Megathrust earthquake
| Part of a series on |
| Earthquakes |
|---|
| Types |
|
|
| Causes |
| Characteristics |
|
|
| Measurement |
| Prediction |
| Other topics |
|
Earth Sciences Portal Category • Related topics |
Megathrust earthquakes occur at subduction zones at destructive plate boundaries (convergent boundaries), where one tectonic plate is subducted (forced underneath) by another. Due to the shallow dip of the plate boundary, which causes large sections to get stuck, these type of earthquakes are the planet's most powerful, with moment magnitudes (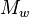 ) that can exceed 9.0. Since 1900, all six earthquakes of magnitude 9.0 or greater have been megathrust earthquakes. No other type of known terrestrial source of tectonic activity has produced earthquakes of this scale.
) that can exceed 9.0. Since 1900, all six earthquakes of magnitude 9.0 or greater have been megathrust earthquakes. No other type of known terrestrial source of tectonic activity has produced earthquakes of this scale.
Terminology
During the rupture, one side of the fault is pushed upwards relative to the other, and it is this type of movement that is known as thrust.[1] They are one type of dip-slip faults. A thrust fault is a reverse fault with a dip of 45° or less.[2] Oblique-slip faults have significant components of different slip styles. The term megathrust does not have a widely accepted rigorous definition, but is used to refer to an extremely large thrust fault, typically formed at the plate interface along a subduction zone such as the Sunda megathrust.[3][4]
Areas
The major subduction zone is associated with the Pacific and Indian Oceans and is responsible for the volcanic activity associated with the Pacific Ring of Fire. Since these earthquakes deform the ocean floor, they almost always generate a significant series of tsunami waves. They are known to produce intense shaking for periods of time that can last for up to a few minutes.
The Big One
"The Big One" is a term often used in casual conversation by residents of California, Oregon, Washington, and British Columbia to describe the megathrust earthquake anticipated as inevitably striking the Cascadia Subduction Zone. Much of the United States infrastructure has been hardened specifically for the anticipation of "The Big One". The name has also been applied to a megathrust earthquake expected to happen in Tokyo, Kantō region, Japan with the epicenter in Sagami Bay where the Philippine Sea Plate and North American Plate movements cause big earthquakes regularly, with an interval of approximately 70 years.[citation needed]
Examples
Examples of megathrust earthquakes are listed in the following table.
| Event | Estimated Magnitude ( 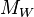 ) ) |
Tectonic Plates Involved | Other Details/Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| 365 Crete earthquake | 8.0+ | African Plate subducting beneath the Aegean Sea Plate |
|
| 869 Jogan Sanriku earthquake | 8.6–9.0 | Pacific Plate subducting beneath the Okhotsk Plate |
|
| 1575 Valdivia earthquake | 8.5 | Nazca Plate subducting beneath the South American Plate | |
| 1700 Cascadia earthquake | 8.7–9.2 | Juan de Fuca Plate subducting beneath the North American Plate |
|
| 1707 Hōei earthquake | 8.6 | Philippine Sea Plate subducting beneath the Eurasian Plate |
|
| 1737 Kamchatka earthquake | 8.3–9.0 | Pacific Plate subducting beneath the Okhotsk Plate |
|
| 1755 Lisbon earthquake | 8.5–9.0 [6] | Hypothesized to be part of a young subduction zone but origin still debated |
|
| 1868 Arica earthquake | 8.5–9.0 | Nazca Plate subducting beneath the South American Plate |
|
| 1877 Iquique earthquake | 8.5–9.0? | Nazca Plate subducting beneath the South American Plate |
|
| 1906 Ecuador-Colombia earthquake | 8.8 | Nazca Plate subducting beneath the South American Plate | |
| 1946 Nankaidō earthquake | 8.1 | Philippine Sea Plate subducting beneath the Eurasian Plate |
|
| 1952 Kamchatka earthquake | 9.0 | Pacific Plate subducting beneath the Okhotsk Plate |
|
| 1957 Andreanof Islands earthquake | 8.6 | Pacific Plate subducting beneath the North American Plate |
|
| 1960 Great Chilean Earthquake | 9.5 | Nazca Plate subducting beneath the South American Plate |
|
| 1964 Alaska earthquake ("Good Friday" earthquake) | 9.2 | Pacific Plate subducting beneath the North American Plate |
|
| 2001 southern Peru earthquake | 8.4 | Nazca Plate subducting beneath the South American Plate |
|
| 2004 Sumatra-Andaman earthquake ("Indian Ocean earthquake") | 9.1–9.3 | India Plate subducting beneath the Burma Plate |
|
| 2010 Maule earthquake ("Chile earthquake") | 8.8 | Nazca Plate subducting beneath the South American Plate |
|
| 2011 Tōhoku earthquake and tsunami | 9.0 | Pacific Plate subducting beneath the Okhotsk Plate[7][8][9] |
|
References
- ↑ Tsunami Terms
- ↑ Earthquake Glossary - dip slip
- ↑ Geophysical literature search showing almost 200 papers with the word "megathrust" in the title University of Strasbourg
- ↑ Park; et al. (2005). "Performance Review of the Global Seismographic Network for the Sumatra-Andaman Megathrust Earthquake". Seismological Research Letters 76 (3): 331–343. doi:10.1785/gssrl.76.3.331.
- ↑ http://ssn.dgf.uchile.cl/home/terrem.html
- ↑ Gutscher, M.-A.; Baptista M.A. & Miranda J.M. (2006). "The Gibraltar Arc seismogenic zone (part 2): Constraints on a shallow east dipping fault plane source for the 1755 Lisbon earthquake provided by tsunami modeling and seismic intensity". Tectonophysics 426: 153–166. Bibcode:2006Tectp.426..153G. doi:10.1016/j.tecto.2006.02.025.
- ↑ "Magnitude 8.9 – NEAR THE EAST COAST OF HONSHU, JAPAN 2011 March 11 05:46:23 UTC". USGS. 11 March 2011. Retrieved 11 March 2011.
- ↑ Kenneth Kidd (12 March 2011). "How ‘mega-thrust" earthquake caught forecasters by surprise". Toronto Star. Retrieved 12 March 2011.
- ↑ Reilly, Michael (11 March 2011<!- – 17:22 GMT -->). "Japan's quake updated to magnitude 9.0". New Scientist (Short Sharp Science ed.). Retrieved 11 March 2011.