Nodularin
| Nodularin | ||
|---|---|---|
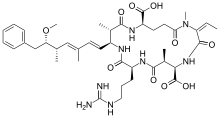 | ||
| Other names Cyclo[(2S,3S,4E,6E,8S,9S)-3-amino-9-methoxy-2,6,8-trimethyl-10-phenyl-4,6-decadienoyl-D-γ-glutamyl-(2Z)-2-(methylamino)-2-butenoyl-(3S)-3-methyl-D-β-aspartyl-L-arginyl] | ||
| Identifiers | ||
| CAS number | 118399-22-7 | |
| KEGG | C15713 | |
| Properties | ||
| Molecular formula | C41H60N8O10 | |
| Molar mass | 824.96 g mol−1 | |
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | ||
| Infobox references | ||
Nodularin-R is a cyclic nonribosomal peptide produced by the planktonic cyanobacterium Nodularia spumigena.[1] This cyanobacterium forms blooms in brackish water bodies throughout the world. The late summer blooms of Nodularia spumigena are among the largest cyanobacterial mass occurrences in the world. Nodularin-R is a pentapeptide and contains several unusual non-proteinogenic amino acids such as methyldehydrobutyrine and the β-amino acid ADDA, (all-S,all-E)-3-amino-9-methoxy-2,6,8-trimethyl-10-phenyldeca-4,6-dienoic acid. Nodularin-R is a cyanotoxin and poses a health risk for wild and domestic animals as well as humans. Nodularin-R is a potent hepatotoxin and may cause serious damage to the liver.
References
- ↑ Sivonen K, Kononen K, Carmichael WW, Dahlem AM, Rinehart KL, Kiviranta J, Niemela SI (1989). "Occurrence of the hepatotoxic cyanobacterium Nodularia spumigena in the Baltic Sea and structure of the toxin". Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 55 (8): 1990–5. PMC 202992. PMID 2506812.