Median aperture
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
| Brain: Median aperture | |
|---|---|
 Scheme of roof of fourth ventricle. The arrow is in the foramen of Magendie. | |
| Latin | apertura mediana ventriculi quarti |
| Gray's | p.798 |
| NeuroNames | hier-638 |
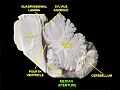
The median aperture ('"medial aperture," "Foramen of Magendie"') drains CSF from the fourth ventricle into the cisterna magna. The two other openings of the fourth ventricle are lateral apertures (foramina of Luschka), one on the left and one on the right, which drain cerebrospinal fluid into the cerebellopontine angle cistern. The median foramen on axial images is posterior to the pons and anterior to the caudal cerebellum. It is surrounded by the obex and gracile tubercles of the medulla, tela choroidea of the fourth ventricle and its choroid plexus, which is attached to the cerebellar vermis.[1]
Eponym
The Foramen of Magendie is named for François Magendie, who first described it.[2]
Additional images
-
Median aperture
References
- Netter, Frank H. (1989) Atlas of Human Anatomy. Summit, NJ: Ciba-Geigy Corporation.
- Williams, Peter L.; Warwick, Roger; Dyson, Mary; & Bannister, Lawrence H. (1989) Gray's Anatomy (37th ed.). New York: Churchill Livingstone.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Median aperture. |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike; additional terms may apply for the media files.