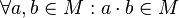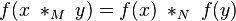Magma (algebra)
In abstract algebra, a magma (or groupoid; not to be confused with groupoids in category theory) is a basic kind of algebraic structure. Specifically, a magma consists of a set  equipped with a single binary operation
equipped with a single binary operation 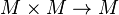 .
.
A binary operation is closed by definition, but no other axioms are imposed on the operation.
The term magma for this kind of structure was introduced by Nicolas Bourbaki. The term groupoid is an older, but still commonly used alternative which was introduced by Øystein Ore.
| Algebraic structures |
|---|
|
Group-like |
|
Ring-like |
Definition
A magma is a set  matched with an operation "
matched with an operation " " that sends any two elements
" that sends any two elements 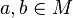 to another element
to another element  . The symbol "
. The symbol " " is a general placeholder for a properly defined operation. To qualify as a magma, the set and operation
" is a general placeholder for a properly defined operation. To qualify as a magma, the set and operation 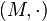 must satisfy the following requirement (known as the magma axiom):
must satisfy the following requirement (known as the magma axiom):
- For all
 ,
,  in
in  , the result of the operation
, the result of the operation  is also in
is also in  .
.
And in mathematical notation:
Etymology
In French, the word "magma" has multiple common meanings, one of them being "jumble". It is likely that the French Bourbaki group referred to sets with well-defined binary operations as magmas with the "jumble" definition in mind.
Types of magmas
Magmas are not often studied as such; instead there are several different kinds of magmas, depending on what axioms one might require of the operation. Commonly studied types of magmas include
- quasigroups—nonempty magmas where division is always possible;
- loops—quasigroups with identity elements;
- semigroups—magmas where the operation is associative;
- semilattices—semigroups where the operation is commutative and idempotent;
- monoids—semigroups with identity elements;
- groups—monoids with inverse elements, or equivalently, associative loops or nonempty associative quasigroups;
- abelian groups—groups where the operation is commutative.

- Note that both divisibility and invertibility
- imply the cancellation property.
Morphism of magmas
A morphism of magmas is a function  mapping magma
mapping magma  to magma
to magma  , that preserves the binary operation:
, that preserves the binary operation:
where  and
and 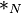 denote the binary operation on
denote the binary operation on  and
and  respectively.
respectively.
Combinatorics and parentheses
For the general, non-associative case, the magma operation may be repeatedly iterated. To denote pairings, parentheses are used. The resulting string consists of symbols denoting elements of the magma, and balanced sets of parenthesis. The set of all possible strings of balanced parenthesis is called the Dyck language. The total number of different ways of writing  applications of the magma operator is given by the Catalan number
applications of the magma operator is given by the Catalan number  . Thus, for example,
. Thus, for example, 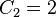 , which is just the statement that
, which is just the statement that  and
and 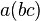 are the only two ways of pairing three elements of a magma with two operations. Less trivially,
are the only two ways of pairing three elements of a magma with two operations. Less trivially, 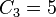 :
:  ,
, 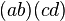 ,
,  ,
, 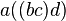 , and
, and 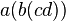 .
.
A shorthand is often used to reduce the number of parentheses. This is accomplished by using juxtaposition in place of the operation. For example, if the magma operation is  , then
, then 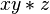 abbreviates
abbreviates  . Further abbreviations are possible by inserting spaces, for example by writing
. Further abbreviations are possible by inserting spaces, for example by writing 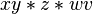 in place of
in place of  . Of course, for more complex expressions the use of parenthesis turns out to be inevitable. A way to avoid completely the use of parentheses is prefix notation.
. Of course, for more complex expressions the use of parenthesis turns out to be inevitable. A way to avoid completely the use of parentheses is prefix notation.
Free magma
A free magma  on a set
on a set  is the "most general possible" magma generated by the set
is the "most general possible" magma generated by the set  (i.e., there are no relations or axioms imposed on the generators; see free object). It can be described, in terms familiar in computer science, as the magma of binary trees with leaves labeled by elements of
(i.e., there are no relations or axioms imposed on the generators; see free object). It can be described, in terms familiar in computer science, as the magma of binary trees with leaves labeled by elements of  . The operation is that of joining trees at the root. It therefore has a foundational role in syntax.
. The operation is that of joining trees at the root. It therefore has a foundational role in syntax.
A free magma has the universal property such that, if  is a function from the set
is a function from the set  to any magma
to any magma  , then there is a unique extension of
, then there is a unique extension of  to a morphism of magmas
to a morphism of magmas 
See also: free semigroup, free group, Hall set, Wedderburn–Etherington number
Classification by properties
| Group-like structures | |||||
| Totality* | Associativity | Identity | Inverses | Commutativity | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Magma | Yes | No | No | No | No |
| Semigroup | Yes | Yes | No | No | No |
| Monoid | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No |
| Group | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
| Abelian Group | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Loop | Yes | No | Yes | Yes** | No |
| Quasigroup | Yes | No | No | No | No |
| Groupoid | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
| Category | No | Yes | Yes | No | No |
| Semicategory | No | Yes | No | No | No |
| *Closure, which is used in many sources to define group-like structures, is an equivalent axiom to totality, though defined differently. | |||||
| **Each element of a loop has a left and right inverse, but these need not coincide. | |||||
A magma (S, *) is called
- unital if it has an identity element,
- medial if it satisfies the identity xy * uz = xu * yz (i.e. (x * y) * (u * z) = (x * u) * (y * z) for all x, y, u, z in S),
- left semimedial if it satisfies the identity xx * yz = xy * xz,
- right semimedial if it satisfies the identity yz * xx = yx * zx,
- semimedial if it is both left and right semimedial,
- left distributive if it satisfies the identity x * yz = xy * xz,
- right distributive if it satisfies the identity yz * x = yx * zx,
- autodistributive if it is both left and right distributive,
- commutative if it satisfies the identity xy = yx,
- idempotent if it satisfies the identity xx = x,
- unipotent if it satisfies the identity xx = yy,
- zeropotent if it satisfies the identity xx * y = yy * x = xx,
- alternative if it satisfies the identities xx * y = x * xy and x * yy = xy * y,
- power-associative if the submagma generated by any element is associative,
- left-cancellative if for all x, y, and z, xy = xz implies y = z
- right-cancellative if for all x, y, and z, yx = zx implies y = z
- cancellative if it is both right-cancellative and left-cancellative
- a semigroup if it satisfies the identity x * yz = xy * z (associativity),
- a semigroup with left zeros if there are elements x for which the identity x = xy holds,
- a semigroup with right zeros if there are elements x for which the identity x = yx holds,
- a semigroup with zero multiplication or a null semigroup if it satisfies the identity xy = uv, for all x,y,u and v
- a left unar if it satisfies the identity xy = xz,
- a right unar if it satisfies the identity yx = zx,
- trimedial if any triple of its (not necessarily distinct) elements generates a medial submagma,
- entropic if it is a homomorphic image of a medial cancellation magma.
If  is instead a partial operation, then S is called a partial magma.
is instead a partial operation, then S is called a partial magma.
Generalizations
See n-ary group.
See also
- Magma category
- Auto magma object
- Universal algebra
- Magma computer algebra system, named after the object of this article.
- An example of a commutative non-associative magma
- Algebraic structures whose axioms are all identities
- Groupoid algebra
|
References
- M. Hazewinkel (2001), "Magma", in Hazewinkel, Michiel, Encyclopedia of Mathematics, Springer, ISBN 978-1-55608-010-4
- M. Hazewinkel (2001), "Free magma", in Hazewinkel, Michiel, Encyclopedia of Mathematics, Springer, ISBN 978-1-55608-010-4
- Weisstein, Eric W., "Groupoid", MathWorld.