Neoxanthin
| Neoxanthin | |
|---|---|
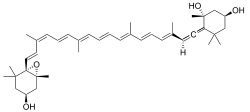 | |
| IUPAC name (1R,3S)-6-((R,3E,5E,7E,9E,11E,13E,15Z,17E)-18-((1S,4S,6R)-4-hydroxy-2,2,6-trimethyl-7-oxabicyclo[4.1.0]heptan-1-yl)-3,7,12,16-tetramethyloctadeca-1,3,5,7,9,11,13,15,17-nonaen-1-ylidene)-1,5,5-trimethylcyclohexane-1,3-diol | |
| Other names Foliaxanthin; Neoxanthine | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | 14660-91-4 |
| PubChem | 5281247 |
| ChemSpider | 4444659 |
| Jmol-3D images | {{#if:CC(/C=C/[C@@]12[C@@](O2)(C)C[C@@H](O)CC1(C)C)=C/C=C/C(C)=C/C=C/C=C(C)/C=C/C=C(C)/C([H])=[C@@]=C3C(C)(C)C[C@H](O)C[C@]3(O)C|Image 1 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| Molecular formula | C40H56O4 |
| Molar mass | 600.87 g mol−1 |
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |
| Infobox references | |
Neoxanthin is a carotenoid and xanthophyll. In plants, it is an intermediate in the biosynthesis of the plant hormone abscisic acid. It is produced from violaxanthin by the action of neoxanthin synthase.[1] It is a major xanthophyll found in green leafy vegetables such as spinach.
References
- ↑ Bouvier, Florence; D'harlingue, Alain; Backhaus, Ralph A.; Kumagai, Monto H.; Camara, Bilal (2000). "Identification of neoxanthin synthase as a carotenoid cyclase paralog". European Journal of Biochemistry 267 (21): 6346–6352. doi:10.1046/j.1432-1327.2000.01722.x. PMID 11029576.