Matrix gamma distribution
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
| Notation | 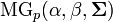 |
|---|---|
| Parameters | shape parameter (real)
|
| Support |  positive-definite real positive-definite real 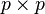 matrix matrix |
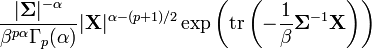
| |
In statistics, a matrix gamma distribution is a generalization of the gamma distribution to positive-definite matrices.[1] It is a more general version of the Wishart distribution, and is used similarly, e.g. as the conjugate prior of the precision matrix of a multivariate normal distribution and matrix normal distribution. The compound distribution resulting from compounding a matrix normal with a matrix gamma prior over the precision matrix is a generalized matrix t-distribution.[citation needed]
This reduces to the Wishart distribution with 
See also
- inverse matrix gamma distribution.
- matrix normal distribution.
- matrix t-distribution.
- Wishart distribution.
Notes
- ↑ Iranmanesha, Anis, M. Arashib and S. M. M. Tabatabaeya (2010). "On Conditional Applications of Matrix Variate Normal Distribution". Iranian Journal of Mathematical Sciences and Informatics, 5:2, pp. 33–43.
References
- Gupta, A. K.; Nagar, D. K. (1999) Matrix Variate Distributions, Chapman and Hall/CRC ISBN 978-1584880462
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike; additional terms may apply for the media files.

 scale (
scale ( is the
is the