Multiplicity (mathematics)
In mathematics, the multiplicity of a member of a multiset is the number of times it appears in the multiset. For example, the number of times a given polynomial equation has a root at a given point.
The notion of multiplicity is important to be able to count correctly without specifying exceptions (for example, double roots counted twice). Hence the expression, "counted with multiplicity".
If multiplicity is ignored, this may be emphasized by counting the number of distinct elements, as in "the number of distinct roots". However, whenever a set (as opposed to multiset) is formed, multiplicity is automatically ignored, without requiring use of the term "distinct".
Multiplicity of a prime factor
In the prime factorization, for example,
- 60 = 2 × 2 × 3 × 5
the multiplicity of the prime factor 2 is 2, while the multiplicity of each of the prime factors 3 and 5 is 1. Thus, 60 has 4 prime factors, but only 3 distinct prime factors.
Multiplicity of a root of a polynomial
Let F be a field and p(x) be a polynomial in one variable and coefficients in F. An element a ∈ F is called a root of multiplicity k of p(x) if there is a polynomial s(x) such that s(a) ≠ 0 and p(x) = (x − a)ks(x). If k = 1, then a is called a simple root.
For instance, the polynomial p(x) = x3 + 2x2 − 7x + 4 has 1 and −4 as roots, and can be written as p(x) = (x + 4)(x − 1)2. This means that 1 is a root of multiplicity 2, and −4 is a 'simple' root (of multiplicity 1). Multiplicity can be thought of as "How many times does the solution appear in the original equation?".
The discriminant of a polynomial is zero only if the polynomial has a multiple root.
Behavior of a polynomial function near a root in relation to its multiplicity
Let f(x) be a polynomial function. Then, if f is graphed on a Cartesian coordinate system, its graph will cross the x-axis at real zeros of odd multiplicity and will bounce off (not go through) the x-axis at real zeros of even multiplicity. In addition, if f(x) has a zero with a multiplicity greater than 1, the graph will be tangent to the x-axis, in other words it will have slope 0 there.
In general, a polynomial with an n-fold root will have a derivative with an (n−1)-fold root at that point.
Intersection multiplicity
In algebraic geometry, the intersection of two sub-varieties of an algebraic variety is a finite union of irreducible varieties. To each component of such an intersection is attached an intersection multiplicity. This notion is local in the sense that it may be defined by looking what occurs in a neighborhood of any generic point of this component. It follows that without loss of generality, we may consider, for defining the intersection multiplicity, the intersection of two affines varieties (sub-varieties of an affine space).
Thus, given two affine varieties V1 and V2, let us consider an irreducible component W of the intersection of V1 and V2. Let d be the dimension of W, and P be any generic point of W. The intersection of W with d hyperplanes in general position passing through P has an irreducible component that is reduced to the single point P. Therefore, the local ring at this component of the coordinate ring of the intersection has only one prime ideal, and is therefore an Artinian ring. This ring is thus a finite dimensional vector space over the ground field. Its dimension is the intersection multiplicity of V1 and V2 at W.
This definition allows to state precisely Bézout's theorem and its generalizations.
This definition generalizes the multiplicity of a root of a polynomial in the following way. The roots of a polynomial f are points on the affine line, which are the components of the algebraic set defined by the polynomial. The coordinate ring of this affine set is ![R=K[X]/\langle f\rangle ,](/2014-wikipedia_en_all_02_2014/I/media/c/7/d/4/c7d4ea4a15ee4fa1817f9536247b744a.png) where K is an algebraically closed field containing the coefficients of f. If
where K is an algebraically closed field containing the coefficients of f. If 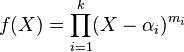 is the factorization of f, then the local ring of R at the prime ideal
is the factorization of f, then the local ring of R at the prime ideal 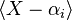 is
is ![K[X]/\langle (X-\alpha )^{{m_{i}}}\rangle .](/2014-wikipedia_en_all_02_2014/I/media/e/0/a/b/e0ab12e8f8bdd6f3a1b024c97890f812.png) This is a vector space over K, which has the multiplicity
This is a vector space over K, which has the multiplicity  of the root as a dimension.
of the root as a dimension.
This definition of intersection multiplicity, which is essentially due to Jean-Pierre Serre in his book Local algebra, works only for the set theoretic components (also called isolated components) of the intersection, not for the embedded components. Theories have been developed for handling the embedded case (see intersection theory for details).
In complex analysis
Let z0 be a root of a holomorphic function ƒ , and let n be the least positive integer such that, the nth derivative of ƒ evaluated at z0 differs from zero. Then the power series of ƒ about z0 begins with the nth term, and ƒ is said to have a root of multiplicity (or “order”) n. If n = 1, the root is called a simple root (Krantz 1999, p. 70).
We can also define the multiplicity of the zeroes and poles of a meromorphic function thus: If we have a meromorphic function ƒ = g/h, take the Taylor expansions of g and h about a point z0, and find the first non-zero term in each (denote the order of the terms m and n respectively). if m = n, then the point has non-zero value. If m > n, then the point is a zero of multiplicity m − n. If m < n, then the point has a pole of multiplicity n − m.
See also
- Zero (complex analysis)
- Set (mathematics)
- Fundamental theorem of algebra
- Fundamental theorem of arithmetic
- Algebraic multiplicity and geometric multiplicity of an eigenvalue
- Frequency (statistics)
References
- Krantz, S. G. Handbook of Complex Variables. Boston, MA: Birkhäuser, 1999. ISBN 0-8176-4011-8.