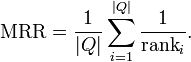Mean reciprocal rank
Mean reciprocal rank is a statistic measure for evaluating any process that produces a list of possible responses to a sample of queries, ordered by probability of correctness. The reciprocal rank of a query response is the multiplicative inverse of the rank of the first correct answer. The mean reciprocal rank is the average of the reciprocal ranks of results for a sample of queries Q:[1]
The reciprocal value of the mean reciprocal rank corresponds to the harmonic mean of the ranks.
Example
For example, suppose we have the following three sample queries for a system that tries to translate English words to their plurals. In each case, the system makes three guesses, with the first one being the one it thinks is most likely correct:
| Query | Results | Correct response | Rank | Reciprocal rank |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| cat | catten, cati, cats | cats | 3 | 1/3 |
| torus | torii, tori, toruses | tori | 2 | 1/2 |
| virus | viruses, virii, viri | viruses | 1 | 1 |
Given those three samples, we could calculate the mean reciprocal rank as (1/3 + 1/2 + 1)/3 = 11/18 or about 0.61.
This basic definition does not specify what to do if...
- none of the proposed results are correct (use mean reciprocal rank 0), or if
- there are multiple correct answers in the list. Consider using mean average precision (MAP).
See also Information retrieval and Question answering.[2]