Named graph
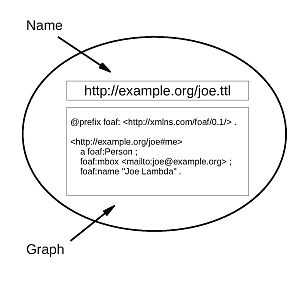
Named graphs are a key concept of Semantic Web architecture in which a set of Resource Description Framework statements (a graph) are identified using a URI,[1] allowing descriptions to be made of that set of statements such as context, provenance information or other such metadata.
Named graphs are a simple extension of the RDF data model[2] through which graphs can be created but the model lacks an effective means of distinguishing between them once published on the Web at large.
Named graphs and HTTP
One conceptualization of the Web is as a graph of document nodes identified with URIs and connected by hyperlink arcs which are expressed within the HTML documents. By doing a HTTP GET on a URI (usually via a Web browser), a somehow-related document may be retrieved. This "follow your nose" approach also applies to RDF documents on the Web in the form of Linked Data, where typically an RDF syntax is used to express data as a series of statements, and URIs within the RDF point to other resources. This Web of data has been described by Tim Berners-Lee as the "Giant Global Graph".[3]
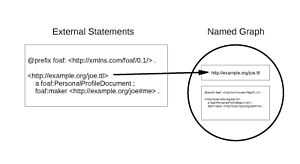
Named graphs are a formalization of the intuitive idea that the contents of an RDF document (a graph) on the Web can be considered to be named by the URI of the document. This considerably simplifies techniques for managing chains of provenance for pieces of data and enabling fine-grained access control to the source data. Additionally trust can be managed through the publisher applying a digital signature to the data in the named graph. (Support for these facilities was originally intended to come from RDF reification, however that approach proved problematic.[4])
Named graphs and RDF stores
While named graphs may appear on the Web as simple linked documents (i.e. Linked Data), they are also very useful for managing sets of RDF data within an RDF store. In particular, the scope of a SPARQL query may be limited to a specific set of named graphs.
Example
Assume the following (Turtle) RDF document has been placed in a SPARQL-capable store with the name http://example.org/joe.
@prefix foaf: <http://xmlns.com/foaf/0.1/> . <http://example.org/joe#me> a foaf:Person . <http://example.org/joe#me> foaf:homepage <http://example.org/joe/INDEX.html> . <http://example.org/joe#me> foaf:mbox <mailto:joe@example.org> . <http://example.org/joe#me> foaf:name "Joe Lambda" .
This data has been written in a more verbose form than necessary to show the triple structures
The homepage of the person with the email address mailto:joe@example.org can be obtained using the SPARQL query:
PREFIX foaf: <http://xmlns.com/foaf/0.1/> SELECT ?homepage FROM NAMED <http://example.org/joe> WHERE { GRAPH ?g { ?person foaf:homepage ?homepage . ?person foaf:mbox <mailto:joe@example.org> . } }
The FROM NAMED here identifies the target graph for the query.
Named graphs and quads
Prior to the publication of the papers describing named graphs, there was considerable discussion about fulfilling their role within a store by using an arity above that of RDF triple statements: where triples have the form <subject> <predicate> <object>, quads would have a form along the lines of <context> <subject> <predicate> <object>. Named graphs can be represented this way, as <graphname> <subject> <predicate> <object>, with the advantage that the <graphname> part will be a URI, giving the quad Web-global scope compared to arbitrary local statement names.
Formal definition
See.[5] If link broken try.[6]
Specifications
There is currently no specification for named graphs in themselves beyond that described in[5] and[6] (which includes syntaxes for representing named graphs), however they do form part of the SPARQL Protocol and RDF Query Language specification.
Proposed specifications
- TriX (syntax) - Named Graphs in XML
- TriG (syntax) - Named Graphs in Turtle
See also
- Jeni Tennison (2011-07-05). "What Do URIs Mean Anyway?". Jeni's Musings. Jeni Tennison. Retrieved 6 July 2011.
References
- ↑ strictly speaking a URIRef
- ↑ http://www.w3.org/TR/PR-rdf-syntax/ "Resource Description Framework (RDF) Model and Syntax Specification"
- ↑ Giant Global Graph
- ↑ Reification of RDF and N3)
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Named Graphs, Provenance and Trust
- ↑ 6.0 6.1