Nonconcatenative morphology
Nonconcatenative morphology, also called discontinuous morphology and introflection, is a form of word formation in which the root is modified and which does not involve stringing morphemes together.[1]
Types of nonconcatenative morphology
Ablaut
In English, for example, while plurals are usually formed by adding the suffix -s, certain words use nonconcatenative processes for their plural forms:
- foot /fʊt/ → feet /fiːt/;
and many irregular verbs form their past tenses, past participles, or both in this manner:
- freeze /ˈfriːz/ → froze /ˈfroʊz/, frozen /ˈfroʊzən/.
This specific form of nonconcatenative morphology is known as base modification or ablaut, a form in which part of the root undergoes a phonological change without necessarily adding new phonological material. (In traditional Indo-Europeanist usage, these changes are termed ablaut only when they result from vowel gradations in Proto-Indo-European. Changes such foot/feet, which are due to the influence of a vanished front vowel at a later period, are termed umlaut.)
Other forms of base modification include lengthening of a vowel, as in Hindi:
- /mar-/ "die" ↔ /maːr-/ "kill"
or change in tone or stress:
- Chalcatongo Mixtec /káʔba/ "filth" ↔ /káʔbá/ "dirty"
- English record /ˈrɛkərd/ (noun) ↔ /rɨˈkɔrd/ "to make a record"
Transfixation
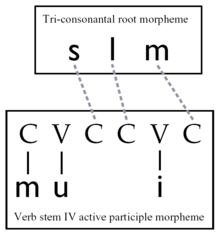
Another form of nonconcatenative morphology is known as transfixation, in which vowel and consonant morphemes are interdigitized. For example, depending on the vowels, the Arabic consonantal root k-t-b can have different but semantically related meanings. Thus, [kataba] 'he wrote' and [kitaːb] 'book' both come from the root k-t-b. Words from k-t-b are formed by filling in the vowels, e.g. kitāb "book", kutub "books", kātib "writer", kuttāb "writers", kataba "he wrote", yaktubu "he writes", etc. In the analysis provided by McCarthy's account of nonconcatenative morphology, the consonantal root is assigned to one tier, and the vowel pattern to another.[2]
Reduplication
Yet another common type of nonconcatenative morphology is reduplication, a process in which all or part of the root is reduplicated. In Sakha, this process is used to form intensified adjectives:
/k̠ɨhɨl/ "red" ↔ /k̠ɨp-k̠ɨhɨl/ "flaming red".
Truncation
A final common type of nonconcatenative morphology is variously referred to as truncation, deletion, or subtraction; the morpheme is sometimes called a disfix. This process removes phonological material from the root.
Semitic languages
Nonconcatenative morphology is extremely well developed in the Semitic languages, where it forms the basis of virtually all higher-level word formation (as with the example given in the diagram). This is especially pronounced in Arabic, where it is also used to form approximately 90% of all plurals; see broken plural.
See also
References
- ↑ Haspelmath, Martin (2002). Understanding Morphology. New York: Oxford University Press. ISBN 0-340-76026-5.
- ↑ McCarthy, John J. (1981). "A Prosodic Theory of Nonconcatenative Morphology". Linguistic Inquiry 12: 373–418.