Memphis Facula
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
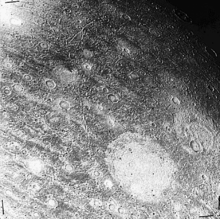
A Voyager 2 image of Memphis Facula on Ganymede (white patch on lower right)
Memphis Facula is a palimpsest, or "ghost crater", on Ganymede, the largest of the Jovian satellites.
About 360 km across,[1] it is situated in the south western part of Galileo Regio, a huge almost circular dark region on Ganymede's north eastern flank. Although almost level today, it is a relic of a massive impact and once was a deep impact crater whose walls have slumped and its floor has risen isostatically, smoothing out the remaining topography with slush.
The morphology of the larger palimpsests like Memphis Facula suggests that Ganymede's icy crust at the time of impact was about 10 km thick and was penetrated by the impact, allowing the slush and fluid beneath to fill and level out the crater.
See also
References
- Harland, D. M.; Jupiter Odyssey, Springer Praxis (2000), p. 136
- ↑ "Ganymede: Memphis Facula". Gazetteer of Planetary Nomenclature. USGS Astrogeology. Retrieved 2012-03-12.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike; additional terms may apply for the media files.