Methacrylamide
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
| Methacrylamide | |
|---|---|
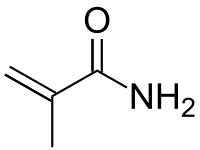 | |
| IUPAC name Methacrylamide | |
| Other names 2-Methacrylamide; 2-Methyl-2-propenamide; 2-Methylacrylamide; 2-Methylpropenamide; α-Methyl acrylic amide; Methacrylic acid amide; Methacrylic amide; Methylacrylamide | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | 79-39-0 |
| PubChem | 6595 |
| ChemSpider | 6346 |
| Jmol-3D images | Image 1 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| Molecular formula | C4H7NO |
| Molar mass | 85.10 g mol−1 |
| Appearance | White odorless crystals[1] |
| Density | 1.10-1.12 g/cm3[1] |
| Melting point | 106 to 109 °C; 223 to 228 °F; 379 to 382 K ([1]) |
| Boiling point | 215 °C; 419 °F; 488 K ([1]) |
| Solubility in water | 202 g/L (20 °C)[1] |
| Hazards | |
| Autoignition temperature | 510 °C (950 °F)[1] |
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |
| Infobox references | |
Methacrylamide is an industrial chemical used in the production of polymers and copolymers.
References
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike; additional terms may apply for the media files.