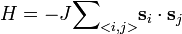N-vector model
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
The n-vector model or O(n) model is one of the many highly simplified models in the branch of physics known as statistical mechanics. In the n-vector model, n-component, unit length, classical spins  are placed on the vertices of a lattice. The Hamiltonian of the n-vector model is given by:
are placed on the vertices of a lattice. The Hamiltonian of the n-vector model is given by:
where the sum runs over all pairs of neighboring spins  and
and  denotes the standard Euclidean inner product. Special cases of the n-vector model are:
denotes the standard Euclidean inner product. Special cases of the n-vector model are:
 || The Self-Avoiding Walks (SAW)
|| The Self-Avoiding Walks (SAW) || The Ising model
|| The Ising model  || The XY model
|| The XY model  || The Heisenberg model
|| The Heisenberg model || Toy model for the Higgs sector of the Standard Model
|| Toy model for the Higgs sector of the Standard Model
The general mathematical formalism used to describe and solve the n-vector model and certain generalizations are developed in the article on the Potts model.
References
- P.G. de Gennes, Phys. Lett. A, 38, 339 (1972) noticed that the
 case corresponds to the SAW.
case corresponds to the SAW. - George Gaspari, Joseph Rudnick, Phys. Rev. B, 33, 3295 (1986) discuss the model in the limit of
 going to 0.
going to 0.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike; additional terms may apply for the media files.