Metalaxyl
| Metalaxyl | ||
|---|---|---|
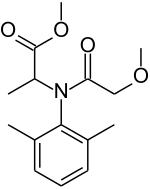 | ||
| IUPAC name 2-[(2,6-dimethylphenyl)- (2-methoxy-1-oxoethyl) amino]propanoic | ||
| Identifiers | ||
| CAS number | 57837-19-1 | |
| PubChem | 42586 | |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL105809 | |
| Jmol-3D images | Image 1 | |
| ||
| Properties | ||
| Molecular formula | C15H21NO4 | |
| Molar mass | 279.33 g/mol | |
| Appearance | Fine white powder | |
| Density | 1.20g/cm3 at 20 °C | |
| Melting point | 71-72 °C[1] | |
| Boiling point | 295.9 °C at 760 mm Hg | |
| Solubility in water | 8,400 mg/L at 22 °C | |
| log P | 1.65 (octanol/water)[2] | |
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | ||
| Infobox references | ||
Metalaxyl is a phenylamide fungicide with systemic function. Its chemical name is methyl N-(methoxyacetyl)-N-(2,6-xylyl)-DL-alaninate. It can be used to control Pythium in a number of vegetable crops, and Phytophthora in peas. Metalaxyl-M is the trade name of the optically pure stereoisomer.
It is the active ingredient in the seed treatment agent Apron XL LS.[3]
The fungicide has suffered severe resistance problems. The fungicide was marketed for use against Phytophthora infestans. However in the summer of 1980, in the Republic of Ireland, the crop was devastated by a potato blight epidemic after a resistant race of the oomycete appeared.[4] Irish farmers later successfully sued the company for their losses.[citation needed] Maximum pesticide residue limits for the EU/UK are set at 0.5 mg/kg for oranges and 1.0 mg/kg for apples
References
- ↑ O'Neil, M.J. (ed.). The Merck Index - An Encyclopedia of Chemicals, Drugs, and Biologicals. 13th Edition, Whitehouse Station, NJ: Merck and Co., Inc., 2001., p. 1058
- ↑ Hansch, C., Leo, A., D. Hoekman. Exploring QSAR - Hydrophobic, Electronic, and Steric Constants. Washington, DC: American Chemical Society., 1995., p. 134
- ↑ http://www.gov.mb.ca/agriculture/crops/vegetablecrops/pdf/bmz10s02.pdf
- ↑ Working on potato blight in Northern Ireland