Nicotianamine
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
| Nicotianamine | |
|---|---|
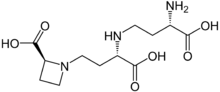 | |
| IUPAC name N-(N-(3-amino-3-carboxypropyl)-3-amino-3-carboxypropyl)azetidine-2-carboxylic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | 34441-14-0 |
| PubChem | 7705 |
| ChemSpider | 8058557 |
| Jmol-3D images | {{#if:C1CN([C@@H]1C(=O)O)CC[C@@H](C(=O)O)NCC[C@@H](C(=O)O)N|Image 1 |
| |
| Properties | |
| Molecular formula | C12H21N3O6 |
| Molar mass | 303.31164 g/mol |
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |
| Infobox references | |
Nicotianamine is an angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitor. A metal-chelating molecule, it is ubiquitous in higher plants.[1] Biochemically, it is synthesized by the enzyme nicotianamine synthase, which uses three molecules of S-adenosylmethionine.[2]
References
- ↑ Takahashi M, Terada Y, Nakai I, Nakanishi H, Yoshimura E, Mori S, Nishizawa NK. (2003). "Role of nicotianamine in the intracellular delivery of metals and plant reproductive development". The Plant Cell 15 (6): 1263–80.
- ↑ Zheng L, Cheng Z, Ai C, Jiang X, Bei X, Zheng Y, Glahn RP, Welch RM, Miller DD, Lei XG, Shou H. (2010). "Nicotianamine, a novel enhancer of rice iron bioavailability to humans". PLOS 5 (4): e10190. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0010190.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike; additional terms may apply for the media files.