Mare Acidalium quadrangle
| Mare Acidalium quadrangle | |
|---|---|
 Map of Mare Acidalium quadrangle from Mars Orbiter Laser Altimeter (MOLA) data. The highest elevations are red and the lowest are blue. | |
| Coordinates | 47°30′N 30°00′W / 47.5°N 30°WCoordinates: 47°30′N 30°00′W / 47.5°N 30°W |
The Mare Acidalium quadrangle is one of a series of 30 quadrangle maps of Mars used by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) Astrogeology Research Program. The quadrangle is located in the northeastern portion of Mars’ western hemisphere and covers 300° to 360° east longitude (0° to 60° west longitude) and 30° to 65° north latitude. The quadrangle uses a Lambert conformal conic projection at a nominal scale of 1:5,000,000 (1:5M). The Mare Acidalium quadrangle is also referred to as MC-4 (Mars Chart-4).[1]
The southern and northern borders of the quadrangle are approximately 3,065 km and 1,500 km wide, respectively. The north to south distance is about 2,050 km (slightly less than the length of Greenland).[2] The quadrangle covers an approximate area of 4.9 million square km, or a little over 3% of Mars’ surface area.[3]
This area contains many bright spots on a dark background that may be mud volcanoes. There are also some gullies that are believed to have formed by relatively recent flows of liquid water.[4]
Origin of Name
Mare Acidalium (Acidalian Sea) is the name of a telescopic albedo feature located at 45° N and 330° E on Mars. The feature was named for a well or fountain in Boeotia, Greece. According to classical tradition, it is a location where Venus and the Graces bathed. The name was approved by the International Astronomical Union (IAU) in 1958.[5]
Physiography and Geology
The quadrangle contains many interesting features, including gullies and possible shorelines of an ancient northern ocean. Some areas are densely layered. The boundary between the southern highlands and the northern lowlands lies in Mare Acidalium.[6] The "Face on Mars," of great interest to the general public, is located near 40.8 degrees north and 9.6 degrees west, in an area called Cydonia. When Mars Global Surveyor examined it with high resolution, the face turned out to just be an eroded mesa.[7] Mare Acidalium contains the Kasei Valles system of canyons. This huge system is 300 miles wide in some places—Earth's Grand Canyon is only 18 miles wide.[8]
Gullies
The HiRISE image below of Acidalia Colles shows gullies in the northern hemisphere. Gullies occur on steep slopes, especially craters. Gullies are believed to be relatively young because they have few, if any craters, and they lie on top of sand dunes which are themselves young. Usually, each gully has an alcove, channel, and apron. Although many ideas have been put forward to explain them, the most popular involve liquid water either coming from an aquifer or left over from old glaciers.[4]
-
Acidalia Colles Gullies and other features, as seen by HiRISE. The scale bar is 1,000 meters long.
-

Context for next image of Bamberg crater. Box shows where the next image came from. This is a CTX image from Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter.
-

Gullies and massive flow of material, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program. Gullies are enlarged in next two images. Location is Bamberg crater.
-

Close up view of some gullies, as seen by HiRISE under the HiWish program.
-

Close up view of another gully in same HiRISE picture. Picture taken under HiWish program.
-
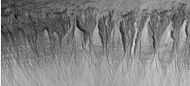
Gullies, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program.
-

Gullies in a crater, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program.
-

Close-up of gullies in a crater from previous image. Image taken by HiRISE under HiWish program.
There is evidence for both theories. Most of the gully alcove heads occur at the same level, just as one would expect of an aquifer. Various measurements and calculations show that liquid water could exist in an aquifer at the usual depths where the gullies begin.[9] One variation of this model is that rising hot magma could have melted ice in the ground and caused water to flow in aquifers. Aquifers are layers that allow water to flow. They may consist of porous sandstone. This layer would be perched on top of another layer that prevents water from going down (in geological terms it would be called impermeable). The only direction the trapped water can flow is horizontally. The water could then flow out onto the surface when the aquifer reaches a break, like a crater wall. Aquifers are quite common on Earth. A good example is "Weeping Rock" in Zion National Park Utah.[10]
On the other hand there is evidence for the alternative theory because much of the surface of Mars is covered by a thick smooth mantle that is thought to be a mixture of ice and dust. This ice-rich mantle, a few yards thick, smoothes the land, but in places it has a bumpy texture, resembling the surface of a basketball. Under certain conditions the ice could melt and flow down the slopes to create gullies. Since there are few craters on this mantle, the mantle is relatively young. An excellent view of this mantle is in the picture of the Ptolemaeus Crater Rim, as seen by HiRISE.
Changes in Mars's orbit and tilt cause significant changes in the distribution of water ice from polar regions down to latitudes equivalent to Texas. During certain climate periods water vapor leaves polar ice and enters the atmosphere. The water comes back to ground at lower latitudes as deposits of frost or snow mixed generously with dust. The atmosphere of Mars contains a great deal of fine dust particles. Water vapor condenses on the particles, then the heavier particles with the water coating fall and pile up on the ground. When ice at the top of the mantling layer goes back into the atmosphere, it leaves behind dust, which insulates the remaining ice.[11]
Craters
Impact craters generally have a rim with ejecta around them, in contrast volcanic craters usually do not have a rim or ejecta deposits.[12] Sometimes craters display layers. Since the collision that produces a crater is like a powerful explosion, rocks from deep underground are tossed unto the surface. Hence, craters can show us what lies deep under the surface.
-
Kunowsky Crater Floor, as seen by HiRISE. The scale bar is 500 meters long.
-
Bonestell Crater, as seen by HiRISE. Scale bar is 1000 meters long.
-
Arandas Crater, as seen by HiRISE. Click on image for a better view of North and South Walls, as well as central hills. Scale bar is 1000 meters long.
-

Exhumed Crater in Mare Acidalium, as seen by Mars Global Surveyor.
-

Group of craters that may have struck the surface at the same time after an asteroid broke up. If the craters were formed at different times, they would have wiped away parts of the others. Picture was taken by HiRISE, under HiWish program. Image located in Terra Cimmeria.
-

Crater with ejecta, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program. The box shows area enlarged in next image.
-

Enlarged view of crater ejecta showing channel with a deposit at the end, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program.
-

Close-up of surface near ejecta of crater, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program. Melted ice from ground water may have formed small channel.
-

Crater wall covered with a smooth mantle, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program.
Mud volcanoes
Large areas of Mare Acidalium display bright spots on a dark background. It has been suggested that the spots are mud volcanoes.[13] More than 18,000 of these features, which have an average diameter of about 800 meters, have been mapped.[14] Mare Acidalium would have received large quantities of mud and fluids form outflow channels, so much mud may have accumulated there. The bright mounds have been found to contain crystalline ferric oxides. Mud volcanism here may be highly significant because long lived conduits for upwelling groundwater could have been produced. These could have been habitats for micro organisms. Mud volcanoes could have brought up samples from deep zones that could therefore be sampled by robots.[15]
-
Craters with white centers in Mare Acidalium. Sand dunes are visible in low areas in image. Some of the features may be mud volcanoes. Picture taken by Mars Global Surveyor under the MOC Public Targeting Program.
-

Mud volcanoes near the edge of the ejecta of a nearby crater, as seen by HiRISE under the HiWish program.
Gallery
-
Cliff in Kasei Valles system, as seen by HiRISE.
-
Enlargement of cliff in Kasei Valles system in previous image showing boulders and their tracks, as seen by HiRISE. Click on image to see a boulder only 2.2 yards across (smaller than a bedroom).
-
CTX image showing the context for the next image of a fault.
-
Close-up of a possible fault in Mare Acidalium, as seen by HiRISE under the HiWish program. A circle is drawn around crater to show that it may be off round because of movement of the fault. Many other faults are in the region.
-

Stream meander and cutoff, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program.
See also
- Climate of Mars
- Impact crater
- List of quadrangles on Mars
- Martian Gullies
- Water on Mars
References
- ↑ Davies, M.E.; Batson, R.M.; Wu, S.S.C. “Geodesy and Cartography” in Kieffer, H.H.; Jakosky, B.M.; Snyder, C.W.; Matthews, M.S., Eds. Mars. University of Arizona Press: Tucson, 1992.
- ↑ Distances calculated using NASA World Wind measuring tool. http://worldwind.arc.nasa.gov/.
- ↑ Approximated by integrating latitudinal strips with area of R^2 (L1-L2)(cos(A)dA) from 30° to 65° latitude; where R = 3889 km, A is latitude, and angles expressed in radians. See: http://stackoverflow.com/questions/1340223/calculating-area-enclosed-by-arbitrary-polygon-on-earths-surface.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Heldmann, J. and M. Mellon. Observations of martian gullies and constraints on potential formation mechanisms. 2004. Icarus. 168: 285-304.
- ↑ USGS Gazetteer of Planetary Nomenclature. Mars. http://planetarynames.wr.usgs.gov/.
- ↑ http://hirise.lpl.arizona.edu/PSP_010354_2165
- ↑ http://mars.jpl.nasa.gov/mgs/msss/camera/images/moc_5_24_01/face/index.html
- ↑ http://hiroc.lpl.arizona.edu/images/PSP/diafotizo.php?ID=PSP_001640_2125
- ↑ Heldmann, J. and M. Mellon. 2004. Observations of martian gullies and constraints on potential formation mechanisms. Icarus. 168:285-304
- ↑ Harris, A and E. Tuttle. 1990. Geology of National Parks. Kendall/Hunt Publishing Company. Dubuque, Iowa
- ↑ MLA NASA/Jet Propulsion Laboratory (2003, December 18). Mars May Be Emerging From An Ice Age. ScienceDaily. Retrieved February 19, 2009, from http://www.sciencedaily.com /releases/2003/12/031218075443.htmAds by GoogleAdvertise
- ↑ Hugh H. Kieffer (1992). Mars. University of Arizona Press. ISBN 978-0-8165-1257-7. Retrieved 7 March 2011.
- ↑ Grotzinger, J. and R. Milliken (eds.) 2012. Sedimentary Geology of Mars. SEPM
- ↑ Oehler, D. and C. Allen. 2010. Evidence for pervasive mud volcanism in Acidalia Planitia, Mars. Icarus: 208. 636-657.
- ↑ Oehler, D, and C. Allen. 2011. Evidence for pervasive mud volcanism in Acidalia Planitia, Mars. Icarus. 208: 636-657.


| Quadrangles on Mars | |||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MC-01 Mare Boreum (features) | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| MC-05 Ismenius Lacus (features) |
MC-06 Casius (features) |
MC-07 Cebrenia (features) |
MC-02 Diacria (features) |
MC-03 Arcadia (features) |
MC-04 Acidalium (features) | ||||||||||||||||||
| MC-12 Arabia (features) |
MC-13 Syrtis Major (features) |
MC-14 Amenthes (features) |
MC-15 Elysium (features) |
MC-08 Amazonis (features) |
MC-09 Tharsis (features) |
MC-10 Lunae Palus (features) |
MC-11 Oxia Palus (features) | ||||||||||||||||
| MC-20 Sinus Sabaeus (features) |
MC-21 Iapygia (features) |
MC-22 Mare Tyrrhenum (features) |
MC-23 Aeolis (features) |
MC-16 Memnonia (features) |
MC-17 Phoenicis Lacus (features) |
MC-18 Coprates (features) |
MC-19 Margaritifer Sinus (features) | ||||||||||||||||
| MC-27 Noachis (features) |
MC-28 Hellas (features) |
MC-29 Eridania (features) |
MC-24 Phaethontis (features) |
MC-25 Thaumasia (features) |
MC-26 Argyre (features) | ||||||||||||||||||
| MC-30 Mare Australe (features) | |||||||||||||||||||||||










