N-Oxalylglycine
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
| N-Oxalylglycine | |
|---|---|
 | |
| IUPAC name N-Oxalylglycine[citation needed] | |
| Other names [(Carboxymethyl)amino](oxo)acetic acid[citation needed] | |
| Identifiers | |
| Abbreviations | NOG[citation needed] |
| CAS number | 5262-39-5 |
| PubChem | 3080614 |
| ChemSpider | 2338366 |
| MeSH | oxalylglycine |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:44482 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL90852 |
| Jmol-3D images | Image 1 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| Molecular formula | C4H5NO5 |
| Molar mass | 147.09 g mol−1 |
| Appearance | colourless crystals |
| log P | 1.232 |
| Acidity (pKa) | 2.827 |
| Basicity (pKb) | 11.170 |
| Related compounds | |
| Related alkanoic acids | |
| Related compounds | N-Acetylglycinamide |
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |
| Infobox references | |
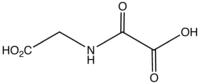
N-Oxalylglycine is the organic compound with the formula HO2CC(O)NHCH2CO2H. This colourless solid is used as an inhibitor of α-ketoglutarate-dependent enzymes.[1] It is isosteric with α-ketoglutaric acid. Such enzymes are pervasive and, for example, are required for the synthesis of 4-hydroxyproline.
References
- ↑ Hausinger, R. P."Fe(II)/α-ketoglutarate-dependent hydroxylases and related enzymes" Critical Reviews of Biochemical Molecular Biology 2004, 39: pp 21-68. doi:10.1080/10409230490440541
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike; additional terms may apply for the media files.