MOPS
| MOPS | |
|---|---|
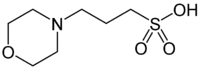 | |
| IUPAC name 3-morpholinopropane-1-sulfonic acid | |
| Other names 3-(N-morpholino)propanesulfonic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | 1132-61-2 |
| PubChem | 2723950 |
| ChemSpider | 63972 |
| Jmol-3D images | Image 1 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| Molecular formula | C7H15NO4S |
| Molar mass | 209.2633 |
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |
| Infobox references | |
MOPS is the common name for the compound 3-(N-morpholino)propanesulfonic acid, a buffer introduced by Good et al. in the 1960s. It is a structural analog to MES.[1] Its chemical structure contains a morpholine ring. HEPES is a similar pH buffering compound that contains a piperazine ring. With a pKa of 7.20, MOPS is an excellent buffer for many biological systems at near-neutral pH.
Applications
MOPS is frequently used as a buffering agent in biology and biochemistry. It has been tested and recommended for polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis.[2] Usage above 20 mM in mammalian cell culture work is not recommended.[3]
See also
References
- ↑ Good, Norman E.; Winget, G. Douglas; Winter, Wilhelmina; Connolly, Thomas N.; Izawa, Seikichi; Singh, Raizada M. M. (1966). "Hydrogen Ion Buffers for Biological Research". Biochemistry 5 (2): 467–77. doi:10.1021/bi00866a011. PMID 5942950.
- ↑ Thomas, J; Hodes, ME (1981). "A new discontinuous buffer system for the electrophoresis of cationic proteins at near-neutral pH". Analytical Biochemistry 118 (1): 194–6. doi:10.1016/0003-2697(81)90178-0. PMID 6278979.
- ↑ Eagle, H. (1971). "Buffer Combinations for Mammalian Cell Culture". Science 174 (4008): 500–3. doi:10.1126/science.174.4008.500. PMID 5110427.
External links
- Safety information
- Sigma Aldrich Buffer Calculator - Useful tool to calculate weight, volume, or concentration from molecular weight.
- Recipe for MOPS buffer on OpenWetWare