Nelarabine
 | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Systematic (IUPAC) name | |
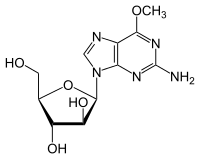
| (2R,3S,4S,5R)-2-(2-amino-6-methoxy-purin-9-yl)-5-(hydroxymethyl)oxolane-3,4-diol | |
| Clinical data | |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | monograph |
| Licence data | EMA:Link, US FDA:link |
| Pregnancy cat. | D (US) |
| Legal status | ℞-only (US) |
| Routes | Intravenous |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | n/a |
| Protein binding | <25% |
| Metabolism | By adenosine deaminase, to 9-β-D-arabinofuranosylguanine |
| Half-life | 30 minutes (nelarabine) 3 hours (ara-G) |
| Excretion | Renal |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | 121032-29-9 |
| ATC code | L01BB07 |
| PubChem | CID 3011155 |
| DrugBank | DB01280 |
| ChemSpider | 2280207 |
| UNII | 60158CV180 |
| KEGG | D05134 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL1201112 |
| Chemical data | |
| Formula | C11H15N5O5 |
| Mol. mass | 297.268 g/mol |
| SMILES
| |
| |
| | |
Nelarabine is a chemotherapy drug used in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. It was previously known as 506U78.
Nelarabine is a purine nucleoside analog converted to its corresponding arabinosylguanine nucleotide triphosphate (araGTP), resulting in inhibition of DNA synthesis and cytotoxicity. Pre-clinical studies suggest that T-cells are particularly sensitive to nelarabine. In October 2005, it was approved by the FDA for T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia and T-cell lymphoblastic lymphoma that has not responded to or has relapsed following treatment with at least two chemotherapy regimens. It was later approved in the European Union in the October of 2005. Complete responses have been achieved with this medication.
It is marketed in the US as Arranon and as Atriance in the EU by GlaxoSmithKline.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||