Nitrosylsulfuric acid
| Nitrosylsulfuric acid | |
|---|---|
 | |
 | |
| IUPAC name Nitrosylsulfuric acid | |
| Other names nitrosonium bisulfate, chamber crystals | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | 7782-78-7 |
| PubChem | 82157 |
| ChemSpider | 74147 |
| Jmol-3D images | Image 1 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
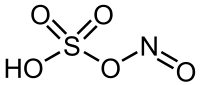
| Molecular formula | HNO5S |
| Molar mass | 127.08 g/mol |
| Appearance | pale yellow crystals |
| Density | 1.612 g/mL in 40% sulfuric acid soln |
| Melting point | 73.5 °C |
| Boiling point | decomposes |
| Solubility in water | decomposes |
| Solubility | soluble in H2SO4 |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | oxidizer |
| Related compounds | |
| Other anions | NOCl |
| Other cations | NaHSO4 |
| Related compounds | NOBF4 |
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |
| Infobox references | |
Nitrosylsulfuric acid is the chemical compound with the formula NOHSO4. It is a colourless solid that is used industrially in the production of caprolactam.[1]
Synthesis and reactions
A typical procedure entails dissolving sodium nitrite in concentrated sulfuric acid in an ice bath:[2][3]
- HNO2 + H2SO4 → NOHSO4 +H2O
The molecule can also be viewed as the mixed acid anhydride of sulfuric acid and nitrous acid. Alternatively, it can be prepared by the reaction of nitric acid and sulfur dioxide.[4]
NOHSO4 is useful in organic chemistry to prepare diazonium salts from amines. Related NO-delivery reagents include nitrosonium tetrafluoroborate ([NO]BF4) and nitrosyl chloride.
References
- ↑ Ritz, J.; Fuchs, H.; Kieczka, H.; Moran, W. C. (2002). "Caprolactam". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a05_031.
- ↑ Hodgson, H. H.; Mahadevan, A. P.; Ward, E. R. (1955), "1,4-Dinitronaphthalene", Org. Synth.; Coll. Vol. 3: 341 (diazodization followed by treatment with nitrite)
- ↑ Sandin, R. B.; Cairns, T. L. (1943), "1,2,3-Triiodo-5-nitrobenzene", Org. Synth.; Coll. Vol. 2: 604 (diazodization followed by treatment with iodide)
- ↑ Coleman, G. H.; Lillis, G. A.; Goheen, G. E. (1939). "Nitrosyl Chloride". Inorganic Syntheses 1: 55–59. doi:10.1002/9780470132326.ch20. This procedure generates the nitrosylsulfuric acid as an intermediate en route to NOCl.