Moment (physics)
| Classical mechanics |
|---|
|
Fundamental concepts |
|
Core topics |
In physics, moment relates to the perpendicular distance from a point to a line or a surface, and is derived from the mathematical concept of moments.[1] It is frequently used in combination with other physical quantities as in moment of inertia, moment of force, moment of momentum, magnetic moment and so on.
Moment is also used colloquially for different physical quantities that depend upon distance. For example, in engineering and kinesiology the term moment is often used instead of the more complete term moment of force. A moment of force is the product of the distance of a force from an axis times the magnitude of the force, i.e., F × d, where F is the magnitude of the force and d is the moment of the force. See torque for a more complete description of moments of force or couple for the related concept free moment of force also known as a force couple.
It may also be used when the distance is squared, as in moment of inertia. The moment of inertia is the "second moment" of mass of a physical object. This is the object's resistance or inertia to changes in its angular motion. It is roughly the sum of the squared distances (i.e., moments) of the object's mass particles about a particular axis 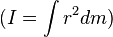 .
.
See also
- Mechanical equilibrium – applies when an object is balanced so that the sum of the clockwise moments about a pivot is equal to the sum of the anticlockwise moments about the same pivot
- Moment of force – see also the article couple (mechanics)
- Moment of inertia –
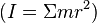 is analogous to mass in discussions of rotational motion.
is analogous to mass in discussions of rotational motion. - Moment of momentum –
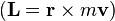 is the rotational analog of linear momentum.
is the rotational analog of linear momentum. - Magnetic moment –
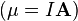 is a dipole moment measuring the strength and direction of a magnetic source.
is a dipole moment measuring the strength and direction of a magnetic source. - Electric dipole moment – a dipole moment measuring the charge difference and direction between two or more charges. For example, the electric dipole moment between a charge of –q and q separated by a distance of d is
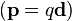
- List of area moments of inertia
- List of moments of inertia
References
- ↑ Robertson, D.G.E.; Caldwell, G.E.; Hamill, J.; Kamen, G.; and Whittlesey, S.N. (2004) Research Methods in Biomechanics. Champaign, IL:Human Kinetics Publ., p. 285.
External links
| Look up moment in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. |