Magnetic impedance
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
| Magnetic circuits |
|---|
Conventional magnetic circuits |
Phasor magnetic circuits |
Related concepts |
Gyrator-capacitor model variables |
Magnetic impedance (SI Unit: -Ω−1) is the ratio of a sinusoidal magnetic tension  to a sinusoidal magnetic current
to a sinusoidal magnetic current 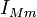 in a gyrator-capacitor model. Analogous to electrical impedance, magnetic impedance is likewise a complex variable.
in a gyrator-capacitor model. Analogous to electrical impedance, magnetic impedance is likewise a complex variable.
Magnetic impedance is also called the full magnetic resistance. It is derived from:
 , the effective magnetic resistance (real)
, the effective magnetic resistance (real) , the reactive magnetic resistance (imaginary)
, the reactive magnetic resistance (imaginary)
The phase angle  of the magnetic impedance is equal to:
of the magnetic impedance is equal to:
See also
References
- Pohl R. W. ELEKTRIZITÄTSLEHRE. – Berlin-Göttingen-Heidelberg: SPRINGER-VERLAG, 1960.
- Popov V. P. The Principles of Theory of Circuits. – M.: Higher School, 1985, 496 p. (In Russian).
- Küpfmüller K. Einführung in die theoretische Elektrotechnik, Springer-Verlag, 1959.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike; additional terms may apply for the media files.










