Mycenaean Greece
| Part of a series on the |
| History of Greece |
|---|
 |
|
History by topic
|
|
|
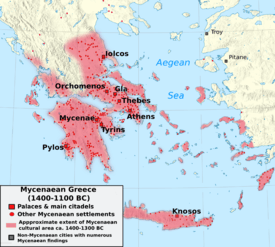
Mycenaean Greece was the last phase of the Bronze Age in Ancient Greece (ca. 1600–1100 BC). It takes its name from the archaeological site of Mycenae in Argolis, Peloponnese, southern Greece. Other major sites included Tiryns in Argolis, Pylos in Messenia, Athens in Attica, Thebes and Orchomenus in Boeotia, and Iolkos in Thessaly, while Crete and the site of Knossos also became a part of the Mycenaean world. Mycenaean settlement sites also appeared in Epirus,[1][2] Macedonia,[3][4] on islands in the Aegean Sea, on the coast of Asia Minor, the Levant,[5] Cyprus,[6] and Italy.[7]
Mycenaean civilization perished with the collapse of Bronze-Age civilization in the eastern Mediterranean, which is commonly attributed to the Dorian invasion, although alternative theories propose also natural disasters and climatic changes. This period of Greek history is the historical setting of much ancient Greek literature and myth, including the epics of Homer.[8]
Mycenaean civilization
Mycenaean civilization originated and evolved from the society and culture of the Early and Middle Helladic periods in mainland Greece.[9] It emerged at ca. 1600 BC, when Helladic culture in mainland Greece was transformed under influences from Minoan Crete.
Mycenaean artifacts have been found well outside the limits of the Mycenaean world: namely Mycenaean swords are known from as far away as Georgia in the Caucasus,[10] an amber object inscribed with Linear B symbols has been found in Bavaria, Germany[11] and Mycenaean bronze double axes and other objects dating from 13th century BC have been found in Ireland and in Wessex and Cornwall in England.[12][13]
Quite unlike the Minoans, whose society benefited from trade, the Mycenaeans advanced through conquest. Mycenaean civilization was dominated by a warrior aristocracy. Around 1400 BC, the Mycenaeans extended their control to Crete, center of the Minoan civilization (which had been crippled by the Minoan eruption of the Santorini/Thera volcano), and adopted a form of the Minoan script (called Linear A) to write their early form of Greek in Linear B.

Not only did the Mycenaeans defeat the Minoans, but according to later Hellenic legend they defeated Troy, presented in epic as a city-state that rivaled Mycenae in power. Because the only evidence for the conquests is Homer's Iliad and other texts steeped in mythology, the existence of Troy and the historicity of the Trojan War is uncertain. In 1876, the German archaeologist Heinrich Schliemann uncovered ruins at Hissarlik in western Asia Minor (modern-day Turkey) that he claimed were those of Troy. Some sources claim these ruins do not match well with Homer's account of Troy,[14] but others disagree.[15]
The Mycenaeans buried their nobles in beehive tombs (tholos tombs), large circular burial chambers with a high vaulted roof and a straight entry passage lined with stone. They often buried daggers or some other form of military equipment with the deceased. The nobility were frequently buried with gold masks, tiaras, armor, and jeweled weapons. Mycenaeans were buried in a sitting position, and some of the nobility underwent mummification, whereas Homer's Achilles and Patroclus were not buried but cremated, in Iron-Age fashion, and honoured with a gold urn, instead of gold masks.
Historical correlations

From a chronological perspective, the Late Helladic period (LH, 1550–1060 BC) is the time when Mycenaean Greece flourished under new influences from Minoan Crete and the Cyclades. Those who made LH pottery sometimes inscribed their work in Linear B, a syllabic script recognizable as a form of Greek. LH is divided into I, II, and III; of which I and II overlap Late Minoan ware and III overtakes it. LH III is further subdivided into IIIA, IIIB, and IIIC.
Late Helladic pottery typically stored such goods as olive oil and wine. LHI ware had reached Santorini just before the Thera eruption. LHIIB began during LMIB, and has been found in Egypt during the reign of Tuthmosis III. LHIIB spanned the LMIB/LMII destruction on Crete, which is associated with the Greek takeover of the island.

LHIIIA:1 corresponds with the reign of Amenhotep III, who recorded with the heading ti-n3-y 'Danaans' (Mycenaean *Danawoi, later Greek loses w, the digamma ϝ, before a vowel) the apparently equal cities d-y-q-e-i-s 'Thebes' (Mycenaean *Thegʷais, the gʷ develops into b in later Greek) and m-w-k-i-n-u 'Mycenae' (Mycenaean *Mukanai). LHIIIA:1 also corresponds with the time of Attarsiya, the Man of Ahhiya, who alternately attacked and aided the rebel Madduwatta of Zippasla.[16] Ahhiya and its LHIIIA:2-B derivative, Ahhiyawa, can be linked to Greece only indirectly. The Hittites did not use any term approximating ti-n3-y; and they did not link Ahhiya, with these cities, or any other projected LBA names of known Greek cities. Also, no "Attarsiyas layer" of LHIIIA:1 has yet been found in western Anatolia. Still, Ahhiya must refer to a powerful people off the coast of Miletus, and Greece is the best available option at this time.
LHIIIA:1-period ti-n3-y/"Ahhiya" (and for that matter LHIIIA:1 Greece) did not feature otherwise in the inscriptions of the great kings of the Bronze Age, and certainly not as a coherent state.
LHIIIA:2 ware was in the Uluburun shipwreck, and was in use at Miletus before Mursili II burned it in circa 1320 BC. At this time, actual maritime trade was the specialty of the Cypriots and Phoenicians (so the presence of LH ware does not necessarily mean the presence of Mycenaeans).
During the LHIIIA:2 period, kings of "Ahhiyawa" began to come to the attention of the Hittites, possibly as rulers of the "Achaean" states. In LHIIIB, they rose almost to the status of the Great Kings in Egypt and Assyria. LHIIIB is also the period of Linear B script at the mainland palaces; prior to then, Linear B was in use primarily in the Cyclades and Crete. The term "Submycenaean" was introduced in 1934 by T. C. Skeat,[17] but this is now regarded as a pottery style rather than a distinct period. Current opinion sees this style as the final stage of Late Helladic IIIC (and perhaps not even a very significant one).[18] Arne Furumark already termed it LHIIIC:2 in his monumental "Mycenaean Pottery: Analysis and Classification" (Stockholm 1941). This pottery is best known from the cemeteries of Kerameikos in Athens, the island of Salamis located in the Saronic Gulf off Attica, Skoubris in Lefkandi (Euboea), and the markets of Athens (Agora), Tiryns, and Mycenae.
Identity
Since the decipherment of the somewhat younger Linear B tablets, it is thought that the people we call Mycenaeans might have been Achaeans or later subjected by them. No written source found at a Mycenaean site reveals what they called themselves. Upon a reading of the Iliad, where the residents of the Peloponnesus and adjacent islands are often called Achaeans, and taking into account mention of the Ahhiyawa in Hittite sources from the Late Bronze Age,[19] the theory suggests itself that the Mycenaeans could possibly even be Achaeans.[20] The Tawagalawa Letter written by an unnamed Hittite king of the empire period (14th–13th century BC) to the king of Ahhiyawa, treating him as an equal, suggests that Miletus (Millawanda) was under his control and refers to an earlier "Wilusa episode" involving hostility on the part of Ahhiyawa.[21] Ahhiya(wa) has been identified with the Achaeans of the Trojan War and the city of Wilusa with the legendary city of Troy. However, the exact relationship of the term Ahhiyawa to the Achaeans beyond a similarity in pronunciation is hotly debated by scholars, even following the discovery that Mycenaean Linear B is an early form of Greek; the earlier debate was summed up in 1984 by Hans G. Güterbock of the Oriental Institute.[22]
Political organization
Mycenaean world
Given the absence of direct sources, the political organization of the Mycenaean world cannot be determined with absolute certainty; however, it was the Neolithic agrarian village (6000 BC) that constituted the foundation of Bronze Age political culture in Greece.[23] In the tradition recorded centuries later in Homer, there were several states, the cities of the Iliad: Mycenae, Pylos, Orchomenos—which are known to archaeology—and perhaps also unconfirmed Sparta or Ithaca. Only the states of Pylos and Knossos are clearly attested in the Linear B texts. Even so, it is impossible to know which was the dominant political center in Argolis, if there indeed was one. Possible candidates are Mycenae, Tiryns, Argos, Athens, Gla, and Iolcos. In Argolis, Mycenae seems to have enjoyed a hegemonial position for some time, while in Boiotia the rulers of the great fortification of Gla probably played a leading role. The existence of a persistent unified state in Greece during the Mycenaean era is unlikely, especially due to lack of some important preconditions, such as an educated bureaucracy. Even the Minoan writing, imported from Crete, seems not to have been in widespread use in mainland Greece.[24]
States of Pylos and Knossos
On a smaller scale, some uncertain information about the internal organization of the best-known kingdoms, Pylos and Knossos, can be gleaned from sources in Linear B.
The state appears to have been ruled by a king, the wa-na-ka (ϝάναξ, wánax), whose role was no doubt military, judicial, and religious. He is identifiable in the Homeric anax (ἄναξ, "divine lord", "sovereign", "host"). Nine occurrences of the word in texts having to do with offerings suggest that the sovereigns of Pylos and Knossos were probably worshipped, but the term "for the king" is usually accompanied by another name. The term qa-si-re-u (cf. βασιλεύς, "basileús"), which was later used in Greece for "king" , seems that was used for the "chief" of any group of people. (Later Homer mentions many basilees in Ithaca).[25]
The land possessed by the king is usually the te-me-no (τέμενος / "témenos"). Other important land owners were the ra-wa-ke-ta ("lāwāgetas"), the leader of the people, and the te-re-ta ("telestai"), the officials. Lawagetas could be the leader of the army, but it is not confirmed by the inscriptions. The e-qe-ta ("equetai"), literally, "the companions" or "followers", were a group of nobles (aristocrats), who followed the king in peace and war.[25]
Besides the members of the court, there were other dignitaries in charge of local territorial administration. The kingdom of Pylos was divided into two great provinces, the de-we-ra ka-ra-i-ja, the near province, and the pe-ra-ko-ra-i-ja, the far province, around the town of re-u-ko-to-ro. The kingdom was further subdivided into sixteen districts. To manage these districts, the king named a ko-re-te (koreter, '"governor") and a po-ro-ko-re-te (prokoreter, "deputy"). A da-mo-ko-ro (damokoros, "one who takes care of a damos"), was an official appointment probably in charge of the commune. The communal land was held at the hands of da-mo (literally, "people", cf. δῆμος, dễmos), or "plot holders" that probably expressed the voice of the district.[25] A council of elders was chaired, the ke-ro-si-ja (cf. γερουσία, gerousía). It is, incidentally, interesting to note that in Classical Greece, the basileus is the king, the monarch, as if between the disintegration of Mycenaean society and the Classical Age no higher authority survived — de facto, and then, over the generations, de jure — than the communal official.[25]
Society
Mycenaean society appears to have been divided into two groups of free men: the king's entourage, who conducted administrative duties at the palace, and the people, da-mo (demos), who lived at the commune level; these last were watched over by royal agents and were obliged to perform duties for and pay taxes to the palace.[25]
Among those who evolved in the palace setting could be found well-to-do high officials who probably lived in the vast residences found in proximity to Mycenaean palaces, but also others, tied by their work to the palace and not necessarily better off than the members of the da-mo: craftsmen, farmers, and perhaps merchants, to name a few. On a lower rung of the social ladder were found the slaves, do-e-ro (masculine) and do-e-ra (feminine) (cf. δούλος, doúlos). These are recorded in the texts as working either for the palace or for specific deities.[25]
Mycenaean contacts
By the close of the Bronze Age (up to Late Helladic IIIC) contacts between the Aegean and its neighbours were well established. Mycenaean connections extended as far as southern Spain[26] while Mycenaean pottery, for example, has been found in Sardinia,[27] Southern Italy and Sicily,[28] Asia Minor[29] (i.e. Milawatta or Miletus, Iasus and Ephesus[30][31][32] where high-quality Palace style and Mycenaean ceramics have been recovered[33]) Cyprus,[34] the Levant,[35] and Egypt (especially Tell el Amarna[36]). The circulation of goods and produce between centres are attested in Linear B records, though evidence of direct exchange is not.
Economy
The economic organization of the Mycenaean kingdoms known from the texts seems to have been bipartite: a first group worked in the orbit of the palace, while another was self-employed. This reflects the societal structure seen above. However, there was nothing to prevent a person working for the palace from running his own business. The economy was supervised by scribes, who made note of incoming and outgoing products, assigned work, and were in charge of the distribution of rations. The du-ma-te seems to have been a sort of supervising quartermaster.
Agriculture
The territory of the Mycenaean kingdoms of Pylos and Knossos was divided into two parts: the ki-ti-me-na, the palace land, and the ke-ke-me-na, the communal land, cultivated by those the texts call ka-ma-na-e-we, undoubtedly the da-mo. The palace lands are those attested in the texts. One part makes up the te-me-no of the wa-ka-na and of the ra-wa-ge-ta, as seen above. The other part was granted as a perquisite to members of the palace administration. These lands might be worked by slaves or by free men to whom the land had been leased.
Agricultural production in these kingdoms reflected the traditional "Mediterranean trilogy": grain, olives, and grapes. The grains cultivated were wheat and barley. Olive orchards were planted for the production of olive oil. This was not only a foodstuff, it was much used as a body oil and in perfume. Grapes were also cultivated, and several varieties of wine were produced. Besides these, flax was grown for linen clothing and sesame for its oil, and trees were planted, such as the fig.
Livestock consisted primarily of sheep and goats. Cows and pigs were less common. Horses were kept chiefly for the pulling of chariots in battle.
Industry

The organization of artisanal labor is especially well known in the case of the palace. The archives of Pylos show a specialized workforce, each worker belonging to a precise category and assigned to a specific place in the stages of production, notably in textiles.
The textile industry was one of the principal sectors of the Mycenaean economy. The tablets of Knossos reveal the entire chain of production, from the flocks of sheep to the stocking of the palace storerooms with the finished product, through the shearing and the sorting of the wool in the workshops, as well as working conditions in those workshops. The palace of Pylos employed around 550 textile workers. At Knossos, there were some 900. Fifteen different textile specialties have been identified. Next to wool, flax was the fiber most used.
The metallurgical industry is well attested at Pylos, where 400 workers were employed. It is known from the sources that metal was distributed to them, that they might carry out the required work: on average, 3.5 kilograms (7.7 lb) of bronze per smith. On the other hand, it is not known how they were paid — they are mysteriously absent in the ration distribution lists. At Knossos, several tablets testify to the making of swords, but with no mention of the true industry of metallurgy.
The industry of perfumery is attested as well. Tablets describe the making of perfumed oil. It is known, too, from the archaeology that the workers attached to the palace included other kinds of artisans: goldsmiths, ivory-carvers, stonecarvers, and potters, for example. Olive oil was also made there. Certain areas of endeavor were turned toward export.
Commerce
Commerce remains curiously absent from the written sources. Thus, once the perfumed oil of Pylos has been stored in its little jars, the inscriptions do not reveal what became of it. Large stirrup jars that once contained oil have been found at Thebes in Boeotia. They carry inscriptions in Linear B indicating their place of origin, western Crete. However, Cretan tablets say nothing about the exportation of oil. There is little information about the distribution route of textiles. It is known that the Minoans exported fine fabrics to Egypt; the Mycenaeans no doubt did the same. Indeed, it is probable that they borrowed knowledge of navigational matters from the Minoans, as is evidenced by the fact that their maritime commerce did not take off until after the founding of the Minoan civilization. Despite the lack of sources, it is probable that certain products, notably fabrics and oil, even metal objects, were meant to be sold outside the kingdom, for they were made in quantities too great to be consumed solely at home.

Archaeology can, however, shed some light on the matter of the exportation of Mycenaean products outside of Greece. A number of vases have been found in the Aegean, in Anatolia, the Levant, Egypt and farther west in Sicily, even in Central Europe and as far away as Great Britain.[37] In a general way, the circulation of Mycenaean goods is traceable thanks to nodules, ancestors of the modern label. They consisted of small balls of clay, molded with the fingers around a lanyard (probably of leather) with which they were attached to the object. The nodule displayed the imprint of a seal and an ideogram representing the object. Other information was sometimes added: quality, origin, destination, etc.
Fifty-six nodules found at Thebes in 1982 carry an ideogram representing an ox. Thanks to them, the itinerary of these bovines can be reconstructed. From all over Boeotia, even from Euboea, they were taken to Thebes to be sacrificed. The nodules served to prove that they were not stolen animals and to prove their origin. Once the animals arrived at their destination, the nodules were removed and gathered to create a book-keeping tablet. The nodules were used for all sorts of objects and explain how Mycenaean book-keeping could have been so rigorous. The scribe did not have to count the objects themselves, he could base his tables upon the nodules.
Religion
The religious element is difficult to identify in Mycenaean civilization, especially as regards archaeological sites, where it remains problematic to pick out a place of worship with certainty. John Chadwick points out that at least six centuries lie between the earliest presence of proto-Greek speakers in Hellas and the earliest Linear B inscriptions, during which concepts and practices will have fused with indigenous beliefs, and—if cultural influences in material culture reflect influences in religious beliefs—with Minoan religion.[38] As for these texts, the few lists of offerings that give names of gods as recipients of goods reveal nothing about religious practices, and there is no surviving literature. John Chadwick rejected a confusion of Minoan and Mycenaean religion derived from archaeological correlations[39] and cautioned against "the attempt to uncover the prehistory of classical Greek religion by conjecturing its origins and guessing the meaning of its myths"[40] above all through treacherous etymologies.[41] Moses I. Finley detected very few authentic Mycenaean reflections in the eighth-century Homeric world, in spite of its "Mycenaean" setting.[42] However, Nilsson asserts, based not on uncertain etymologies but on religious elements and on the representations and general function of the gods, that a lot of Minoan gods and religious conceptions were fused in the Mycenaean religion. From the existing evidence, it seems that the Mycenaean religion was the mother of the Greek religion.[43] The Mycenaean pantheon already included many divinities that can be found in Classical Greece.[44]
Poseidon (Po-se-da-o) seems to have occupied a place of privilege. He was a chthonic deity, connected with the earthquakes (E-ne-si-da-o-ne: earth shaker), but it seems that he also represented the river spirit of the underworld as it often happens in Northern European folklore.[45] Also to be found are a collection of "Ladies". On a number of tablets from Pylos, we find Po-ti-ni-ja (Potnia, "lady" or "mistress") without any accompanying word. It seems that she had an important shrine at the site Pakijanes near Pylos.[46] In an inscription at Knossos in Crete, we find the "mistress of the Labyrinth" (da-pu-ri-to-jo po-ti-ni-ja), who calls to mind the myth of the Minoan labyrinth.[47] The title was applied to many goddesses. In a Linear B tablet found at Pylos, the "two queens and the king" (wa-na-ssoi, wa-na-ka-te) are mentioned, and John Chadwick relates these with the precursor goddesses of Demeter, Persephone and Poseidon.[48][49]
Demeter and her daughter Persephone, the goddesses of the Eleusinian mysteries, were usually referred to as "the two goddesses" or "the mistresses" in historical times.[50] Inscriptions in Linear B found at Pylos, mention the goddesses Pe-re-swa, who may be related with Persephone, and Si-to po-ti-ni-ja,[51] who is an agricultural goddess.[46] A cult title of Demeter is "Sito" (σίτος: wheat).[52] The mysteries were established during the Mycenean period (1500 BC) at the city of Eleusis[53] and it seems that they were based on a pre-Greek vegetation cult with Minoan elements.[54] The cult was originally private and there is no information about it, but certain elements suggest that it could have similarities with the cult of Despoina ("the mistress") - the precursor goddess of Persephone - in isolated Arcadia that survived up to classical times. In the primitive Arcadian myth, Poseidon, the river spirit of the underworld, appears as a horse (Poseidon Hippios). He pursues Demeter who becomes a mare and from the union she bears the fabulous horse Arion and a daughter, "Despoina", who obviously originally had the shape or the head of a mare. Pausanias mentions animal-headed statues of Demeter and of other gods in Arcadia.[55] At Lycosura on a marble relief, appear figures of women with the heads of different animals, obviously in a ritual dance.[56] This could explain a Mycenaean fresco from 1400 BC that represents a procession with animal masks[57] and the procession of "daemons" in front of a goddess on a goldring from Tiryns.[58] The Greek myth of the Minotaur probably originated from a similar "daemon".[59] In the cult of Despoina at Lycosura, the two goddesses are closely connected with the springs and the animals, and especially with Poseidon and Artemis, the "mistress of the animals" who was the first nymph. The existence of the nymphs was bound to the trees or the waters which they haunted.
Artemis appears as a daughter of Demeter in the Arcadian cults and she became the most popular goddess in Greece.[60] The earliest attested forms of the name Artemis are the Mycenaean Greek a-te-mi-to and a-ti-mi-te, written in Linear B at Pylos.[61] Her precursor goddess (probably the Minoan Britomartis) is represented between two lions on a Minoan seal and also on some goldrings from Mycenae.[62] The representations are quite similar with those of "Artemis Orthia" at Sparta. In her temple at Sparta, wooden masks representing human faces have been found that were used by dancers in the vegetation-cult.[63] Artemis was also connected with the Minoan "cult of the tree," an ecstatic and orgiastic cult, which is represented on Minoan seals and Mycenaean gold rings.[64]
Paean (Pa-ja-wo) is probably the precursor of the Greek physician of the gods in Homer's Iliad. He was the personification of the magic-song which was supposed to "heal" the patient. Later it became also a song of victory (παιάν). The magicians was also called "seer- doctors" (ιατρομάντεις), a function which was also applied later to Apollo.[65]
Athena (A-ta-na) appears in a Linear B inscription at Knossos from the Late Minoan II-era. The form A-ta-na po-ti-ni-ja (mistress Athena) is similar with the later Homeric form.[66] She was probably the goddess of the palace who is represented in the famous "Procession-fresco" at Knossos.[67] In a Mycenaean fresco, there is a composition of two women extending their hands towards a central figure who is covered by an enormous figure-eight shield. The central figure is the war-goddess with her palladium (classical antiquity), or her palladium in an aniconic representation.[46]
Dionysos (Di-wo-ni-so) also appears in some inscriptions. His name is interpreted as "son of Zeus" and probably has a Thraco-Phrygian origin. Later his cult is related with Boeotia and Phocis, where it seems that was introduced before the end of the Mycenean age. This may explain why his myths and cult were centered in Thebes, and why the mountain Parnassos in Phocis was the place of his orgies. However, in the Homeric poems he is the consort of the Minoan vegetation goddess Ariadne.[68] He is the only Greek god who dies in order to be reborn, as it often appears in the religions of the Orient.[69] His myth is related with the Minoan myth of the "divine child" who was abandoned by his mother and then brought up by the powers of nature. Similar myths appear in the cults of Hyakinthos (Amyklai), Erichthonios (Athens), and Ploutos (Eleusis).[70]
Other divinities who can be found in later periods have been identified, such as the couple Zeus–Hera, Hephaestus, Ares, Hermes, Eileithyia, and Erinya. Hephaestus, for example, is likely associated with A-pa-i-ti-jo at Knossos whereas Apollo is mentioned only if he is identified with Paiāwōn; Aphrodite, however, is entirely absent.[71] Qo-wi-ja ("cow-eyed") is a standard Homeric ephithet of Hera.[51] Ares has appeared under the name Enyalios (assuming that Enyalios is not a separate god) and though the importance of Areias is unknown, it does resemble the name of the god of war.[72] Eleuthia is associated with Eileithuia, the Homeric goddess of child-birth.[73]
There were some sites of importance for cults, such as Lerna, typically in the form of house sanctuaries since the free-standing temple containing a cult image in its cella with an open-air altar before it was a later development. Certain buildings found in citadels having a central room, the megaron, of oblong shape surrounded by small rooms may have served as places of worship. Aside from that, the existence of a domestic cult may be supposed. Some shrines have been located, as at Phylakopi on Melos, where a considerable number of statuettes discovered there were undoubtedly fashioned to serve as offerings, and it can be supposed from archaeological strata that sites such as Delphi, Dodona, Delos, Eleusis, Lerna, and Abae were already important shrines, and in Crete several Minoan shrines show continuity into LMIII, a period of Minoan-Mycenaean culture.
Architecture
Fortresses
The principal Mycenaean towns were well fortified. The town could be situated on an acropolis as in Athens or Tiryns, against a large hill as in Mycenae, or on the coastal plain, like Gla or Pylos. Besides the citadels, there are also isolated forts that undoubtedly served to militarily control territory. Mycenaean walls were often made in a fashion called cyclopean, which means that they were constructed of large, unworked boulders up to eight meters (26 ft.) thick, loosely fitted without the clay mortar of the day. Different types of entrances or exits can be seen: monumental gates, access ramps, hidden doors, and vaulted galleries for escaping in case of a siege. Fear of attack meant that the chosen site must have a cistern or well at its disposal.
Habitations
The Mycenaean sites are composed of different types of residences. The smallest are rectangular in form and measure between 5 and 20 metres (16–66 ft.) on a side. These were the houses of the lowest classes. They could have one or several rooms; the latter become more widespread in more recent periods. On a more developed level are found larger residences, measuring about 20 to 35 meters (66 to 115 ft.) on a side, made up of many rooms and central courtyards. Their layout resembles that of a palace. It is not, however, certain that these were indeed the residences of the Mycenaean aristocrats; another theory is that they were palace annexes, being often situated next to them.
Palaces
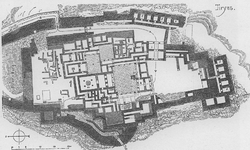
The best examples of the Mycenaean palace are seen in the excavations at Mycenae, Tiryns, and Pylos. That these were administrative centers is shown by the records found there. From an architectural point of view, they were the heirs of the Minoan palaces and also of other palaces built on the Greek mainland during the Bronze Age. They were ranged around a group of courtyards each opening upon several rooms of different dimensions, such as storerooms and workshops, as well as reception halls and living quarters. The heart of the palace was the megaron. This was the throne room, laid out around a circular hearth surrounded by four columns, the throne generally being found on the right-hand side upon entering the room. The staircases found in the palace of Pylos indicate palaces had two stories. Located on the top floor were probably the private quarters of the royal family and some storerooms. These palaces have yielded a wealth of artifacts and fragmentary frescoes.
The most recent find is a Mycenaean palace near the village of Xirokambi, in Laconia. As of early 2009, the excavation is at its first stages and artifacts uncovered so far include clay vessels and figurines, frescoes and three Linear B tablets. Preliminary findings indicate that one of the tablets contains an inventory of about 500 daggers and another is an inventory for textiles. The discovery was announced at the Athens Archaeological Society on April 28, 2009.[74]
Architectural elements
Roof tiles
Contrary to an often held view, some Mycenaean representative buildings already featured roofs made of fired tiles, as in Gla and Midea.[75]
Art and craftwork

Vessels
The Mycenaeans made a great deal of pottery. Archaeologists have found a great quantity of pottery from the Mycenaean age, of widely diverse styles — stirrup jars, pitchers, kraters, chalices sometimes called "champagne coupes" after their shape, etc. The vessels vary in size. Their conformations remained quite consistent throughout the Mycenaean period, up through LHIIIB, when production increased considerably, notably in Argolis whence came great numbers exported outside Greece. The products destined for export were generally more luxurious and featured heavily worked painted decorations incorporating mythic, warrior, or animal motifs. Another type of vessel, in metal (normally bronze), has been found in sizeable quantities at Mycenaean sites. The forms of these were tripods, basins, or lamps. A few examples of vessels in faience and ivory are also known.
Figures and figurines
The Mycenaean period has not yielded sculpture of any great size. The statuary of the period consists for the most part of small terracotta figurines found at almost every Mycenaean site in mainland Greece, in tombs, in settlement debris, and occasionally in cult contexts (Tiryns, Agios Konstantinos on Methana). The majority of these figurines are female and anthropomorphic or zoomorphic. The female figurines can be subdivided into three groups which were popular at different periods: the earliest are the Phi-type, which look like the Greek letter phi and their arms give the upper body of the figurine a rounded shape. The Psi-type looks like the letter Greek psi: these have outstretched upraised arms. The latest (12th century BC) are the Tau-type: these figurines look like the Greek letter tau with folded(?) arms at right angles to the body. Most figurines wear a large 'polos' hat.[76] They are painted with stripes or zigzags in the same manner as the contemporary pottery and presumably made by the same potters. Their purpose is uncertain, but they may have served as both votive objects and toys: some are found in children's graves but the vast majority of fragments are from domestic rubbish deposits.[77] The presence of many these figurines on sites where worship took place in the Archaic and Classical periods (circa 200 below the sanctuary of Athena at Delphi, others at the temple of Aphaia on Aegina, at the sanctuary of Apollo Maleatas above Epidauros and at Amyklae near Sparta), suggests both that many were indeed religious in nature, perhaps as votives, but also that later places of worship may well have first been used in the Mycenaean period.[78]
Larger male, female or bovine terracotta wheelmade figures are much rarer. An important group was found in the Temple at Mycenae together with coiled clay snakes,[79] while others have been found at Tiryns and in the East and West Shrines at Phylakopi on the island of Melos.[80]
Frescoes

The painting of the Mycenaean age was much influenced by that of the Minoan age. Fragments of wall paintings have been found in or around the palaces (Pylos, Mycenae, Tiryns) and in domestic contexts (Zygouries).[81] The largest complete wall painting depicting three female figures, probably goddesses, was found in the so-called Cult Centre at Mycenae.[82] Various themes are represented: hunting, bull leaping (tauromachy), battle scenes, processions, etc. Some scenes may be part of mythological narratives, but if so their meaning eludes us. Other frescoes include geometric or stylised motifs, also used on painted pottery (see above).
Arms

Military items have been found among the treasures of the Mycenaean age. The most impressive work is that of the Dendra panoply, a complete suit of Mycenaean armor and the oldest form of metal armor.[83] The cuirass is made up of bronze plates sewn to a leather garment. The weight of this armor must have hindered the mobility of a warrior, and it is for this reason it is supposed that it was worn by a warrior riding in a chariot.
The typical Mycenaean helmet, in use from the 17th to the 10th centuries BC,[84] was made of cut segments of boar's tusk sewn to a leather or cloth backing.[85] This type is illustrated in ivory relief plaques found in the shaft graves of the 17th and 16th centuries BC and in wall paintings of that era from Akrotiri on Thera (Santorini) and of the 13th century BC in the so-called Palace of Nestor at Pylos. Groups of boar's tusk plates from the helmets themselves have been found at many sites, including Mycenae, Prosymna, Thermon and Elateia, as well as in southern Italy. This is the type of helmet which is described by Homer several hundred years later.[86]
Two types of shields were used: the "figure eight" or "fiddle" shield, and a rectangular type, the "tower" shield, rounded on the top.[87] They were made of wood and leather, and were of such a large size that if he wished to a warrior could crouch behind his shield and have his whole body covered.
Offensive arms were made of bronze. Spears and javelins have been found, and also an assortment of swords of different sizes, designed for striking with the point and with the edge.[88] Daggers and arrows, attesting to the existence of archery, compose the remainder of the armament found from this period.[89]
Funerary practices
The usual form of burial in the Late Helladic was inhumation.[90] The dead were almost always buried in cemeteries outside the residential zones and only exceptionally within the settlements (the most famous burials in Grave Circle A originally lay outside the citadel and were only brought within it when the citadel wall was extended circa 1250 BC).

The earliest Mycenaean burials were mostly in individual graves in the form of a pit or a stone lined cist and offerings were limited to pottery and occasional items of jewellery. A large cemetery with burials of this kind spread around the northern and western slopes of the citadel at Mycenae.[91] Groups of pit or cist graves containing elite members of the community were sometimes covered by a tumulus (mound) in the manner established since the Middle Helladic period.[92] It has been argued that this form dates back to the oldest periods of Indo-European settlement in Greece, and that its roots are to be found in the Balkan cultures of the 3rd millennium BC, and even the Kurgan culture;[93] however, Mycenaean burials are in actuality an indigenous phenomenon/development of mainland Greece with the Shaft Graves housing native rulers.[94] Pit and cist graves remained in use for single burials throughout the Mycenaean period alongside more elaborate family graves (see below).[95]
The Shaft Graves at Mycenae within Grave Circles A and B belong to the same period and seem to represent an alternative manner of grouping elite or royal burials – and isolating them from those of the majority. Grave Circle B is the earlier of the two groups, already in use in the MH period, and contains lavish grave goods – gold and silver, jewellery, weapons and pottery. Circle A, excavated by Heinrich Schliemann, enclosed fewer but extraordinarily well provided graves.
Beginning also in the Late Helladic are to be seen communal tombs of rectangular form.[96] It is difficult to establish whether the different forms of burial represent a social hierarchization, as was formerly thought, with the tholoi being the tombs of the elite rulers, the individual tombs those of the leisure class, and the communal tombs those of the people. Cremations increased in number over the course of the period, becoming quite numerous in LHIIIC. The most impressive tombs of the Mycenaean era are the monumental royal tombs of Mycenae, undoubtedly intended for the royal family of the city. The most famous is the Tomb of Agamemnon (the Treasury of Atreus), which is in the form of a tholos. Nearby are other tombs (known as "Circle A"), popularly identified with Clytemnestra and Aigisthos. All contained impressive treasures, exhumed by Schliemann during the excavation of Mycenae. It has been argued that different dynasties or factions may have competed through conspicuous burial, whereby grave circle A represents a new faction in the ascendancy (at this time, LHI, the relative wealth and consistency of 'B' burials declines).[97] The Mycenaean "tholoi" may, again, represent another factional grouping, or a further formalization in burial practices by the faction previously buried in A. Nevertheless, there is a demonstrably apparent expansion in relative size, wealth/cost expenditure, and visibility in the construction of these graves over this period, coinciding with increased foreign/trading contacts and the further entrenchment of the palatial economy.
Destruction
The timing and interpretation of the end Mycenaean period poses an array of questions that have yet to be answered. The end of LHIIIB1 was marked by some destruction, in particular at Mycenae. By LHIIIB2, an augmentation of the Mycenaean systems of defense can be seen, a sign of increasing insecurity. But this does not seem to have been a period of crisis, because these levels have yielded archaeological material that shows a degree of wealth in no way inferior to that of previous periods. The end of this period is nevertheless marked by a number of destructions in the greater part of the Mycenaean sites on mainland Greece.
LHIIIC saw a decrease in the number of sites in Greece, which might have been considerable in certain regions (nine-tenths of the sites in Boeotia disappeared, and two-thirds in Argolis). Moreover, populations movements, with some Mycenaeans fleeing to Cyprus, as well as other Greek islands and coastal parts of Anatolia have been noted. Yet certain sites such as Mycenae and Tiryns continued to be inhabited, and the material culture found there continues to exhibit Mycenaean traits, such that LHIIIC is considered to be a level of Mycenaean civilization. However, a new type of ceramic appeared, called "Barbarian Ware" because it was formerly attributed to foreign invaders, and there was also a continuing increase in the practice of cremation.
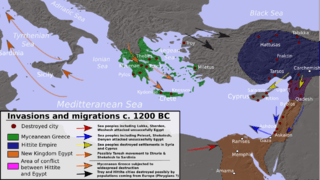
Several explanations have been advanced for the causes of the decline of Mycenaean civilization in this period. Those concerning natural factors (climate change, earthquakes) are considered more controversial. The two most common theories are population movement and internal conflict. The first attributes the destruction of Mycenaean sites to invaders; sometimes the Dorians or the Sea People are invoked.
Some scholars believe that the destruction of the Mycenaean centres, was caused by the wandering of northern people. They destroyed the palace of Iolcos (LHIIIC-1), the palace of Thebes (late LHIIIB), then they crossed Isthmus of Corinth (end of LHIIIB) they destroyed Mycenae, Tiryns and Pylos, and finally returned northward. However, Pylos was destroyed by a sea-attack, probably by the Sea People.[98] The invaders didn't leave behind traces of weapons or graves, and it cannot be proved that all the sites were destroyed about the same time.[99]
The movements of people to the Middle East at this period, are mentioned in Egyptian inscriptions calling the invaders by the name of the Sea People, are quite real. It is known that these people were responsible for numerous destructions in Anatolia and the Levant, and finally they attacked Egypt in several phases (circa 1301-1164 BC). Mention of a people called Eqwesh who attacked Egypt during the reign of Merneptah, in an Egyptian text of the 12th century BC has caused specialists to suppose that the Mycenaeans had taken part in these invasions (this is not certain).[100] A country Danaja (Danaans) with a city Mukana (probably: Mycenea) is mentioned in inscriptions from Egypt.[101]
Emily Vermeule suggests that the breaking-up of the commercial networks at the end of 13th century BC, was disastrous for Greece, and it was followed by the attack of the Sea People who were searching for new lands.[102] However, most of the destroyed Mycenaean sites are far from the sea, and the expedition against Troy at the end of this period shows that the sea was safe. Desborough believes that the sea was safe in central and south Aegean in this period.[103]
There is the second theory, which has the Mycenaean civilization falling in the course of internal societal conflicts brought on by a rejection of the palatial system by the most underprivileged strata of society, who were impoverished at the end of the Late Helladic. This hypothesis is sometimes joined with the preceding one, mingling social divisions with ethnic divisions. However, social revolutions couldn't break out almost simultaneously throughout Greece.[104] Mylonas believes that some developments in Argolis and attempts for recovery after 1200 BC, can be explained by internal fighting, and by pressure created by the Dorians. Even if the Dorians were one of the causes of the Bronze age collapse, there is evidence that they brought with them some new elements of culture, a cist grave completely different from the Mycenaean "tholos", and a new dialect of Greek, Doric. It seems that the Doric tribes moved southward gradually over a number of years, and they devastated the territory, until they managed to establish themselves in the Mycenaean centres.[105]
In this context, it has to be stressed that the beginning of the Iron Age made large numbers of comparatively cheap weapons accessible. This economic factor is also seen as a root cause of the appearance of the "Sea Peoples" in Egypt and the destruction of Ugarit and the Hittite Empire.
Whatever were the causes, the Mycenaean civilization had definitely disappeared after LHIIIC, when the sites of Mycenae and Tirynth were again destroyed and lost their importance. This end, during the last years of the 12th century BC, occurs after a slow decline of the Mycenaean civilization, which lasted many years before dying out. The beginning of the 11th century BC opens a new context, that of the protogeometric, the beginning of the geometric period, the Greek Dark Ages of traditional historiography.
See also
- Mycenae
- Mycenaean language
- Linear B
- Achaeans (Homer)
- Helladic
- Bronze Age
- Aegean civilization
- Greek Dark Ages
References
Citations
- ↑ Hammond 1976, p. 139: "Moreover, in this area a small tholos-tomb with Mycenaean pottery of III B style and a Mycenaean acropolis have been reported at Kiperi near Parga, and another Mycenaean acropolis lay above the Oracle of the Dead on the hill called Xylokastro."
- ↑ Tandy 2001, p. xii (Fig. 1); p. 2: "The strongest evidence for Mycenaean presence in Epirus is found in the coastal zone of the lower Acheron River, which in antiquity emptied into a bay on the Ionian coast known from ancient sources as Glykys Limin (Figure 2-A)."
- ↑ Borza 1992, p. 64: "The existence of a Late Bronze Age Mycenaean settlement in the Petra not only confirms its importance as a route from an early period, but also extends the limits of Mycenaean settlement to the Macedonian frontier."
- ↑ Aegeo-Balkan Prehistory – Mycenaean Sites
- ↑ van Wijngaarden 2002, Part II: The Levant, pp. 31–124; Bietak & Czerny 2007, Sigrid Deger-Jalkotzy, "Mycenaeans and Philistines in the Levant", pp. 501–629.
- ↑ van Wijngaarden 2002, Part III: Cyprus, pp. 125–202.
- ↑ Peruzzi 1980; van Wijngaarden 2002, Part IV: The Central Mediterranean, pp. 203–260.
- ↑ The extent to which Homer attempted to or succeeded in recreating a "Mycenaean" setting is examined in Moses I. Finley The World of Odysseus, 1954.
- ↑ Dickinson 1977, pp. 32, 53, 107–108; Dickinson 1999, pp. 97–107.
- ↑ Boston University – The Historical Society
- ↑ Amber object bearing Linear B symbols from the Freising district of Germany, excavations in the years 1994–1997.
- ↑ Budin 2009, p. 53: "One of the most extraordinary examples of the extent of Mycenaean influence was the Pelynt Dagger, a fragment of a Late Helladic III sword, which has come to light in the tomb of a Wessex chieftain in southern England!"
- ↑ Feuer 2004, p. 259.
- ↑ Burkert 1987, p. 121; Meyer, E. RE Suppl. XIV, pp. 813–815.
- ↑ See sources cited at Homeric Troy.
- ↑ Translation of the Sins of Madduwatta
- ↑ Skeat 1934.
- ↑ Dickinson 2006, pp. 14–15.
- ↑ Güterbock 1983, pp. 133–138; Mellink 1983, pp. 138–141.
- ↑ Huxley 1960; see Achaeans (Homer)#Hittite documents.
- ↑ Translation of the Tawagalawa Letter
- ↑ Güterbock 1984, pp. 114–122.
- ↑ Thomas 1995, p. 350.
- ↑ Bengtson 2009, pp. 15–25.
- ↑ 25.0 25.1 25.2 25.3 25.4 25.5 Chadwick 1976, Chapter 5: Social Structure and Administrative System, pp. 69–83.
- ↑ de la Cruz 1988, pp. 77–92; Ridgway 1992, p. 3; Runnels & Murray 2001, p. 15.
- ↑ Feuer 2004, pp. 155–157; Balmuth & Tykot 1998, "The Mycenaeans in Sardinia", p. 400; Runnels & Murray 2004, p. 15.
- ↑ Ridgway 1992, p. 4; Taylour 1958; Fisher 1998; Runnels & Murray 2001, p. 15; Vianello 2005, "Eastern Sicily and the Aeolian Islands", p. 51; Feuer 2004, pp. 155–157; van Wijngaarden 2002, Part IV: The Central Mediterranean, pp. 203-260.
- ↑ Runnels & Murray 2001, p. 15.
- ↑ Hooker 1976, p. 115.
- ↑ Castleden 2005, p. 194: "The Mycenaean colonies in Anatolia were emphatically confined to a narrow coastal strip in the west. There were community-colonies at Ephesus, Iasos and Miletus, but they had little effect on the interior..."
- ↑ Gitin et al. 1998, p. 40: "To sum up, Bronze Age Miletus was settled mainly by Mycenaeans in the second and probably also in the third building period."
- ↑ Preziosi & Hitchcock 1999, p. 195.
- ↑ Kling 1989; Nikolaou 1973; International Archaeological Symposium 1973.
- ↑ Stubbings 1951, IV: Mycenaean II Pottery in Syria and Palestine; V: Mycenaean III Pottery in Syria and Palestine.
- ↑ Petrie 1894.
- ↑ Castleden 2005.
- ↑ Chadwick 1976, p. 88.
- ↑ As explicitly expressed in Martin P. Nilsson, The Minoan-Mycenaean Religion and Its Survival in Greek Religion, 1927.
- ↑ Chadwick 1976, p. 84.
- ↑ Chadwick 1976, p. 87: "Words that are not understood are constantly deformed to give them meanings. Mere resemblance is of course nearly always deceptive."
- ↑ Finley 1954.
- ↑ Nilsson 1967, Volume I, p. 339.
- ↑ Paul, Adams John (10 January 2010). "Mycenaean Divinities". Northridge, CA: California State University. Retrieved 25 September 2013.
- ↑ Nilsson 1940.
- ↑ 46.0 46.1 46.2 Mylonas 1966, p. 159.
- ↑ Chadwick 1976, pp. 92–93.
- ↑ Mylonas 1966, p. 159: "Wa-na-ssoi, wa-na-ka-te, (to the two queens and the king). Wanax is best suited to Poseidon, the special divinity of Pylos. The identity of the two divinities addressed as wanassoi, is uncertain."
- ↑ Chadwick 1976, p. 76.
- ↑ Nilsson 1967, Volume I, p. 463.
- ↑ 51.0 51.1 Chadwick 1976, p. 95.
- ↑ Eustathius of Thessalonica, scholia on Homer, 265.
- ↑ Mylonas 1961.
- ↑ Nilsson 1967, Volume I, p. 475.
- ↑ Pausanias. Description of Greece, VIII-25.4, VIII-37.1ff, VIII.42.
- ↑ Nilsson 1967, Volume I, pp. 479–480.
- ↑ Robertson 1959, p. 31; National Archaeological Museum of Athens, No. 2665.
- ↑ Nilsson 1967, Volume I, p. 293.
- ↑ Nilsson 1967, Volume I, pp. 227, 297.
- ↑ Pausanias. Description of Greece, VIII-37.6.
- ↑ Chadwick & Baumbach 1963, p. 176f.
- ↑ Nilsson 1967, Volume I, pp. 273, 295.
- ↑ Nilsson 1967, Volume I, pp. 162, 310, 489.
- ↑ Nilsson 1967, Volume I, pp. 281, 283, 301, 487.
- ↑ Nilsson 1967, Volume I, pp. 500–504; Chadwick 1976, p. 88: "Pa-ja-wo suggested Homeric Paieon, which earlier would have been Paiawon, later Paidn, an alternative name of Apollo, if not again a separate god."
- ↑ Kn V 52 (text 208 in Ventris and Chadwick); Chadwick 1976, p. 88.
- ↑ Hagg & Wells 1978, Arne Furumark, "Aegean Society", p. 14: "Atano is identical with the Greek Athana (that she was originally the Minoan "palace goddess" was rightly concluded long ago by Martin P. Nilsson)."
- ↑ Nilsson 1967, Volume I, pp. 565–568.
- ↑ Nilsson 1967, Volume I, p. 215.
- ↑ Nilsson 1967, Volume I, pp. 215–219.
- ↑ Chadwick 1976, p. 99.
- ↑ Chadwick 1976, pp. 95, 99.
- ↑ Chadwick 1976, p. 98.
- ↑ Ταράντου, Σοφία (28 April 2009). "Βρήκαν μυκηναϊκό ανάκτορο". Ethnos.gr. Retrieved 25 September 2013.
- ↑ Wikander 1990, p. 288; Shear 2000, p. 134.
- ↑ French 1971, pp. 101–187.
- ↑ See account of their use in K.A. and Diana Wardle "The Child's Cache at Assiros, Macedonia", in Sally Crawford and Gillian Shepherd (eds): Children, Childhood and Society: Institute for Archaeology and Antiquity Interdisciplinary Studies (Volume I) Oxford: Archaeopress, 2007.
- ↑ Hägg & Marinatos 1981, Robin Hägg, "Official and Popular Cults in Mycenaean Greece", pp. 35–39.
- ↑ Moore, Taylour & French 1999.
- ↑ Renfrew, Mountjoy & Macfarlane 1985.
- ↑ Immerwahr 1990.
- ↑ Taylour 1969, pp. 91–97; Taylour 1970, pp. 270–280.
- ↑ Modern Reconstruction of the Dendra Panoply.
- ↑ Wardle & Wardle 1997, p. 65 (Fig. 21); pp. 69–70.
- ↑ Mycenaean Helmet.
- ↑ Homer. The Iliad, 10.260–10.265.
- ↑ Mycenaean "Figure Eight" Shield, Fresco; Mycenaean "Figure Eight" Shield, Drawing
- ↑ Mycenaean Swords; Mycenaean Type G Sword (Horn Sword).
- ↑ Mycenaean Dagger.
- ↑ Cavanagh & Mee 1998.
- ↑ Taylour, French & Wardle 2007; Alden 2000.
- ↑ Pelon 1976.
- ↑ Hammond 1967, p. 90.
- ↑ Dickinson 1977, pp. 33–34, 53, 59–60.
- ↑ Lewartowski 2000.
- ↑ Papadimitriou 2001.
- ↑ See Graziado 1991 for a more comprehensive discussion of these trends, in addition to a sophisticated study of the grave goods in particular burials.
- ↑ Mylonas 1966, pp. 227–228.
- ↑ Chadwick 1976, p. 178.
- ↑ Drews 1993, p. 49.
- ↑ Beekes 2010, Entry #6541.
- ↑ Vermeule 1960, p. 67.
- ↑ Mylonas 1966, pp. 230–231.
- ↑ Blegen, quoted in J. Alsop, From the Silent Earth, New York: Harper, 1964.
- ↑ Mylonas 1966, pp. 231–232.
Sources
- Alden, Maureen Joan (2000). Well Built Mycenae (Volume 7): The Prehistoric Cemetery - pre-Mycenaean and Early Mycenaean Graves. Oxford: Oxbow Books. ISBN 978-1-84-217018-2.
- Balmuth, Miriam S.; Tykot, Robert H. (1998). Studies in Sardinian Archaeology, Volume 5. Ann Arbor, MI: Oxbow Books.
- Beekes, Robert Stephen Paul (2010). Greek Etymological Dictionary. Leiden: Brill. ISBN 978-9-00-417418-4.
- Bengtson, Hermann (2009) [1965]. Griechische Geschichte: Von den Anfängen bis in die Römische Kaiserzeit. München: C.H. Beck. ISBN 978-3-40-658940-9.
- Bietak, Manfred; Czerny, Ernst (2007). The Synchronisation of Civilisations in the Eastern Mediterranean in the Second Millennium B.C. III, Proceedings of the SCIEM 2000 – 2nd EuroConference, Vienna, 28th of May – 1st of June 2003. Vienna: Verlag der Österreichischen Akademie der Wissenschaften. ISBN 978-3-70-013527-2.
- Borza, Eugene N. (1992). In the Shadow of Olympus: The Emergence of Macedon. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press. ISBN 978-0-691-00880-6.
- Budin, Stephanie Lynn (2009) [2004]. The Ancient Greeks: An Introduction. Oxford and New York: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-537984-6.
- Burkert, Walter (1987) [1985]. Greek Religion: Archaic and Classical. Oxford and Malden: Blackwell Publishing Limited. ISBN 978-1-11-872499-6.
- Castleden, Rodney (2005). The Mycenaeans. London and New York: Routledge. ISBN 0-415-36336-5.
- Cavanagh, William G.; Mee, Christopher (1998). A Private Place: Death in Prehistoric Greece [SIMA 125]. Jonsered: Paul Aströms Förlag. ISBN 978-9-17-081178-4.
- Chadwick, John; Baumbach, Lydia (1963). "The Mycenaean Greek Vocabulary". Glotta (Vandenhoeck & Ruprecht (GmbH & Co. KG)) 41 (3/4): 157–271.
- Chadwick, John (1976). The Mycenaean World. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-29037-6.
- de la Cruz, José Clemente Martín (1988). "Mykenische Keramik aus Bronzezeitlichen Siedlungsschichten von Montoro am Guadalquivir". Madrider Mitteilungen (29): 77–92.
- Dickinson, Oliver (1977). The Origins of Mycenaean Civilization. Götenberg: Paul Aströms Förlag.
- Dickinson, Oliver (December 1999). "Invasion, Migration and the Shaft Graves". Bulletin of the Institute of Classical Studies 43 (1). pp. 97–107. doi:10.1111/j.2041-5370.1999.tb00480.x.
- Dickinson, Oliver (2006). The Aegean from Bronze Age to Iron Age: Continuity and Change between the Twelfth and Eighth Centuries BC. New York, NY: Routledge. ISBN 978-0-20-396836-9.
- Drews, Robert (1993). The End of the Bronze Age. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press. ISBN 978-0-69-102591-9.
- Feuer, Bryan Avery (2004). Mycenaean Civilization: An Annotated Bibliography through 2002. Jefferson, NC: McFarland & Company, Inc. ISBN 978-0-78-641748-3.
- Finley, Moses I. (1954). The World of Odysseus. New York, NY: New York Review Books. ISBN 978-1-59-017017-5.
- Fisher, Elizabeth A. (1998). The Mycenaeans and Apulia. An Examination of Aegean Bronze Age Contacts with Apulia in Eastern Magna Grecia. Jonsered, Sweden: Astrom.
- French, Elizabeth Bayard (1971). "The Development of Mycenaean Terracotta Figurines". Annual of the British School of Archaeology at Athens 66: 101–187.
- Graziado, Giampaolo (July 1991). "The Process of Social Stratification at Mycenae in the Shaft Grave Period: A Comparative Examination of the Evidence". American Journal of Archaeology (Archaeological Institute of America) 95 (3): 403–440.
- Gitin, Seymour; Mazar, Amihay; Stern, Ephraim; Dothan, Trude Krakauer (1998). Mediterranean Peoples in Transition: Thirteenth to Early Tenth Centuries BCE. Jerusalem: Israel Exploration Society. ISBN 978-9-65-221036-4.
- Güterbock, Hans G. (April 1983). "The Hittites and the Aegean World: Part 1. The Ahhiyawa Problem Reconsidered". American Journal of Archaeology 87 (2): 133–138.
- Güterbock, Hans G. (June 1984). "Hittites and Akhaeans: A New Look". Proceedings of the American Philosophical Society 128 (2): 114–122.
- Hammond, Nicholas G.L. (1967). "Tumulus Burial in Albania, the Grave Circles of Mycenae, and the Indo-Europeans". Annual of the British School at Athens 62.
- Hagg, Robin; Wells, Berit (1978). Opuscula Atheniensia XII. Lund: Paul Astroms Forlag. ISBN 978-9-18-508612-2.
- Hägg, Robin; Marinatos, Nannó (1981). Sanctuaries and Cults in the Aegean Bronze Age: Proceedings of the First International Symposium at the Swedish Institute in Athens, 12-13 May, 1980. Stockholm: Svenska Institutet i Athen. ISBN 978-9-18-508643-6.
- Hammond, Nicholas G.L. (1976). Migrations and Invasions in Greece and Adjacent Areas. Park Ridge, NJ: Noyes Press. ISBN 978-0-8155-5047-1.
- Hooker, J.T. (1976). Mycenaean Greece. London: Routledge & Kegan Paul.
- Huxley, G.L. (1960). Achaeans and Greeks. Oxford and New York: Oxford University Press.
- Immerwahr, Sara A. (1990). Aegean Painting in the Bronze Age. University Park: Pennsylvania State University Press. ISBN 978-0-27-100628-4.
- International Archaeological Symposium (1973). Acts of the International Arghaeological [sic] Symposium "The Mycenaeans in the Eastern Mediterranean", Nicosia, 27th March–2nd April 1972. Nicosia: Nicosia Department of Antiquities, Cyprus.
- Kling, Barbara (1989). Mycenaean IIIC:1b and Related Pottery in Cyprus. Lund: P. Aströms Förlag. ISBN 978-9-18-609893-3.
- Lewartowski, Kazimierz (2000). Late Helladic Simple Graves: A Study of Mycenaean Burial Customs (BAR International Series 878). Oxford: Archaeopress. ISBN 978-1-84-171079-2.
- Mellink, Machteld J. (April 1983). "The Hittites and the Aegean World: Part 2. Archaeological Comments on Ahhiyawa-Achaians in Western Anatolia". American Journal of Archaeology 87 (2): 138–141.
- Moore, A.D.; Taylour, W.D.; French, Elizabeth Bayard (1999). Well Built Mycenae (Volume 10): The Temple Complex. Warminster, England: Aris & Phillips. ISBN 978-1-84-217000-7.
- Mylonas, George Emmanuel (1961). Eleusis and the Eleusinian Mysteries. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press.
- Mylonas, George Emmanuel (1966). Mycenae and the Mycenaean Age. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press.
- Nikolaou, Kyriakos (1973). The First Myceneans in Cyprus. Nicosia: Department of Antiquities, Cyprus.
- Nilsson, Martin Persson (1940). Greek Popular Religion. New York: Columbia University Press.
- Nilsson, Martin Persson (1967). Geschichte der Griechischen Religion (3rd ed.). Munich: C.H. Beck Verlag.
- Papadimitriou, Nikolas (2001). Built Chamber Tombs of Middle and Late Bronze Age Date in Mainland Greece and the Islands (BAR International Series 925). Oxford: John and Erica Hedges Ltd. and Archaeopress. ISBN 978-1-84-171170-6.
- Pelon, Olivier (1976). Tholoi, Tumuli et Cercles Funéraires. Paris: Diffusion de Boccard.
- Peruzzi, Emilio (1980). Mycenaeans in Early Latium. Rome: Edizioni dell'Ateneo & Bizzarri.
- Petrie, Sir William Matthew Flinders (1894). Tell el-Amarna. London: Methuen & Co.
- Preziosi, Donald; Hitchcock, Louise A. (1999). Aegean Art and Architecture. Oxford: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-284208-4.
- Renfrew, Colin; Mountjoy, Penelope A.; Macfarlane, Callum (1985). The Archaeology of Cult: The Sanctuary at Phylakopi. London: British School of Archaeology at Athens. ISBN 978-0-50-096021-9.
- Ridgway, David (1992). The First Western Greeks. Cambridge and New York: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-52-142164-5.
- Robertson, Martin (1959). Les Grands siècles de la peinture: La peinture Grecque. Genève-Paris: Skira.
- Runnels, Curtis Neil; Murray, Priscilla (2001). Greece before History: An Archaeological Companion and Guide. Stanford, CA: Stanford University Press. ISBN 978-0-8047-4050-0.
- Shear, Ione Mylonas (January 2000). "Excavations on the Acropolis of Midea: Results of the Greek–Swedish Excavations under the Direction of Katie Demakopoulou and Paul Åström". American Journal of Archaeology 104 (1): 133–134.
- Skeat, T.C. (1934). The Dorians in Archaeology. London: de la More Press.
- Stubbings, Frank H. (1951). Mycenaean Pottery from the Levant. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
- Tandy, David W. (2001). Prehistory and History: Ethnicity, Class and Political Economy. Montréal, Québec, Canada: Black Rose Books Limited. ISBN 1-55164-188-7.
- Taylour, Lord William; French, Elizabeth Bayard; Wardle, K.A. (2007). Well Built Mycenae (Volume 13): The Helleno-British Excavations within the Citadel at Mycenae 1959-1969. Warminster, England: Aris & Phillips. ISBN 978-1-84-217295-7.
- Taylour, Lord William (1969). "Mycenae, 1968". Antiquity 43: 91–97.
- Taylour, Lord William (1970). "New Light on Mycenaean Religion". Antiquity 44: 270–280.
- Taylour, Lord William (1958). Mycenaean Pottery in Italy and Adjacent Areas. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
- Thomas, Carol G. (1995). "The Components of Political Identity in Mycenaean Greece". Aegaeum 12: 349–354.
- van Wijngaarden, Geert Jan (2002). Use and Appreciation of Mycenaean Pottery in the Levant, Cyprus and Italy (1600–1200 BC). Amsterdam: Amsterdam University Press. ISBN 978-9-05-356482-0.
- Vermeule, Emily Townsend (March 1960). "The Fall of the Mycenaean Empire". Archaeology (Archaeological Institute of America) 13 (1): 66–76. doi:10.2307/41663738.
- Vianello, Andrea (2005). Late Bronze Age Mycenaean and Italic Products in the West Mediterranean: A Social and Economic Analysis. Oxford: Archaeopress. ISBN 978-1-84-171875-0.
- Wardle, K.A.; Wardle, Diana (1997). Cities of Legend: The Mycenaean World. London: Bristol Classical Press. ISBN 978-1-85-399355-8.
- Wikander, Örjan (January–March 1990). "Archaic Roof Tiles the First Generations". Hesperia 59 (1): 285–290.
Further reading
- Barlow, Jane Atwood; Bolger, Diane L.; Kling, Barbara (1991). Cypriot Ceramics: Reading the Prehistoric Record. Philadelphia, PA: University of Pennsylvania Museum of Archaeology and Anthropology. ISBN 978-0-92-417110-9.
- Doumas, Christos (1980). Thera and the Aegean World II: Papers Presented at the Second International Scientific Congress, Santorini, Greece, August 1978. London: Thera and the Aegean World. ISBN 978-0-95-061332-1.
- French, Elizabeth Bayard (2002). Mycenae: Agamemnon's Capital. Stroud: Tempus. ISBN 0-7524-1951-X.
- Hänsel, B. (ed.); Podzuweit, Christian (1982). "Die mykenische Welt und Troja". Südosteuropa zwischen 1600 und 1000 V. Chr. (in German). Berlin: Moreland Editions. pp. 65–88.
- Higgins, Reynold Alleyne (1997). Minoan and Mycenaean Art. London and New York: Thames & Hudson. ISBN 978-0-50-020303-3.
- Mountjoy, Penelope A. (1986). Mycenaean Decorated Pottery: A Guide to Identification (Studies in Mediterranean Archaeology 73). Göteborg: Paul Aströms Forlag. ISBN 978-9-18-609832-2.
- Nur, Amos; Cline, Eric (2000). "Poseidon's Horses: Plate Tectonics and Earthquake Storms in the Late Bronze Age Aegean and Eastern Mediterranean". Journal of Archaeological Science 27 (1): 43–63.
- Taylour, Lord William (1990) [1964]. The Mycenaeans. London: Thames & Hudson Limited. ISBN 978-0-50-027586-3.
- Vermeule, Emily; Karageorghis, Vassos (1982). Mycenaean Pictorial Vase Painting. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press. ISBN 978-0-67-459650-4.
- Weiss, Barry (June 1982). "The Decline of Late Bronze Age Civilization as a Possible Response to Climatic Change". Climatic Change 4 (2): 173–198. ISSN 0165-0009.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Mycenaean culture. |
- Godart, Louis (2013) [January 1997]. "Les citadelles mycéniennes" (in French). Clio.
- Hemingway, Seán; Hemingway, Colette (2000–2013). "Heilbrunn Timeline of Art History: Mycenaean Civilization". The Metropolitan Museum of Art.
- Horejs, Barbara; Pavúk, Peter, eds. (2007). "The Aegeo-Balkan Prehistory Project". The Aegeo-Balkan Prehistory Team.
- Rutter, Jeremy B. "Prehistoric Archeology of the Aegean". Hanover, NH: Dartmouth College.
- Salimbetti, Andrea (30 September 2013). "The Greek Age of Bronze".
- "The Mycenaeans and Italy: The Archaeological and Archaeometric Ceramic Evidence". University of Glasgow School of Humanities.
- Wright, James C. (2002). "The Nemea Valley Archaeological Project: Internet Edition". Bryn Mawr College Department of Classical and Near Eastern Archaeology.
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

