Mental nerve
| Nerve: Mental nerve | |
|---|---|
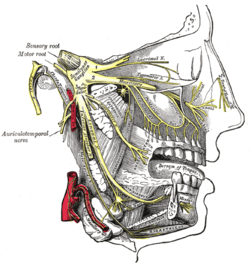 | |
| Distribution of the maxillary and mandibular nerves, and the submaxillary ganglion. (Mental nerve visible at bottom right, at chin.) | |
 | |
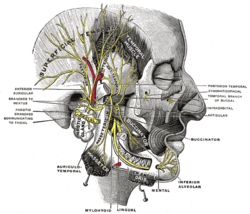
| Sensory areas of the head, showing the general distribution of the three divisions of the fifth nerve. (Mental nerve labeled at bottom left, near chin, in yellow.) | |
| Latin | nervus mentalis |
| Gray's | p.897 |
| Innervates | chin, lower lip |
| From | inferior alveolar nerve |
Mental nerve is a general somatic afferent (sensory) nerve which provides sensation to the anterior aspects of the chin and lower lip as well as the buccal gingivae of the mandibular anterior teeth and the premolars. It is a branch of the posterior trunk of the inferior alveolar nerve, which is itself a branch of the mandibular division of the trigeminal nerve (CN V).
The nerve emerges at the mental foramen in the mandibula, and divides beneath the Depressor anguli oris muscle into three branches:
These branches communicate freely with the facial nerve.
Anesthesia
The mental nerve can be blocked with local anesthesia, a procedure used in surgery of the chin, lower lip and buccal mucosa from midline to the second premolar. In this technique, local anesthetic is infiltrated in the soft tissue surrounding the mental foramen.
External links
- 23:st-0610 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center - "Anatomy of the Superficial Face - Nerves"
- Mental+nerve at eMedicine Dictionary
- MedEd at Loyola GrossAnatomy/h_n/cn/cn1/cnb3.htm
- cranialnerves at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University) (V)
Additional images
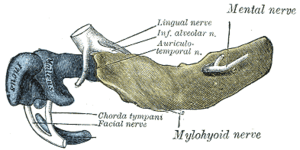

This article incorporates text from a public domain edition of Gray's Anatomy.
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||