Nigericin
| Nigericin | |
|---|---|
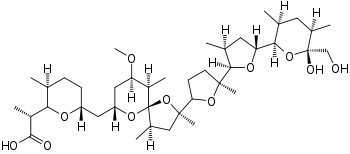 | |
| IUPAC name (2R)-2-[(2R,3S,6R)-6-[[(2S,4R,5R,7R,9R,10R)- 2-[(2R,5S)-5-[(2R,3S,5R)-5-[(2S,3S,5R,6R)-6-hydroxy- 6-(hydroxymethyl)-3,5-dimethyl-2-tetrahydropyranyl]-3-methyl- 2-tetrahydrofuranyl]-5-methyl-2-tetrahydrofuranyl]-9-methoxy- 2,4,10-trimethyl-1,6-dioxaspiro[4.5]decan-7-yl]methyl]-3-methyl- 2-tetrahydropyranyl]propanoic acid | |
| Other names Polyetherin A, Azalomycin M, Helixin C, Helix C | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | 28380-24-7 |
| PubChem | 34230 |
| ChemSpider | 10196461 |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:7569 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL405862 |
| Jmol-3D images | {{#if:OC(=O)[C@H](C)[C@@H]1O[C@H](CC[C@@H]1C)C[C@H]6O[C@]2(O[C@@](C)(C[C@H]2C)[C@H]3CC[C@](C)(O3)[C@@H]4O[C@H](C[C@@H]4C)[C@H]5O[C@@](O)(CO)[C@H](C)C[C@@H]5C)[C@H](C)[C@H](OC)C6|Image 1 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| Molecular formula | C40H68O11 |
| Molar mass | 724.96132 |
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |
| Infobox references | |
Nigericin is an antibiotic derived from Streptomyces hygroscopicus. Its isolation was described in the 1950s,[1] and in 1968 the structure could be elucidated by X-ray crystallography.[2] The structure and properties of nigericin are similar to the antibiotic monensin. Commercially it is obtained as a byproduct, or contaminant, at the fermentation of Geldanamycin. It is also called Polyetherin A, Azalomycin M, Helixin C, Antibiotic K178, Antibiotic X-464.
Nigericin acts as an H+, K+, Pb2+ ionophore. Most commonly it is an antiporter of H+ and K+.
In the past nigericin was used as an antibiotic active against gram positive bacteria. It inhibits the Golgi functions in Eukaryotic cells. Nigericin exhibits anti-HIV activity.
References
- ↑ Graven SN, Estrada-O S, Lardy HA (1966). "Alkali metal cation release and respiratory inhibition induced by nigericin in rat liver mitochondria". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 56 (2): 654–8. doi:10.1073/pnas.56.2.654. PMC 224422. PMID 5229984.
- ↑ Steinrauf LK, Pinkerton M, Chamberlin JW (1968). "The structure of nigericin". Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 33 (1): 29–31. doi:10.1016/0006-291X(68)90249-0. PMID 5696503.
External references
Commercial supplier of nigericin sodium
| |||||