Medicarpin
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
| Medicarpin | ||
|---|---|---|
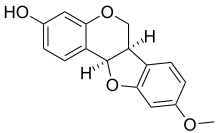 | ||
| IUPAC name 9-Methoxy-6a,11a-dihydro-6H-[1]benzofuro[3,2‑c]chromen-3-ol | ||
| Other names 3-Hydroxy-9-methoxypterocarpan | ||
| Identifiers | ||
| CAS number | 32383-76-9 | |
| PubChem | 623060 | |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL238823 | |
| Jmol-3D images | Image 1 | |
| ||
| Properties | ||
| Molecular formula | C16H14O4 | |
| Molar mass | 270.27 g/mol | |
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | ||
| Infobox references | ||
Medicarpin is a pterocarpan, a derivative of isoflavonoids.
Natural occurrences
Medicarpin is found in Medicago truncatula and Swartzia madagascariensis. It can also be found in Maackia amurensis cell cultures.[1]
The root nodule formation by Sinorhizobium meliloti[2] is apparently dependent on the flavonoids pathway.[3]
Metabolism
Pterocarpin synthase has 3 substrates : medicarpin, NADP+ and H2O, and 3 products : vestitone, NADPH and H+.[4]

References
- ↑ Isoflavonoid production by callus cultures of Maackia amurensis. S.A Fedoreyev, T.V Pokushalov, M.V Veselova, L.I Glebko, N.I Kulesh, T.I Muzarok, L.D Seletskaya, V.P Bulgakov and Yu.N Zhuravlev, Fitoterapia, 1 August 2000, Volume 71, Issue 4, Pages 365–372, doi:10.1016/S0367-326X(00)00129-5
- ↑ Dakora, F. D., Joseph, C. M., & D. A. Phillips (1993). "Alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) Root Exudates Contain Isoflavonoids in the Presence of Rhizobium meliloti.". Plant Physiol. 101 (3): 819–824. PMC 158695. PMID 12231731.
- ↑ Wasson, A. P. (2006). "Silencing the Flavonoid Pathway in Medicago truncatula Inhibits Root Nodule Formation and Prevents Auxin Transport Regulation by Rhizobia". The Plant Cell Online 18: 1617. doi:10.1105/tpc.105.038232.
- ↑ Lining Guo, Richard A. Dixon and Nancy L. Paival (1994). "Conversion of Vestitone to Medicarpin in Alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) Is Catalyzed by Two Independent Enzymes. Identification, Purification, and Characterization of Vestitone Reductase and 7,2’-Dihydroxy-4’-MethoxyIsoflavanol Dehydratase". Journal of Biological Chemistry 269 (35): 22372–22378. PMID 8071365.
| |||||||||||
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike; additional terms may apply for the media files.