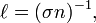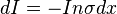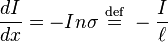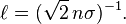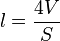Mean free path
In physics, the mean free path is the average distance travelled by a moving particle (such as an atom, a molecule, a photon) between successive impacts (collisions), [2] which modify its direction or energy or other particle properties.
Derivation

Imagine a beam of particles being shot through a target, and consider an infinitesimally thin slab of the target (Figure 1). The atoms (or particles) that might stop a beam particle are shown in red. The magnitude of the mean free path depends on the characteristics of the system the particle is in:
Where  is the mean free path, n is the number of target particles per unit volume, and
is the mean free path, n is the number of target particles per unit volume, and 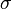 is the effective cross sectional area for collision.
is the effective cross sectional area for collision.
The area of the slab is  and its volume is
and its volume is  . The typical number of stopping atoms in the slab is the concentration n times the volume, i.e.,
. The typical number of stopping atoms in the slab is the concentration n times the volume, i.e.,  . The probability that a beam particle will be stopped in that slab is the net area of the stopping atoms divided by the total area of the slab.
. The probability that a beam particle will be stopped in that slab is the net area of the stopping atoms divided by the total area of the slab.
where 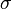 is the area (or, more formally,
the "scattering cross-section") of one atom.
is the area (or, more formally,
the "scattering cross-section") of one atom.
The drop in beam intensity equals the incoming beam intensity multiplied by the probability of the particle being stopped within the slab
This is an ordinary differential equation
whose solution is known as Beer-Lambert law and has the form 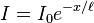 , where x is the distance travelled by the beam through the target and I0 is the beam intensity before it entered the target; ℓ is called the mean free path because it equals the mean distance traveled by a beam particle before being stopped. To see this, note that the probability that a particle is absorbed between x and x + dx is given by
, where x is the distance travelled by the beam through the target and I0 is the beam intensity before it entered the target; ℓ is called the mean free path because it equals the mean distance traveled by a beam particle before being stopped. To see this, note that the probability that a particle is absorbed between x and x + dx is given by
Thus the expectation value (or average, or simply mean) of x is
The fraction of particles that are not stopped (attenuated) by the slab is called transmission  where x is equal to the thickness of the slab x = dx.
where x is equal to the thickness of the slab x = dx.
Mean free path in kinetic theory
In kinetic theory the mean free path of a particle, such as a molecule, is the average distance the particle travels between collisions with other moving particles. The formula 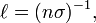 still holds for a particle with a high velocity relative to the velocities of an ensemble of identical particles with random locations. If, on the other hand, the velocities of the identical particles have a Maxwell distribution, the following relationship applies:[3]
still holds for a particle with a high velocity relative to the velocities of an ensemble of identical particles with random locations. If, on the other hand, the velocities of the identical particles have a Maxwell distribution, the following relationship applies:[3]
and it may be shown that the mean free path, in meters, is:[4]
where kB is the Boltzmann constant in J/K, T is the temperature in K, p is pressure in Pascals, and d is the diameter of the gas particles in meters.
Following table lists some typical values for air at different pressures and at room temperature.
| Vacuum range | Pressure in hPa (mbar) | Molecules / cm3 | Molecules / m3 | Mean free path |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ambient pressure | 1013 | 2.7 × 1019 | 2.7 × 1025 | 68 nm[5] |
| Low vacuum | 300 – 1 | 1019 – 1016 | 1025 – 1022 | 0.1 – 100 μm |
| Medium vacuum | 1 – 10−3 | 1016 – 1013 | 1022 – 1019 | 0.1 – 100 mm |
| High vacuum | 10−3 – 10−7 | 1013 – 109 | 1019 – 1015 | 10 cm – 1 km |
| Ultra high vacuum | 10−7 – 10−12 | 109 – 104 | 1015 – 1010 | 1 km – 105 km |
| Extremely high vacuum | <10−12 | <104 | <1010 | >105 km |
Mean free path in radiography

In gamma-ray radiography the mean free path of a pencil beam of mono-energetic photons is the average distance a photon travels between collisions with atoms of the target material. It depends on the material and the energy of the photons:
where μ is the linear attenuation coefficient, μ/ρ is the mass attenuation coefficient and ρ is the density of the material. The Mass attenuation coefficient can be looked up or calculated for any material and energy combination using the NIST databases [6] [7]
In X-ray radiography the calculation of the mean free path is more complicated, because photons are not mono-energetic, but have some distribution of energies called spectrum. As photons move through the target material they are attenuated with probabilities depending on their energy, as a result their distribution changes in process called Spectrum Hardening. Because of Spectrum Hardening the mean free path of the X-ray spectrum changes with distance.
Sometimes one measures the thickness of a material in the number of mean free paths. Material with the thickness of one mean free path will attenuate 37% (1/e) of photons. This concept is closely related to Half-Value Layer (HVL); a material with a thickness of one HVL will attenuate 50% of photons. A standard x-ray image is a transmission image, a minus log of it is sometimes referred as number of mean free paths image.
Mean free path in particle physics
In particle physics the concept of the mean free path is not commonly used, being replaced by the similar concept of attenuation length. In particular, for high-energy photons, which mostly interact by electron-positron pair production, the radiation length is used much like the mean free path in radiography.
Mean free path in nuclear physics
Independent particle models in nuclear physics require the undisturbed orbiting of nucleons within the nucleus before they interact with other nucleons. Blatt and Weisskopf, in their 1952 textbook "Theoretical Nuclear Physics" (p. 778) wrote "The effective mean free path of a nucleon in nuclear matter must be somewhat larger than the nuclear dimensions in order to allow the use of the independent particle model. This requirement seems to be in contradiction to the assumptions made in the theory ... We are facing here one of the fundamental problems of nuclear structure physics which has yet to be solved." (quoted by Norman D. Cook in "Models of the Atomic Nucleus" Ed.2 (2010) Springer, in Chapter 5 "The Mean Free Path of Nucleons in Nuclei").[8]
Mean free path in optics
If one takes a suspension of non light absorbing particles of diameter d with a volume fraction Φ, the mean free path [9] of the photons is:
where Qs is the scattering efficiency factor. Qs can be evaluated numerically for spherical particles thanks to the Mie theory calculation
Mean free path in acoustics
In an otherwise empty cavity, the mean free path of a single particle bouncing off the walls is:
where V is volume of the cavity and S is total inside surface area of cavity. This relation is used in the derivation of the Sabine equation in acoustics, using a geometrical approximation of sound propagation.[10]
Examples
A classic application of the mean free path is to estimate the size of atoms or molecules. Another important application is in estimating the resistivity of a material from the mean free path of its electrons.
For example, for sound waves in an enclosure, the mean free path is the average distance the wave travels between reflections off the enclosure's walls.
In aerodynamics, the mean free path is in the same order of magnitude as the shockwave thickness at mach numbers greater than one.
See also
References
- ↑ "NIST: Note - X-Ray Form Factor and Attenuation Databases". Physics.nist.gov. 1998-03-10. Retrieved 2011-11-08.
- ↑ Author: Marion Brünglinghaus, ENS, European Nuclear Society. "Mean free path". Euronuclear.org. Retrieved 2011-11-08.
- ↑ S. Chapman and T.G. Cowling, The mathematical theory of non-uniform gases, 3rd. edition, Cambridge University Press, 1990, ISBN 0-521-40844-X, p. 88
- ↑ "Mean Free Path, Molecular Collisions". Hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu. Retrieved 2011-11-08.
- ↑ Jennings, S (1988). "The mean free path in air". Journal of Aerosol Science 19 (2): 159. doi:10.1016/0021-8502(88)90219-4.
- ↑ Hubbell, J. H.; Seltzer, S. M. "Tables of X-Ray Mass Attenuation Coefficients and Mass Energy-Absorption Coefficients". National Institute of Standards and Technology. Retrieved September 2007.
- ↑ Berger, M. J.; Hubbell, J. H.; Seltzer, S. M.; Chang, J.; Coursey, J. S.; Sukumar, R.; Zucker, D. S. "XCOM: Photon Cross Sections Database". National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST). Retrieved September 2007.
- ↑ Cook, Norman D. Models of the Atomic Nucleus. Heidelberg: Springer. p. 324. ISBN 978-3-642-14736-4.
- ↑ Mengual, O; Meunier, G; Cayré, I; Puech, K; Snabre, P (1999). "TURBISCAN MA 2000: multiple light scattering measurement for concentrated emulsion and suspension instability analysis". Talanta 50 (2): 445–56. doi:10.1016/S0039-9140(99)00129-0. PMID 18967735.
- ↑ Davis, D. and Patronis, E. "Sound System Engineering" (1997) Focal Press, ISBN 0-240-80305-1 p. 173
External links
- Gas Dynamics Toolbox Calculate mean free path for mixtures of gases using VHS model