Macitentan
 | |
|---|---|
| Systematic (IUPAC) name | |
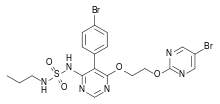
| N-[5-(4-Bromophenyl)-6-[2-[(5-bromo-2-pyrimidinyl)oxy]ethoxy]-4-pyrimidinyl]-N'-propylsulfamide | |
| Clinical data | |
| Trade names | Opsumit |
| Pregnancy cat. | X (US) |
| Legal status | ℞-only (US) FDA approved drug |
| Routes | Oral |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Metabolism | Hydrolysis, oxidation (CYP3A4) |
| Excretion | 2/3 urine, 1/3 faeces |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | 441798-33-0 |
| ATC code | C02KX04 |
| PubChem | CID 16004692 |
| ChemSpider | 13134960 |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:76607 |
| Synonyms | ACT-064992 |
| Chemical data | |
| Formula | C19H20Br2N6O4S |
| Mol. mass | 588.273 g/mol |
| SMILES
| |
| |
Macitentan (trade name Opsumit) is an orphan drug for the treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension. It acts as a dual endothelin receptor antagonist and has been developed by Actelion.[1] A Phase III clinical trial was successfully completed in 2012.[2] The drug received approval from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) on October 13, 2013.[3]
Pharmacokinetics
Macitentan has an active metabolite, ACT-132577, which is an oxidative depropylation product. Both macitentan and ACT-132577 are mainly excreted in form of hydrolysis products via urine (about 2/3 of all metabolites) and faeces (1/3).[4]
Co-administration of ciclosporin has only a slight effect on the concentrations of macitentan and its active metabolite, while rifampicin decreases the area under the curve (AUC) of the drug's blood plasma concentration by 79%, and ketoconazole approximately doubles it. This corresponds to the finding that macitentan is mainly metabolised via the liver enzyme CYP3A4.[5]
References
- ↑ Bolli, M. H.; Boss, C.; Binkert, C.; Buchmann, S.; Bur, D.; Hess, P.; Iglarz, M.; Meyer, S.; Rein, J.; Rey, M.; Treiber, A.; Clozel, M.; Fischli, W.; Weller, T. (2012). "The Discovery of N-[5-(4-Bromophenyl)-6-[2-[(5-bromo-2-pyrimidinyl)oxy]ethoxy]-4-pyrimidinyl]-N′-propylsulfamide (Macitentan), an Orally Active, Potent Dual Endothelin Receptor Antagonist". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 55 (17): 7849–7861. doi:10.1021/jm3009103. PMID 22862294.
- ↑ "Macitentan". Actelion. Retrieved 22 August 2012.
- ↑ ACTELION RECEIVES US FDA APPROVAL OF OPSUMIT (MACITENTAN) FOR THE TREATMENT OF PULMONARY ARTERIAL HYPERTENSION. Actelion. Retrieved 22 October 2013.
- ↑ Bruderer, S.; Hopfgartner, G. R.; Seiberling, M.; Wank, J.; Sidharta, P. N.; Treiber, A.; Dingemanse, J. (2012). "Absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion of macitentan, a dual endothelin receptor antagonist, in humans". Xenobiotica 42 (9): 901–910. doi:10.3109/00498254.2012.664665. PMID 22458347.
- ↑ Bruderer, S.; Äänismaa, P. I.; Homery, M. C.; Häusler, S.; Landskroner, K.; Sidharta, P. N.; Treiber, A.; Dingemanse, J. (2011). "Effect of Cyclosporine and Rifampin on the Pharmacokinetics of Macitentan, a Tissue-Targeting Dual Endothelin Receptor Antagonist". The AAPS Journal 14 (1): 68–78. doi:10.1208/s12248-011-9316-3. PMC 3282010. PMID 22189899.
External links
| ||||||||||||||