Ndjamena–Djibouti Highway
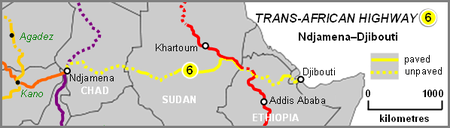
The Ndjamena-Djibouti Highway is Trans-African Highway 6 in the transcontinental road network being developed by the United Nations Economic Commission for Africa (UNECA), the African Development Bank (ADB), and the African Union, connecting the Sahelian region to the Indian Ocean port of Djibouti in the country of Djibouti.
The road passes though Darfur in western Sudan and the town of Al Fashir, scene of the Darfur conflict. Consequently travel through that area and Sudan–Chad border region is unsafe and development of that section is at a standstill.
The route has a length of 4,219 km (2,622 mi) crossing Chad, central Sudan and northern Ethiopia. Less than half of it is paved and a significant proportion of that is in poor condition. Mountainous terrain in Ethiopia presents challenges to highway engineers.
Between Wad Medani in Sudan and Werota in Ethiopia the highway shares the same route as Trans-Africa Highway 4, the Cairo-Cape Town Highway.
The highway is contiguous with the Dakar-Ndjamena Highway with which it will form a complete east-west crossing of the continent of 8,715 km (5,415 mi). The approximate route of the two highways follows a route originally proposed in the French Empire of the late 19th and early 20th centuries, and earlier French attempts to control the transcontinental crossing led to the Fashoda Incident.
See also
References
- African Development Bank/United Nations Economic Commission For Africa: "Review of the Implementation Status of the Trans African Highways and the Missing Links: Volume 2: Description of Corridors". August 14, 2003. Retrieved 14 July 2007.
- Michelin Motoring and Tourist Map: "Africa North and West". Michelin Travel Publications, Paris, 2000.
| ||||||||||
