Nüwa
| Nüwa | |
|---|---|
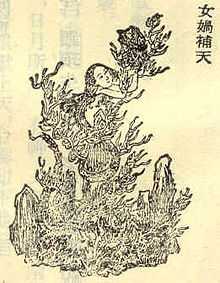 Nuwa repairing the wall of heaven | |
| Spouse(s) | Fu Xi[1] |
| Parents | Jade Emperor |
Nüwa (also Nyuwa, Nuwa, Nü-wa, Nu-wa and Nügua; traditional Chinese: 女媧; simplified Chinese: 女娲; pinyin: Nǚwā; Wade–Giles: Nü3-wa1) is a goddess in ancient Chinese mythology best known for creating mankind and repairing the wall of heaven. Depending on the source, she might be considered the second or even the first Chinese ruler, with most sources not putting her on the role, but only her brother and/or husband Fu Xi.
Description
The legend of Nüwa is told in many ancient texts.
The Shan Hai Jing, dated between the Warring States period and the Han Dynasty, describes Nüwa's intestines as being scattered into ten spirits.[2]
In Liezi (c. 475 - 221 BC), Chapter 5 "Questions of Tang" (Chinese: 卷第五 湯問篇), author Lie Yukou describes Nüwa repairing the original imperfect heaven using five-colored stones, and cutting the legs off a tortoise to use as struts to hold up the sky.
In Songs of Chu (c. 340 - 278 BC), Chapter 3 "Asking Heaven" (Chinese: 问天), author Qu Yuan writes that Nüwa molded figures from the yellow earth, giving them life and the ability to bear children. After demons fought and broke the pillars of the heavens, Nüwa worked unceasingly to repair the damage, melting down the five-coloured stones to mend the heavens.
In Huainanzi (c. 179 - 122 BC), Chapter 6 Lanmingxun (Chinese: 覽冥訓), author Liu An tells that in remote antiquity the four poles of the Universe collapsed and the world descended into chaos; the firmament was no longer able to cover everything and the earth was no longer able to support itself; fires burned wild and waters flooded the land; fierce beasts ate common people, and ferocious birds attacked the old and the weak. So Nüwa tempered the five-colored stones to mend the heavens, cut off the feet of the great turtle to support the four poles, killed the black dragon to help the earth, and gathered the ash of reed to stop the flood. (In a variation of this tale, the four corners of the sky collapsed and the world with its nine regions split open.)

In Shuowen Jiezi (c. 58 - 147 AD), China's earliest dictionary, under the entry for Nüwa author Xu Shen describes her as being both the sister and the wife of Fu Xi. Nüwa and Fu Xi were pictured as having snake like tails interlocked in an Eastern Han Dynasty mural in the Wuliang Temple in Jiaxiang county, Shandong province.
In Duyi Zhi (Chinese: 獨異志; c. 846 - 874 AD), Volume 3, author Li Rong gives this description.
Long ago, when the world first began, there were two people, Nü Kua and her older brother. They lived on Mount K'un-lun. And there were not yet any ordinary people in the world. They talked about becoming husband and wife, but they felt ashamed. So the brother at once went with his sister up Mount K'un-lun and made this prayer: "Oh Heaven, if Thou wouldst send us two forth as man and wife, then make all the misty vapor gather. If not, then make all the misty vapor disperse." At this, the misty vapor immediately gathered. When the sister became intimate with her brother, they plaited some grass to make a fan to screen their faces. Even today, when a man takes a wife, they hold a fan, which is a symbol of what happened long ago.[3]
In Yuchuan Ziji (Chinese: 玉川子集 c. 618 - 907 AD), Chapter 3 (Chinese: "與馬異結交詩" 也稱 "女媧本是伏羲婦"; pinyin: "Yu Mayi Jie Jiao Shi" YeCheng "Nüwa ben shi Fu Xi fu"), author Lu Tong describes Nüwa as the wife of Fu Xi.
In Siku Quanshu, Sima Zhen (679–732) provides commentary on the prologue chapter to Sima Qian's Shiji, "Supplemental to the Historic Record: History of the Three August Ones," wherein it is found that the Three August Ones are Nüwa, Fu Xi, and Shennong; Fu Xi and Nüwa have the same last name, Feng (Chinese: 風). Note: Sima Zhen's commentary is included with the later Siku Quanshu compiled by Ji Yun and Lu Xixiong.
In the collection Four Great Books of Song (c. 960 - 1279 AD), compiled by Li Fang and others, Volume 78 of the book Imperial Readings of the Taiping Era contains a chapter "Customs by Yingshao of the Han Dynasty" in which it is stated that there were no men when the sky and the earth were separated. Thus Nüwa used yellow clay to make people. But the clay was not strong enough so she put ropes into the clay to make the bodies erect. It is also said that she prayed to gods to let her be the goddess of marital affairs. Variations of this story exist.
Roles
Since Nüwa is presented differently in so many myths/legends, it is not accurate to tie her down as a creator, mother, or goddess. Depending on the myth, she is responsible for being a wife, sister, man, tribal leader (or even empress), creator, maintainer, etc. It is not clear from the evidence which view came first. Regardless of the origins, most myths present Nüwa as female in a procreative role after a calamity. She was also known as the creator of humans through clay but there has been many theories to this.
Repairer
The earliest literary role seems to be the upkeep and maintenance of the Wall of Heaven, whose collapse would obliterate everything.
There was a quarrel between two of the more powerful gods, Gong Gong and Zhu Rong and they decided to settle it with fists. When the water god, Gong Gong, saw that he was losing, he smashed his head against Mount Buzhou (不周山), a pillar holding up the sky. The pillar collapsed and caused the sky to tilt towards the northwest and the earth to shift to the southeast. This caused great calamities, such as raging fires, vast floods, and the appearance of fierce man-eating beasts. Nüwa cut off the legs of a giant tortoise and used them to supplant the fallen pillar, alleviating the situation and sealing the broken sky using stones of seven different colors, but she was unable to fully correct the tilted sky. This explains the phenomenon that sun, moon, and stars move towards the northwest, and that rivers in China flow southeast into the Pacific Ocean.
Other versions of the story describe Nüwa going up to heaven and filling the gap with her body (half human half serpent) and thus stopping the flood.[citation needed] According to this legend some of the minorities in South-Western China hail Nüwa as their goddess and some festivals such as the 'Water-Splashing Festival' are in part a tribute to her sacrifices.[citation needed]
Creator
Nüwa is also depicted as a creator deity. However, not many stories ascribe to her the creation of everything; they usually confine her to the creation of humanity.
A legend states that Nüwa existed in the beginning of the world. She felt lonely as there were no animals, so she began to create animals and humans. On the first day she created chickens; on the second, dogs; on the third, sheep; on the fourth, pigs; on the fifth, cows; on the sixth, horses; and on the seventh, humanity. She began creating human beings from yellow clay, sculpting each one individually. After she had created hundreds of figures in this way, she still had more to make but had grown tired of the laborious process. So instead of handcrafting each figure, she dipped a rope in clay and flicked it so blobs of clay landed everywhere; each of these blobs became a common person. Nüwa still laboriously crafted some people out of clay; these people became nobles.
Wife or sister
By the Han Dynasty, she is described in literature with her brother Fu Xi as the first of the Three August Ones and Five Emperors. Paintings depicting them joined as half people-half serpent or dragon date to the Warring States period.
Miao goddess
Nüwa and Fu Xi are also found under different names (Nkauj Muam and Nraug Nus[4]) as originators of mankind through an act of incest after the Flood in legends and myths of the Miao people.
In history
Paintings of Nüwa, and her consort Fu Xi, date to the Warring States period.
Herbert James Allen erroneously translated Tang Dynasty historian Sima Zhen's interpolated prologue to the Han dynasty Sima Qian's Shiji. In one of his more serious flaws, Nüwa was described as male even though the Nü (女) in the name means female and the wa (媧) also contains the female radical.
Appearance in Fengshen Yanyi
Nüwa is featured within the famed Ming dynasty novel Fengshen Bang. As featured within this novel, Nüwa is very highly respected since the time of the Xia Dynasty for being the daughter of the Jade Emperor; Nüwa is also regularly called the "Snake Goddess". After the Shang Dynasty had been created, Nüwa created the five-colored stones to protect the dynasty with occasional seasonal rains and other enhancing qualities. Thus in time, Shang Rong asked King Zhou of Shang to pay her a visit as a sign of deep respect. After Zhou was completely overcome with lust at the very sight of the beautiful ancient goddess Nüwa (who had been sitting behind a light curtain), he would write a small poem on a neighboring wall and take his leave. When Nüwa later returned to her temple after visiting the Yellow Emperor, Nüwa would see the foulness of Zhou's words. In her anger, she swore that the Shang Dynasty will end in payment for his foulness. In her rage, Nüwa would personally ascend to the palace in an attempt to kill the king, but was suddenly struck back by two large beams of red light.
After Nüwa realized that King Zhou was already destined to rule the kingdom for twenty-six more years, Nüwa would summon her three subordinates—the Thousand-Year Vixen (later becoming Daji), the Jade Pipa, and the Nine-Headed Pheasant. With these words, Nüwa would bring destined chaos to the Shang Dynasty, "The luck Cheng Tang won six hundred years ago is dimming. I speak to you of a new mandate of heaven which sets the destiny for all. You three are to enter King Zhou's palace, where you are to bewitch him. Whatever you do, do not harm anyone else. If you do my bidding, and do it well, you will be permitted to reincarnate as human beings." Thus, with these words, Nüwa would never be heard of again, but would still be a major indirect factor towards the Shang Dynasty's fall.
See also
Notes
- ↑ Worshiping the Three Sage Kings and Five Virtuous Emperors - The Imperial Temple of Emperors of Successive Dynasties in Beijing. Beijing: Foreign Language Press. 2007. ISBN 978-7-119-04635-8.
- ↑ "16《大荒西經》". 山海經 [Shan Hai Jing] (in Chinese). 4th Century BC.
- ↑ Tr. by Birrell 1993, p.35
- ↑ See Yees Thoj. "Nkauj Muam Nraug Nus".
References
- Allan, Sarah (1991), The shape of the turtle: myth, art, and cosmos in early China, SUNY series in Chinese philosophy and culture, SUNY Press, ISBN 0-7914-0460-9
- Birrell, Anne (1993), Chinese Mythology: An Introduction, Johns Hopkins University Press.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Nuwa. |