Neo-Inositol
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
| neo-Inositol | |
|---|---|
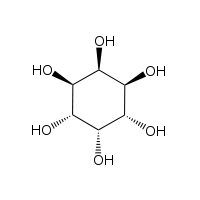 | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | 488-54-0 |
| ChemSpider | 10199749 |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:25492 |
| Jmol-3D images | {{#if:O[C@H]1[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H]1O|Image 1 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| Molecular formula | C6H12O6 |
| Molar mass | 180.16 g mol−1 |
| Melting point | 588 K [1] |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | Irritating to eyes, respiratory system and skin.[2] |
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |
| Infobox references | |
neo-Inositol is one of the stereoisomers of inositol. It is one of the nine isomeric forms of cyclohexanehexol; a group of small and chemically very stable polar molecules that have versatile properties.[3] This stereoisomer is naturally occurring, but only in small amounts. It is also known as (1s,2R,3R,4s,5S,6S)-cyclohexane-1,2,3,4,5,6-hexol or 1,2,3/4,5,6-cyclohexanehexol in the IUPAC naming system.[4]
See also
- allo-Inositol
- cis-Inositol
- D-chiro-Inositol
- L-chiro-Inositol
- epi-Inositol
- muco-Inositol
- scyllo-Inositol
References
- ↑ Watt, S. W.; Chisholm, J. A.; Jones, W.; Motherwell, S. (2004). "A Molecular Dynamics Simulation of the Melting Points and Glass Transition Temperatures of Myo- and Neo-Inositol". Journal of Chemical Physics 121 (19): 9565–9573.
- ↑ "Material Safety Data Sheet". Sigma-Aldrich. Retrieved 9 October 2012.
- ↑ Michell, R. H. (February 2008). "Inositol Derivatives: Evolution and Functions". Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology 9 (2).
- ↑ "Neo-Inositol". Retrieved 9 October 2012.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike; additional terms may apply for the media files.