Macelignan
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
| Macelignan | ||
|---|---|---|
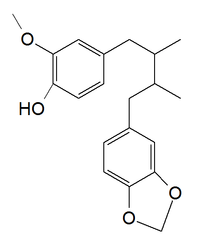 | ||
| IUPAC name (8R, 8′S)-7-(3,4-methylenedioxyphenyl)-7′-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-8,8′-dimethybutane | ||
| Identifiers | ||
| UNII | 8PP3614Z43 | |
| Jmol-3D images | Image 1 | |
| ||
| Properties | ||
| Molecular formula | C20H24O4 | |
| Molar mass | 328.40 g/mol | |
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | ||
| Infobox references | ||
Macelignan is a lignan. It can be found in Myristica fragrans, the nutmeg.
Medical research
One study has shown that macelignan may exert antimicrobial and anticariogenic activity against Streptococcus mutans, but this is not a currently used treatment.[1][2]
References
- ↑ Dental Caries and Medicinal Plants –An Overview. B. Parimala Devi and R. Ramasubramaniaraj, Journal of Pharmacy Research 2009, 2(11),1669-1675 http://jpronline.info/article/view/906/708
- ↑ Anticariogenic activity of macelignan isolated from Myristica fragrans (nutmeg) against Streptococcus mutans. J.Y. Chung, J.H. Choo, M.H. Lee and J.K. Hwang, Phytomedicine, Volume 13, Issue 4, 13 March 2006, Pages 261-266, doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2004.04.007
| |||||||||||||||||
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike; additional terms may apply for the media files.