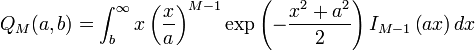Marcum Q-function
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
In statistics, the Marcum-Q-function 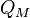 is defined as
is defined as
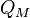 is also defined as
is also defined as
with modified Bessel function  of order M − 1. The Marcum Q-function is used for example as a cumulative distribution function for noncentral chi-squared and Rice distributions.
of order M − 1. The Marcum Q-function is used for example as a cumulative distribution function for noncentral chi-squared and Rice distributions.
The Marcum Q-function is monotonic and log-concave.[1]
References
- Marcum, J. I. (1950) "Table of Q Functions". U.S. Air Force RAND Research Memorandum M-339. Santa Monica, CA: Rand Corporation, Jan. 1, 1950.
- Nuttall, Albert H. (1975): Some Integrals Involving the QM Function, IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 21(1), 95-96, ISSN 0018-9448
- Weisstein, Eric W. Marcum Q-Function. From MathWorld—A Wolfram Web Resource.
- ↑ Yin Sun, Árpád Baricz, and Shidong Zhou (2010) On the Monotonicity, Log-Concavity, and Tight Bounds of the Generalized Marcum and Nuttall Q-Functions. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 56(3), 1166-1186, ISSN 0018-9448
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike; additional terms may apply for the media files.