikings are believed to have engaged in a disordered style of frenetic, furious fighting, leading them to be termed berserkers. They may have induced this mental state through ingestion of materials with psychoactive properties, such as the hallucinogenic mushrooms, Amanita muscaria,[58] or massive amounts of alcohol.[59]
Legacy
Medieval perceptions of the Vikings
In England the Viking Age began dramatically on 8 June 793 when Norsemen destroyed the abbey on the island of Lindisfarne. The devastation of Northumbria's Holy Island shocked and alerted the royal Courts of Europe to the Viking presence. "Never before has such an atrocity been seen," declared the Northumbrian scholar Alcuin of York.[60] More than any other single event, the attack on Lindisfarne demonised perception of the Vikings for the next twelve centuries. Not until the 1890s did scholars outside Scandinavia begin to seriously reassess the achievements of the Vikings, recognizing their artistry, technological skills, and seamanship.[61]
Norse Mythology, sagas, and literature tell of Scandinavian culture and religion through tales of heroic and mythological heroes. However, early transmission of this information was primarily oral, and later texts were reliant upon the writings and transcriptions of Christian scholars, including the Icelanders Snorri Sturluson and Sæmundur fróði. Many of these sagas were written in Iceland, and most of them, even if they had no Icelandic provenance, were preserved there after the Middle Ages due to the continued interest of Icelanders in Norse literature and law codes.
The 200-year Viking influence on European history is filled with tales of plunder and colonization, and the majority of these chronicles came from western witnesses and their descendants. Less common, though equally relevant, are the Viking chronicles that originated in the east, including the Nestor chronicles, Novgorod chronicles, Ibn Fadlan chronicles, Ibn Rusta chronicles, and many brief mentions by the Fosio bishop from the first big attack on the Byzantine Empire. Other chroniclers of Viking history include Adam of Bremen, who wrote, in the fourth volume of his Gesta Hammaburgensis Ecclesiae Pontificum, "[t]here is much gold here (in Zealand), accumulated by piracy. These pirates, which are called wichingi by their own people, and Ascomanni by our own people, pay tribute to the Danish king." In 991, the Battle of Maldon between Viking raiders and the inhabitants of the town of Maldon in Essex, England was commemorated with a poem of the same name.
Post-medieval perceptions of the Vikings

Early modern publications, dealing with what we now call Viking culture, appeared in the 16th century, e.g., Historia de gentibus septentrionalibus (Olaus Magnus, 1555), and the first edition of the 13th-century Gesta Danorum of Saxo Grammaticus in 1514. The pace of publication increased during the 17th century with Latin translations of the Edda (notably Peder Resen's Edda Islandorum of 1665).
In Scandinavia, the 17th-century Danish scholars Thomas Bartholin and Ole Worm and the Swede Olof Rudbeck were the first to set the standard for using runic inscriptions and Icelandic sagas as historical sources.[citation needed] An important early British contributor to the study of the Vikings was George Hicke, who published his Linguarum vett. septentrionalium thesaurus in 1703–05. During the 18th century, British interest and enthusiasm for Iceland and early Scandinavian culture grew dramatically, expressed in English translations of Old Norse texts and in original poems that extolled the supposed Viking virtues.
The word "viking" was first popularised at the beginning of the 19th century by Erik Gustaf Geijer in his poem, The Viking. Geijer's poem did much to propagate the new romanticised ideal of the Viking, which had little basis in historical fact. The renewed interest of Romanticism in the Old North had contemporary political implications. The Geatish Society, of which Geijer was a member, popularised this myth to a great extent. Another Swedish author who had great influence on the perception of the Vikings was Esaias Tegnér, member of the Geatish Society, who wrote a modern version of Friðþjófs saga ins frœkna, which became widely popular in the Nordic countries, the United Kingdom, and Germany.

Fascination with the Vikings reached a peak during the so-called Viking Revival in the late 18th and 19th centuries. In Britain this took the form of Septentrionalism, in Germany that of "Wagnerian" pathos or even Germanic mysticism, and in the Scandinavian countries that of Romantic nationalism or Scandinavism. Pioneering 19th-century scholarly editions of the Viking Age began to reach a small readership in Britain, archaeologists began to dig up Britain's Viking past, and linguistic enthusiasts started to identify the Viking-Age origins of rural idioms and proverbs. The new dictionaries of the Old Norse language enabled the Victorians to grapple with the primary Icelandic sagas.[62]
Until recently, the history of the Viking Age was largely based on Icelandic sagas, the history of the Danes written by Saxo Grammaticus, the Russian Primary Chronicle, and The War of the Irish with the Foreigners. Few scholars still accept these texts as reliable sources, as historians now rely more on archeology and numismatics, disciplines that have made valuable contributions toward understanding the period.[63]
The figure of the Viking in 20th-century politics
The romanticised idea of the Vikings constructed in scholarly and popular circles in northwestern Europe in the 19th and early 20th centuries was a potent one, and the figure of the Viking became a familiar and malleable symbol in different contexts in the politics and political ideologies of 20th-century Europe.[64] In Normandy, which had been settled by Vikings, the Viking ship became an uncontroversial regional symbol. In Germany, awareness of Viking history in the 19th century had been stimulated by the border dispute with Denmark over Schleswig-Holstein and the use of Scandinavian mythology by Richard Wagner. The idealised view of the Vikings appealed to Germanic supremacists who transformed the figure of the Viking in accordance with the racialist ideology of the Germanic master race.[65] Building on the linguistic and cultural connections between Norse-speaking Scandinavians and other Germanic groups in the distant past, Scandinavian Vikings were portrayed in Nazi Germany as a pure Germanic type. The cultural phenomenon of Viking expansion was re-interpreted for use as propaganda to support the extreme militant nationalism of the Third Reich, and ideologically informed interpretations of Viking paganism and the Scandinavian use of runes were employed in the construction of Nazi mysticism. Other political organizations of the same ilk, such as the former Norwegian fascist party Nasjonal Samling, similarly appropriated elements of the modern Viking cultural myth in their symbolism and propaganda. In communist Russia, the ideology of Slavic racial purity led to the complete denial that Scandinavians had played a part in the emergence of the principalities of the Rus', which were supposed to have been founded by Slavs. Evidence to the contrary was suppressed until the 1990s. The city of Novgorod now enthusiastically acknowledges its Viking history and has included a Viking ship in its logo.[66]
The Vikings in modern music, literature, and popular culture


Led by the operas of German composer Richard Wagner, such as Der Ring des Nibelungen, Vikings and the Romanticist Viking Revival have inspired many creative works. These have included novels directly based on historical events, such as Frans Gunnar Bengtsson's The Long Ships (which was also released as a 1963 film), and historical fantasies such as the film The Vikings, Michael Crichton's Eaters of the Dead (movie version called The 13th Warrior), and the comedy film Erik the Viking. The vampire Eric Northman, in the HBO TV series True Blood, was a Viking prince before being turned into a vampire. Vikings appear in several books by the Danish American writer Poul Anderson, while British explorer, historian, and writer Tim Severin authored a trilogy of novels in 2005 about a young Viking adventurer Thorgils Leifsson, who travels around the world.
In 1962, American comic book writer Stan Lee and his brother Larry Lieber, together with Jack Kirby, created the Marvel Comics superhero Thor, which they based on the Norse god of the same name. The character is featured in the 2011 Marvel Studios film Thor and its sequel Thor: The Dark World and also appears in the 2012 film The Avengers and its associated animated series.
Since the 1960s, there has been rising enthusiasm for historical reenactment. While the earliest groups had little claim for historical accuracy, the seriousness and accuracy of reenactors has increased. The largest such groups include The Vikings and Regia Anglorum, though many smaller groups exist in Europe, the UK, North America, New Zealand, and Australia. Many reenactor groups participate in live-steel combat, and a few have Viking-style ships or boats.
The Minnesota Vikings of the National Football League are so-named due to the large Scandinavian population in the US state of Minnesota.
Modern reconstructions of Viking mythology have shown a persistent influence in late 20th- and early 21st-century popular culture in some countries, inspiring comics, role-playing games, computer games, and music, including Viking metal, a sub-genre of heavy metal music.
Common misconceptions concerning the Vikings
Horned helmets
.JPG)
Apart from two or three representations of (ritual) helmets—with protrusions that may be either stylised ravens, snakes, or horns—no depiction of the helmets of Viking warriors, and no preserved helmet, has horns. In fact, the formal, close-quarters style of Viking combat (either in shield walls or aboard "ship islands") would have made horned helmets cumbersome and hazardous to the warrior's own side.
Historians therefore believe that Viking warriors did not wear horned helmets; whether such helmets were used in Scandinavian culture for other, ritual purposes, however, remains unproven. The general misconception that Viking warriors wore horned helmets was partly promulgated by the 19th-century enthusiasts of Götiska Förbundet, founded in 1811 in Stockholm, Sweden. They promoted the use of Norse mythology as the subject of high art and other ethnological and moral aims.
The Vikings were often depicted with winged helmets and in other clothing taken from Classical antiquity, especially in depictions of Norse gods. This was done to legitimise the Vikings and their mythology by associating it with the Classical world, which had long been idealised in European culture.
The latter-day mythos created by national romantic ideas blended the Viking Age with aspects of the Nordic Bronze Age some 2,000 years earlier. Horned helmets from the Bronze Age were shown in petroglyphs and appeared in archaeological finds (see Bohuslän and Vikso helmets). They were probably used for ceremonial purposes.[67]
Cartoons like Hägar the Horrible and Vicky the Viking, and sports uniforms such as those of the Minnesota Vikings and Canberra Raiders football teams have perpetuated the mythic cliché of the horned helmet.
Viking helmets were conical, made from hard leather with wood and metallic reinforcement for regular troops. The iron helmet with mask and mail was for the chieftains, based on the previous Vendel-age helmets from central Sweden. The only true Viking helmet found is that from Gjermundbu in Norway. This helmet is made of iron and has been dated to the 10th century.
Use of skulls as drinking vessels

The use of human skulls as drinking vessels—another common motif in popular pictorial representations of the Vikings—is also ahistorical. The rise of this legend can be traced to Ole Worm's Runer seu Danica literatura antiquissima (1636), in which Danish warriors drinking ór bjúgviðum hausa (from the curved branches of skulls, i.e., from horns) were rendered as drinking ex craniis eorum quos ceciderunt (from the skulls of those whom they had slain). The skull-cup allegation may also have some history in relation with other Germanic tribes and Eurasian nomads, such as the Scythians and Pechenegs, and the vivid example of the Lombard Alboin, made notorious by Paul the Deacon's History.
There may also be some confusion between "skull" and the Norse/Icelandic word for a drinking cup, skál. This is a common toast in Scandinavian countries.
Barbarity
The image of wild-haired, dirty savages sometimes associated with the Vikings in popular culture is a distorted picture of reality.[1] Non-Scandinavian Christians are responsible for most surviving accounts of the Vikings, and consequently, a strong possibility for bias exists. This attitude is likely attributed to Christian misunderstandings regarding paganism. Viking tendencies were often misreported, and the work of Adam of Bremen, among others, told largely disputable tales of Viking savagery and uncleanliness.[68]
The Anglo-Danes were considered excessively clean by their Anglo-Saxon neighbours, due to their custom of bathing every Saturday and combing their hair often.[citation needed] To this day, Saturday is referred to as laugardagur / laurdag / lørdag / lördag, "washing day", in the Scandinavian languages. Icelanders were known to use natural hot springs as baths, and there is a strong sauna/bathing culture in Scandinavia still.[citation needed]
As for the Vikings in the east, Ibn Rustah notes their cleanliness in carrying clean clothes, whereas Ibn Fadlan is disgusted by all of the men sharing the same, used vessel to wash their faces and blow their noses in the morning. Ibn Fadlan's disgust is possibly because of the contrast to the personal hygiene practises particular to the Muslim world at the time, such as the use of running water and clean vessels. While the example was intended to convey his disgust about certain customs of the Rus', at the same time it recorded that they did wash every morning.[citation needed]
Genetic legacy
Studies of genetic diversity provide some indication of the origin and expansion of the Viking population. The Haplogroup I1 (defined by specific genetic markers on the Y-chromosome) is sometimes referred to as the Viking haplogroup.[citation needed] This mutation occurs with the greatest frequency among Scandinavian males: 35 percent in Norway, Denmark, and Sweden, and peaking at 40 percent within western Finland.[69] It is also common near the southern Baltic and North Sea coasts, and then successively decreasing further to the south geographically.
Genetic studies in the British Isles of the Y-DNA Haplogroup R1a1, seen also across Scandinavia, have demonstrated that the Vikings settled in Britain and Ireland as well as raiding there. Both male and female descent studies show evidence of Norse descent in areas closest to Scandinavia, such as the Shetland and Orkney Islands.[70] Inhabitants of lands farther away show most Norse descent in the male Y-chromosome lines.[71]
A specialised genetic and surname study in Liverpool demonstrated marked Norse heritage: up to 50 percent of males who belonged to original families, those who lived there before the years of industrialization and population expansion.[72] High percentages of Norse inheritance—tracked through R1a1 haplotype signatures—were also found among males in the Wirral and West Lancashire.[73] This was similar to the percentage of Norse inheritance found among males in the Orkney Islands.[74]
Recent research suggests that the Scottish warrior Somerled, who drove the Vikings out of Scotland and was the progenitor of Clan Donald, may himself have been of Viking descent—a member of Haplogroup R1a1.[75]
Well known Vikings and Norsemen of the Viking Age
Known from Viking Age sources
- Bagsecg, a Viking who invaded and pillaged in England in 870, and was killed in 871 at The Battle of Ashdown.
- Cnut the Great, commonly known as 'Canute', king of England and Denmark, Norway, and of some of Sweden, was possibly the greatest Viking king. A son of Sweyn Forkbeard, and grandson of Harold Bluetooth, he was a member of the dynasty that was key to the unification and Christianisation of Denmark. Some modern historians have dubbed him the Emperor of the North because of his position as one of the magnates of medieval Europe and as a reflection of the Holy Roman Empire to the south.
- Egill Skallagrímsson, Icelandic warrior and skald. (See also the medieval tale Egils saga).
- Eric the Victorious, a king of Sweden whose dynasty is the first known to have ruled as kings of the nation. It is possible he was king of Denmark for a time.
- Godfrid, Duke of Frisia, a pillager of the Low Countries and the Rhine area and briefly a lord of Frisia.
- Godfrid Haraldsson, son of Harald Klak and pillager of the Low Countries and northern France.
- Guthrum, coloniser of Danelaw.
- Halfdan, pillaged in England conquered London and Northumbria, later remembered as a son of Ragnar Lodbrok
- Harald Bluetooth (Harald Gormson), who according to the Jelling Stones that he had erected, "won the whole of Denmark and Norway and turned the Danes to Christianity". Father of Sweyn Forkbeard; grandfather of Cnut the Great.
- Harald Fairhair, remembered in the medieval sagas and thus commonly revered in popular histories as the first king of all Norway, who conquered and ruled the whole extent of medieval Norway from 870–930. Now considered by historians to have been the successful ruler of a more limited domain in south-western Norway in the 10th century.
- Harald Hardrada. A half-brother of St Olaf, Harald cut his teeth as a mercenary in Russia and Byzantium before returning to Norway in the mid-1040s. He forced his nephew Magnus the Good to share power with him, and then ruled the whole kingdom alone after the early death of Magnus in 1047. Harald attempted to revive the North Sea domain of Cnut the Great, but having failed to conquer the Danes he died at Stamford Bridge in 1066, during an unsuccessful attempt to conquer England. Harald was the first ruler of Norway successfully to have guaranteed the succession for his own sons. Although it was from him that the medieval Norwegian dynasty descended, his historical importance has been obscured by the treatment of Harald Fairhair and St Olaf (Olaf Haraldsson) in medieval writings.
- Harald Klak (Harald Halfdansson), a 9th-century king in Jutland who made peace with Louis the Pious in order to win Frankish support in his struggle for power. In 826 he became the first Scandinavian ruler to accept baptism, but he was unable to maintain his authority in Jutland and was possibly the first Viking to be granted Frankish land in exchange for protection.
- Ivar the Boneless, remembered as one of the sons of Ragnar Lodbrok, he led an army of Vikings that conquered York. His nickname of "Boneless" has led some to speculate that may have suffered from a physical handicap while others have speculated that it might refer to unusual agility in combat.
- St Olaf (Olav Haraldsson), patron saint of Norway, and king of Norway from 1015 to approx. 1030.
- Olaf Tryggvason, king of Norway from 995 to 1000. Remembered as an aggressive missionary ruler in the medieval Icelandic sagas, in which the extent of his authority has almost certainly been grossly exaggerated.
- Ragnar Lodbrok, captured Paris. Developed into a legendary Viking hero in medieval writings.
- Rollo of Normandy, founder of Normandy.
- Rorik of Dorestad, a Viking lord of Frisia and nephew of Harald Klak.
- Sweyn Forkbeard, king of Denmark, Norway, and England, as well as founder of Swansea ("Sweyn's island"). In 1013, the Danes under Sweyn led a Viking offensive against the Anglo-Saxon kingdom of England. The English king was forced into exile, and in late 1013 Sweyn became King of England, though he died early in 1014, and the former king was brought out of exile to challenge his son.
- Ubbe Ragnarsson, pillaged in England and was killed in 878 at The Battle of Cynwit, another supposed son of the legendary Ragnar Lodbrok.
- William the Conqueror, ruler of Normandy and the victor at the Battle of Hastings in 1066. William was a Norman French-speaking fifth-generation descendant of the Viking war-leader Rollo, the first Scandinavian ruler of Normandy; but Norman historians since Dudo of St. Quentin still celebrated the old Norse heritage of the ducal dynasty. William's great great uncle was the great Danish king Cnut the Great. The Norman assertion of power in England after the successful invasion of 1066 saw the end of the Anglo-Saxon rule in England.
Known from later medieval sources
- Askold and Dir (Old Norse: Hoskuld and Dýri), legendary Swedish conquerors of Kiev.
- Björn Ironside, son of Ragnar Lodbrok, pillaged in Italy.
- Brodir of Man, a Danish Viking who killed the High King of Ireland, Brian Boru.
- Erik the Red, coloniser of Greenland.
- Freydís Eiríksdóttir, a Viking woman who sailed to Vínland.
- Gardar Svavarsson, originally from Sweden, the discoverer of Iceland. There is another contender for the discoverer of Iceland: Naddoddr, a Norwegian/Faeroese Viking explorer.
- Grímur Kamban, a Norwegian or Norwegian/Irish Viking who around 825 was, according to the Færeyinga Saga, the first Nordic settler in the Faeroes.
- Hastein, a chieftain who raided in the Mediterranean, Son of Ragnar Lodbrok.
- Ingólfur Arnarson, coloniser of Iceland.
- Ingvar the Far-Travelled, the leader of the last great Swedish Viking expedition to pillage the shores of the Caspian Sea.
- Leif Ericsson, discoverer of Vínland, son of Erik the Red.
- Naddoddr, a Norwegian/Faeroese Viking explorer.
- Oleg of Kiev (Old Norse: Helgi), Swede who founded Kievan Rus' and led several major raids against Constantinople
- Rurik (Old Norse: Hrörek), Swedish founder of the Rurikid Dynasty in the lands of East Slavs
- Sigmundur Brestisson, Faeroese, a Viking chieftain who, according to the Færeyinga Saga, introduced Christianity and Norwegian supremacy to the Faeroes in 999.
- Thorfinn Karlsefni, explorer who, along with Freydís Eiríksdóttir, sailed to Vínland. His wife Gudridr gave birth to Snorri, the first European known to have been born in the New World.
- Thorgils (Thorgest), founder of Dublin according to Snorri Sturluson.
- Tróndur í Gøtu, a Faeroese Viking chieftain who, according to the Færeyinga Saga, was opposed to the introduction of Christianity to, and the Norwegian supremacy of, the Faeroes.
See also
Notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Roesdahl, pp. 9–22.
- ↑ "Los vikingos en Al-Andalus (abstract available in English)". Jesús Riosalido. 1997. Retrieved 11 May 2010.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Johnni Langer, "The origins of the imaginary viking", Viking Heritage Magazine, Gotland University/Centre for Baltic Studies. Visby (Sweden), n. 4, dez. 2002
- ↑ The Syntax of Old Norse By Jan Terje Faarlund; p 25 ISBN 0-19-927110-0; The Principles of English Etymology By Walter W. Skeat, published in 1892, defined Viking: better Wiking, Icel. Viking-r, O. Icel. *Viking-r, a creek-dweller; from Icel. vik, O. Icel. *wik, a creek, bay, with suffix -uig-r, belonging to Principles of English Etymology By Walter W. Skeat; Clarendon press; Page 479
- ↑ Desmond Collins, Background to Archaeology: Britain in Its European Setting, p.97, Cambridge University Press, 1973
- ↑ See Gunnar Karlsson, "Er rökrétt að fullyrða að landnámsmenn á Íslandi hafi verið víkingar?", The University of Iceland Science web 30 April 2007; Gunnar Karlsson, "Hver voru helstu vopn víkinga og hvernig voru þau gerð? Voru þeir mjög bardagaglaðir?", The University of Iceland Science web 20 December 2006; and Sverrir Jakobsson "Hvaðan komu víkingarnir og hvaða áhrif höfðu þeir í öðrum löndum?", The University of Iceland Science web 13 July 2001 (in Icelandic).
- ↑ Adam of Bremen 2.29.
- ↑ http://www.etymonline.com/index.php?term=Russia
- ↑ http://etymonline.com/index.php?allowed_in_frame=0&search=Varangian&searchmode=none
- ↑ Hall, pp. 8–11
- ↑ Lindqvist, pp. 160–61
- ↑ Sawyer, P H: 1997
- ↑ Jelling stones. Encyclopædia Britannica. 2008.
- ↑ Rundata, DR 42
- ↑ baþum (Sm101), see Nordiskt runnamnslexikon PDF
- ↑ In the nominative: krikiaR (G216). In the genitive: girkha (U922$), k—ika (U104). In the dative: girkium (U1087†), kirikium (SöFv1954;20, U73, U140), ki(r)k(i)(u)(m) (Ög94$), kirkum (U136), krikium (Sö163, U431), krikum (Ög81A, Ög81B, Sö85, Sö165, Vg178, U201, U518), kri(k)um (U792), krikum (Sm46†, U446†), krkum (U358), kr... (Sö345$A), kRkum (Sö82). In the accusative: kriki (Sö170). Uncertain case krik (U1016$Q). Greece also appears as griklanti (U112B), kriklati (U540), kriklontr (U374$), see Nordiskt runnamnslexikon PDF
- ↑ Karusm (Vs1), see Nordiskt runnamnslexikon PDF
- ↑ iaursaliR (G216), iursala (U605†), iursalir (U136G216, U605, U136), see Nordiskt runnamnslexikon PDF
- ↑ lakbarþilanti (SöFv1954;22), see Nordiskt runnamnslexikon PDF
- ↑ luntunum (DR337$B), see Nordiskt runnamnslexikon PDF
- ↑ serklat (G216), se(r)kl... (Sö279), sirklanti (Sö131), sirk:lan:ti (Sö179), sirk*la(t)... (Sö281), srklant- (U785), skalat- (U439), see Nordiskt runnamnslexikon PDF
- ↑ eklans (Vs18$), eklans (Sö83†), ekla-s (Vs5), enklans (Sö55), iklans (Sö207), iklanþs (U539C), ailati (Ög104), aklati (Sö166), akla-- (U616$), anklanti (U194), eg×loti (U812), eklanti (Sö46, Sm27), eklati (ÖgFv1950;341, Sm5C, Vs9), enklanti (DR6C), haklati (Sm101), iklanti (Vg20), iklati (Sm77), ikla-ti (Gs8), i...-ti (Sm104), ok*lanti (Vg187), oklati (Sö160), onklanti (U241), onklati (U344), -klanti (Sm29$), iklot (N184), see Nordiskt runnamnslexikon PDF
- ↑ Hall, 2010, p. 8 and passim.
- ↑ Roesdahl, pp. 16–22.
- ↑ Medieval Archaeology: An Encyclopedia (Pamela Crabtree, ed., 2001), "Vikings," p. 510.
- ↑ Roesdahl, p. 20.
- ↑ Ian Heath, The Vikings, p.4, Osprey Publishing, 1985
- ↑ Block, Leo, To Harness the Wind: A Short History of the Development of Sails, Naval Institute Press, 2002, ISBN 1-55750-209-9
- ↑ 29.0 29.1 Hall, A. R. 1999? "The Home: Food- Fruit, Grain and Vegetable." Viking Age York. The Jorvik Viking Centre.
- ↑ O'Conner, Terry. 1999? "The Home- Food and Meat." Viking Age York. Jorvik Viking Centre.
- ↑ Return of Dublin's Viking Warship. Retrieved 14 November 2007.
- ↑ "Beyond Lands' End: Viking Voyage 1000". Dougcabot.com. Retrieved 21 May 2012.
- ↑ Darrell Markewitz 1998–2010. "IRON SMELTING at the Norse Encampment -Daily Life in the Viking Age circa 1000 AD at Vinland. The Viking Encampment living history program at Parks Canada L'Anse aux Meadows NHSC in Newfoundland". Warehamforge.ca. Retrieved 21 May 2012.
- ↑ C.Michael Hogan. 2011. Norwegian Sea. Eds.Peter Saundry & C.J.Cleveland. Encyclopedia of Earth. National Council for science and the Environment. Washington DC
- ↑ "History of Northumbria: Viking era 866 AD–1066 AD" www.englandnortheast.co.uk.
- ↑ "Identity and Self-Image in Viking Age England" www.allempires.co.uk. 3 October 2007
- ↑ Toyne, Stanley Mease. The Scandinavians in history Pg.27. 1970.
- ↑ The Fate of Greenland's Vikings, by Dale Mackenzie Brown, Archaeological Institute of America, 28 February 2000
- ↑ "The Norse discovery of America". Ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. 4 April 2012. Retrieved 21 May 2012.
- ↑ Ross, Valerie (31 May 2011). "Climate change froze Vikings out of Greenland". Discover (Kalmback Publishing). Retrieved 6 April 2013.
- ↑ Hall, p. 98
- ↑ "Vikings' Barbaric Bad Rap Beginning to Fade". News.nationalgeographic.com. 28 October 2010. Retrieved 21 May 2012.
- ↑ 43.0 43.1 Rudolf Simek, "the emergence of the viking age: circumstances and conditions", "The vikings first Europeans VIII–XI century—the new discoveries of archaeology", other, 2005, pp. 24–25
- ↑ Bruno Dumézil, master of Conference at Paris X-Nanterre, Normalien, aggregated history, author of conversion and freedom in the barbarian kingdoms. 5th–8th centuries (Fayard, 2005)
- ↑ "Franques Royal Annals" cited in Peter Sawyer, "The Oxford Illustrated History of the Vikings", 2001, p. 20
- ↑ Dictionnaire d'histoire de France, Perrin, Alain Decaux and André Castelot, 1981, pages 184/185. ISBN 2-7242-3080-9.
- ↑ "the Vikings" R.Boyer history, myths, dictionary, Robert Laffont several 2008, p96 ISBN 978-2-221-10631-0
- ↑ François-Xavier Dillmann, "Viking civilisation and culture. A bibliography of French-language ", Caen, Centre for research on the countries of the North and Northwest, University of Caen, 1975, p.19, and "Les Vikings: the Scandinavian and European 800–1200", 22nd exhibition of art from the Council of Europe, 1992, p. 26
- ↑ "History of the Kings of Norway" by Snorri Sturlusson translated by Professor of History François-Xavier Dillmann, Gallimard ISBN 2-07-073211-8 pages 15–16, 18, 24, 33–34, 38
- ↑ Macauley Richardson, Lloyd. "Books: Eurasian Exploration" Policy Review. Hoover Institution
- ↑ Crone, Patricia. Meccan trade and the rise of Islam First Georgias Press. 2004.
- ↑ Roesdahl, pp. 295–7
- ↑ Gareth Williams, 'Kingship, Christianity and coinage: monetary and political perspectives on silver economy in the Viking Age', in Silver Economy in the Viking Age, ed. James Graham-Campbell and Gareth Williams, pp. 177–214; ISBN 978-1-59874-222-0
- ↑ Roesdahl, pp. 296
- ↑ The Northern Crusades: Second Edition by Eric Christiansen; ISBN 0-14-026653-4
- ↑ Shona Grimbly (16 August 2013). Encyclopedia of the Ancient World. Routledge. pp. 121–. ISBN 978-1-136-78688-4.
- ↑ Dennis Howard Green; Frank Siegmund (2003). The Continental Saxons from the Migration Period to the Tenth Century: An Ethnographic Perspective. Boydell Press. pp. 306–. ISBN 978-1-84383-026-9.
- ↑ Howard D. Fabing. "On Going Berserk: A Neurochemical Inquiry." Scientific Monthly. 83 [Nov. 1956] p. 232
- ↑ Robert Wernick. The Vikings. Alexandria VA: Time-Life Books. 1979. p. 285
- ↑ English Historical Documents, c. 500–1042 by Dorothy Whitelock; p.776
- ↑ Northern Shores by Alan Palmer; p.21; ISBN 0-7195-6299-6
- ↑ The Viking Revival By Professor Andrew Wawn at bbc
- ↑ The Oxford Illustrated History of the Vikings By Peter Hayes Sawyer ISBN 0-19-820526-0
- ↑ Hall, pp. 220–1; Fitzhugh and Ward, pp. 362–64
- ↑ Fitzhugh and Ward, p. 363
- ↑ Hall, pp. 221
- ↑ Did Vikings really wear horns on their helmets?, The Straight Dope, 7 December 2004. Retrieved 14 November 2007.
- ↑ Williams, G. (2001) How do we know about the Vikings? BBC.co.uk. Retrieved 14 November 2007.
- ↑ "Annals of Human Genetics. Volume 72 Issue 3 Pages 337–348, May 2008". Blackwell-synergy.com. Retrieved 21 May 2012.
- ↑ Helgason, A.; Hickey, E.; Goodacre, S.; Bosnes, V.; Stefánsson, K. R.; Ward, R.; Sykes, B. (2001). "MtDNA and the Islands of the North Atlantic: Estimating the Proportions of Norse and Gaelic Ancestry". The American Journal of Human Genetics 68 (3): 723. doi:10.1086/318785.
- ↑ Roger Highfield, "Vikings who chose a home in Shetland before a life of pillage", Telegraph, 7 Apr 2005, accessed 16 November 2008
- ↑ "Excavating Past Population Structures by Surname-Based Sampling; The Genetic Legacy of the Vikings in Northwest England, Georgina R. Bowden et al., Molecular Biology and Evolution, 20 November 2007". Mbe.oxfordjournals.org. 20 November 2007. Retrieved 21 May 2012.
- ↑ "A Y Chromosome Census of the British Isles, Capelli et al., Current Biology, Vol. 13, May 27, 2003" (PDF). Retrieved 21 May 2012.
- ↑ James Randerson, "Proof of Liverpool's Viking past", The Guardian, 3 Dec 2007, accessed 16 November 2008
- ↑ "DNA shows Celtic hero Somerled's Viking roots". Scotsman. 26 April 2005.
References
- Askeberg, Fritz, 1944: Norden och kontinenten i gammal tid. Studier i forngermansk kulturhistoria. Uppsala: Almqvist & Wiksell.
- Downham, Clare, Viking Kings of Britain and Ireland: The Dynasty of Ívarr to AD 1014. Dunedin Academic Press, 2007. ISBN 9781-903765-89-0
- Fitzhugh, William W., and Ward, Elisabeth I., Vikings: The North Atlantic Saga. Smithsonian Institution Press, 2000. ISBN 9781560989950
- Hadley, D.M., The Vikings in England: Settlement, Society and Culture. Manchester University Press, 2006. ISBN 0-7190-5982-8
- Hall, Richard, Exploring the World of the Vikings. Thames and Hudson, 2007. ISBN 978-0-500-05144-3
- Hall, Richard, Viking Age Archaeology (series Shire Studies), 2010. ISBN 978-0-7478-0063-7
- Heide, Eldar, 2005: «Víking – 'rower shifting'? An etymological contribution». Arkiv för nordisk filologi 120. 41–54.
- Heide, Eldar, 2008: «Viking, week, and Widsith. A reply to Harald Bjorvand». Arkiv för nordisk filologi 123. 23–28.
- Lindqvist, Thomas, 'Early Political Organisation: (a) An Introductory Survey', in The Cambridge History of Scandinavia: Prehistory to 1520, ed. Knut Helle. Cambridge University Press, 2003. ISBN 0-521-47299-7. pp. 160–67.
- Roesdahl, Else. The Vikings. Penguin, 1998. ISBN 0-14-025282-7
- Sawyer, Peter, The Age of the Vikings (second edition) Palgrave Macmillan, 1972. ISBN 0-312-01365-5
- Williams, Gareth, 'Kingship, Christianity and coinage: monetary and political perspectives on silver economy in the Viking Age', in Silver Economy in the Viking Age, ed. James Graham-Campbell and Gareth WIlliams, pp. 177–214; ISBN 978-1-59874-222-0
External links
| Look up Viking in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. |
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Viking Age. |
- Vikings—View videos at The History Channel
- Copenhagen-Portal – The Danish Vikings
- BBC: History of Vikings
- Encyclopædia Britannica: Viking, or Norseman, or Northman, or Varangian (people)
- Borg Viking museum, Norway
- Ibn Fadlan and the Rusiyyah, by James E. Montgomery, with full translation of Ibn Fadlan
- Reassessing what we collect website – Viking and Danish London History of Viking and Danish London with objects and images
- The Viking Answer Lady Webpage
- The Viking Rune: All Things Scandinavian
