Lycia
| Lycia Hittite Lukka Lycian 𐊗𐊕𐊐𐊎𐊆𐊖 (Trm̃mis) Greek Λυκία (Lukia) | |
|---|---|
| Ancient Region of Anatolia | |
 Lycian rock cut tombs of Dalyan | |
| Location | Teke Peninsula, Western Taurus Range, Southern Anatolia |
| State existed |
15th-14th centuries BC (as Lukka) 1250–546 BC |
| Successive languages | Luwian, Lycian, Greek |
| Successive capitals | Xanthos, Patara |
| Achaemenid satrapy | Satrapy Number 1, with other states |
| Roman protectorate | Lycian League |
| Roman province | Lycia, then Lycia with other states |
| Byzantine eparchy | Lukia |
 | |



Lycia (Lycian: 𐊗𐊕𐊐𐊎𐊆𐊖 Trm̃mis; Greek: Λυκία, Turkish: Likya) was a geopolitical region in Anatolia in what are now the provinces of Antalya and Muğla on the southern coast of Turkey, and Burdur Province inland. Known to history since the records of ancient Egypt and the Hittite Empire in the Late Bronze Age, it was populated by speakers of the Luwian language group. Written records began to be inscribed in stone in the Lycian language (a later form of Luwian) after Lycia's involuntary incorporation into the Achaemenid Empire in the Iron Age. At that time (546 BC) the Luwian speakers were decimated, and Lycia received an influx of Persian speakers.
Lycia fought for the Persians in the Persian Wars, but on the defeat of the Achaemenid Empire by the Greeks, it became intermittently a free agent. After a brief membership in the Athenian Empire, it seceded and became independent (its treaty with Athens had omitted the usual non-secession clause), was under the Persians again, revolted again, was conquered by Mausolus of Caria, returned to the Persians, and went under Macedonian hegemony at the defeat of the Persians by Alexander the Great. Due to the influx of Greek speakers and the sparsity of the remaining Lycian speakers, Lycia was totally Hellenized under the Macedonians. The Lycian language disappeared from inscriptions and coinage.
On defeating Antiochus III in 188 the Romans gave Lycia to Rhodes for 20 years, taking it back in 168 BC. In these latter stages of the Roman republic Lycia came to enjoy freedom as part of the Roman protectorate. The Romans validated home rule officially under the Lycian League in 168 BC. This native government was an early federation with republican principles; these later came to the attention of the framers of the United States Constitution, influencing their thoughts.[1]
Despite home rule under republican principles Lycia was not a sovereign state and had not been since its defeat by the Carians. In 43 AD the Roman emperor, Claudius, dissolved the league. Lycia was incorporated into the Roman Empire with a provincial status. It became an eparchy of the Eastern, or Byzantine Empire, continuing to speak Greek even after being joined by communities of Turkish language speakers in the early 2nd millennium. After the fall of the Byzantine Empire in the 15th century, Lycia was under the Ottoman Empire, and was inherited by the Turkish Republic on the fall of that empire. The Greeks were withdrawn when the border between Greece and Turkey was negotiated in 1923.
Lycia today is a substantial component of the Turquoise Coast. It is of interest not only for recreation and sport, but as a location of antiquities going back as early as the Bronze Age. The ruins of ancient Lycia are seemingly everywhere. For reasons unknown, perhaps isolation, recycling of the building stone was minimal compared to other regions.
Geography
The borders of Lycia varied over time but at its centre was the Teke peninsula of southwestern Turkey, which juts into the Mediterranean Sea in a north-south direction, is bounded on the west by the Gulf of Fethiye, and on the east by the Gulf of Antalya. Lycia comprised what is now the westernmost portion of Antalya Province, the easternmost portion of Muğla Province, and the southernmost portion of Burdur Province. In ancient times the surrounding districts were, from west to east, Caria, Pisidia, and Pamphylia, all equally as ancient, and each speaking its own Anatolian language.
The name of the Teke Peninsula comes from the former name of Antalya Province, which was Teke Province, named from the Turkish tribe that settled in the region.
Physical geography
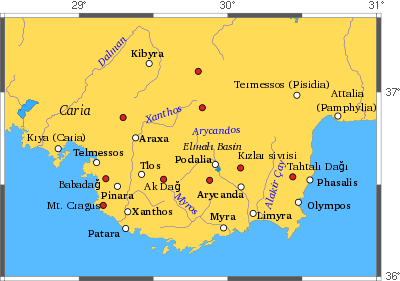
The region is mainly mountainous, with steep slopes often plunging into the sea. Four ridges extend from northeast to southwest, roughly, forming the western extremity of the Taurus Mountains. Furthest west of the four are Boncuk Dağlari, or "the Boncuk Mountains," extending from about Altinyayla, Burdur, southwest to about Oren north of Fethiye. This is a fairly low range peaking at about 2,340 m (7,680 ft). To the west of it the steep gorges of Dalaman Çayi ("the Dalaman River"), the ancient Indus, formed the traditional border between Caria and Lycia. The stream, 229 km (142 mi) long, enters the Mediterranean to the west of modern-day Dalaman. Upstream it is dammed in four places, after an origin in the vicinity of Sarikavak in Denizli Province.
The next ridge to the east is Akdağlari, "the White Mountains," about 150 km (93 mi) long, with a high point at Uyluktepe, "Uyluk Peak," of 3,024 m (9,921 ft). This massif may have been ancient Mount Cragus. Along its western side flows Eşen Çayi, "the Esen River," anciently the Xanthus, Lycian Arñna, originating in the Boncuk Mountains, flowing south, and transecting the several-mile-long beach at Patara. The Xanthus Valley was the country called Tŗmmis in dynastic Lycia, from which the people were the Termilae or Tremilae, or Kragos in the coin inscriptions of Greek Lycia: Kr or Ksan Kr. The name of western Lycia was given by Charles Fellows to it and points of Lycia west of it.
The next ridge to the east, Beydağlari, "the Bey Mountains," peaks at Kizlarsevrisi, 3,086 m (10,125 ft), the highest point of the Teke Peninsula. It is most likely the ancient Masicytus range. Between Beydağlari and Akdağlari is an upland plateau, Elmali, where ancient Milyas was located. The elevation of the town of Elmali, which means "Apple Town," from the density of fruit-bearing groves in the region, is 1,100 m (3,600 ft), which is the highest part of the valley below it. Fellows considered the valley to be central Lycia.
The Akçay, or "White River," the ancient Aedesa, brought water from the slopes to the plain, where it pooled in two lakes below the town, Karagöl and Avlangöl. Currently the two lakes are dry, the waters being captured on an ongoing basis by irrigation systems for the trees. The Aedesa once drained the plain through a chasm to the east, but now flows entirely through pipelines covering the same route, but emptying into the water supplies of Arycanda and Arif. An effort has been made to restore some of the cedar forests cleared in antiquity.[2]
The easternmost ridge extends along the east coast of the Teke Peninsula, and is called, generally, Tahtali Dağlari, "The Tahtali Mountains." The high point within them is Tahtali Dağ, elevation 2,366 m (7,762 ft), dubbed "Mount Olympus" in antiquity by the Greeks, remembering Mount Olympus in Greece.[3] These mountains create a rugged coastline called by Fellows eastern Lycia. Much of it has been reserved as Olimpos Beydağlari Parki. Within the park on the slopes of Mt. Olympus is a U-shaped outcrop, Yanartaş, above Cirali, from which methane gas, naturally perpetually escaping from below through the rocks, feeds eternal flames. This is the location of ancient Mount Chimaera.
Through the cul-de-sac between Baydağlari and Tahtalidağlari, the Alakir Çay ("Alakir River"), the ancient Limyra, flows to the south trickling from the broad valley under superhighway D400 near downtown Kumluca across a barrier beach into the Mediterranean. This configuration is entirely modern. Upstream the river is impounded behind Alakir Dam to form an urban-size reservoir. Below the reservoir a braided stream alternates with a single, small channel flowing through irrigated land. The wide bed gives an indication of the former size of the river. Upstream from the reservoir the stream lies in an unaltered gorge, flowing from the slopes of Baydağlari. The ancient route to Antalya goes up the valley and over the cul-de-sac, as the coast itself is impassible except by boat. The valley was the seat of ancient Solymus, home of the Solymi.
Demography
The ancient sources mention about 70 settlements of Lycia. These are situated either along the coastal strip in the protecting coves or on the slopes and hills of the mountain ranges. They are often difficult to access, which in ancient times was a defensive feature. The rugged coastline favored well-defended ports from which, in troubled times, Lycian pirate fleets sallied forth.
The principal cities of ancient Lycia were Xanthos, Patara, Myra, Pinara, Tlos and Olympos (each entitled to three votes in the Lycian League) and Phaselis. Cities such as Telmessos and Krya were sometimes listed by Classical authors as Carian and sometimes as Lycian.
Features and sights of interest

Although the 2nd-century AD dialogue Erōtes found the cities of Lycia "interesting more for their history than for their monuments, since they have retained none of their former splendor," many relics of the Lycians remain visible today. These relics include the distinctive rock-cut tombs in the sides of cliffs. The British Museum in London has one of the best collections of Lycian artifacts. Letoon, an important center in Hellenic times of worship for the goddess Leto and her twin children, Apollo and Artemis, and nearby Xanthos, ancient capital of Lycia, constitute a UNESCO World Heritage site.[4]
Turkey's first waymarked long-distance footpath, the Lycian Way, follows part of the coast of the region. The establishment of the path is a phase of development of the region as a recreational center. It is part of what is currently being called the Turkish Riviera or the Turquoise Coast, featuring long, sandy beaches at the bases of cliffs and settlements in protected coves that cater to the yachting industry.
Ancient language

The eponymous inhabitants of Lycia, the Lycians, spoke Lycian, a member of the Luwian branch of the Anatolian languages, a subfamily of the Indo-European family. Lycian has been attested only between about 500 BC and no later than 300 BC, in a unique alphabet devised for the purpose from the Greek alphabet of Rhodes. However, the Luwian languages originated in Anatolia during the 2nd millennium BC. The country was known by the name of Lukka then, and was under Hittite rule. The gap must be a gap in the use of writing.
At about 535 BC, before the first appearance of attested Lycian, the Achaemenid Empire overran Lycia. Despite its resistance, because of which the population of Xanthus was decimated, Lycia became part of the Persian Empire. The first coins with Lycian letters on them appeared not long before 500.[5] Lycia prospered under a monarchy set up by the Persians. Subsequently the Lycians were verbose in stone, carving memorial, historical and governmental inscriptions. Not all of these can yet be entirely understood, due to remaining ignorance of the language. The term "dynastic period" is used. If the government was any sort of federal democracy, there is no evidence of it, as the term "dynastic" suggests.
Lycia already had been hosting a small enclave of the Dorian Greeks as Doris for some centuries. Rhodes also was Dorian. After the defeat of the Persians by the Greeks, Lycia became open to further Greek settlement. Inscriptions in Lycian diminished, while those in Greek multiplied. Complete assimilation to Greek occurred in the 4th century, after Lycia had come under Alexander the Great and his fellow Macedonians.[6] There is no agreement yet on which Lycian inscription is the very last. No date is later than 300 at the very latest.
Subsequently the Macedonians were defeated by the Roman Republic, which for most of its final tenure allowed home rule to the Lycians, including their own language, then Greek. Lycia continued under the single empire, and fell naturally into the eastern empire when the division occurred. It was still speaking the Greek of the times when the eastern empire became the Byzantine Empire. In the 2nd millennium Anatolia was infiltrated by Turkish speaking settlers, but they never were very numerous in Lycia. After the fall of the Byzantines in the 15th century, Lycia was under the Ottoman Empire. Turkish and Greek settlements existed side-by-side, each speaking their own language.
All Greek-speaking enclaves in Anatolia were exchanged for Turkish speakers in Greece during the final settlement of the border with Greece at the beginning of the Turkish Republic in 1923. The Turks had won wars with Greece and Armenia in the preceding few years, settling the issue of whether the coast of Anatolia was going to be Greek or Turkish. The intent of the Treaty of Lausanne was to define borders that would not leave substantial populations of one country in another. Some population transfers were enforced. Former Greek villages still stand as ghost towns in Lycia.
History
Proto-history
Lycia has a proto-history little suspected by the historians of the 19th century before the decipherment of Hittite and ancient Egyptian, and the discovery of government records pertaining the Lycia and the Lycians. The records for the most part do not offer positive reports of them. They were rebels, pirates and raiders from the point of view of the Hittite and Egyptian Empires, in reports of official transactions with Lycians in the Late Bronze Age. The Lycians have left no written records of themselves at all from this period, which suggests that they probably were illiterate.
Ancient Egyptian records describe the Lycians as allies of the Hittites. Lycia may have been a member state of the Assuwa league of c. 1250 BC, appearing as Lukka or Luqqa. After the collapse of the Hittite Empire, Lycia emerged as an independent "Neo-Hittite" kingdom. The latter term was assigned to remnant states that continued after the fall of the Hittite Empire. It is entirely conventional; these states were not Hittite in any way. For the most part they spoke languages of the Luwian family.
Age of legend

Civilization in the Mediterranean collapsed into a period of decentralization, migrations and civil and international warfare after about 1200 BC. Lycian proto-history came to an end. There is nothing except legend to fill the gap until history begins with the classical Greek historian, Herodotus, who mentions them extensively. The stories of the early Lycians were told by Greek authors of the classical period. Sufficient gaps in their knowledge exist to cast doubt on the historicity of everything they had to say. They knew nothing of the Hittite Empire or the state of Lycia within it. All memory of the Bronze Age Greek script, Linear B, had been lost. They did not know that Anatolia once spoke languages of the Anatolian language group, or that Lycian was such a language. Except for a few basic generalities, such as that the Lycians probably fought in the Trojan War, nothing mentioned by the works produced under the name of Homer or the other poets, or anything said by Herodotus about Lycians prior to his own time, is generally granted any historical validity.
In the absence of knowledge, the historians of the past often wrote of Lycian legends as though they had a historical basis. However, all the legends are at odds with archaeological and proto-historic realities. It is unlikely, for example, that the Lycians came from Crete. They are known to have been a Luwian-speaking people, and there is not a trace of evidence that Luwians lived on Crete.
According to Herodotus,[7] Europa had (at least) two sons, Sarpedon and Minos. When they contended for the kingship of Crete, their native land, Minos drove Sarpedon and his people, the Termilae, into exile. They landed in Milyas, bearing the ancient name of the country known later as Lycia, which was tenanted by the Solymi. Subsequently Lycus, the son of Pandion II of Athens, driven into exile by his brother, King Aegeus, settled among the Termilae. They named it Lycia after him. Herodotus ends his tale with the observation that the Lycians were matrilineal.
Lycia appears elsewhere in Greek myth, such as in the story of Bellerophon, who eventually succeeded to the throne of the Lycian king Iobates (or Amphianax). Lycia was frequently mentioned by Homer as an ally of Troy. In Homer's Iliad, the Lycian contingent was said to have been led by two esteemed warriors: Sarpedon (son of Zeus and Laodamia) and Glaucus (son of Hippolochus).
Dynastic period
Acquisition by Cyrus the Great
Herodotus writes more credibly of contemporaneous events, especially where they concerned his native land. Asia Minor had been partly conquered by the Iranians, starting with the Scythians, then the Medes. The latter were defeated by the Persians, who incorporated them and their lands into the new Persian Empire. Cyrus the Great, founder of the Achaemenid dynasty, resolved to complete the conquest of Anatolia as a prelude to operations further west, to be carried out by his successors. He assigned the task to Harpagus, a Median general, who proceeded to subdue the various states of Anatolia, one by one, some by convincing them to submit, others through military action.
Arriving at the southern coast of Anatolia in 546 BC, the army of Harpagus encountered no problem with the Carians and their immediate Greek neighbors and alien populations, who submitted peacefully. In the Xanthus Valley an army of Xanthians sallied out to meet them, fighting determinedly, although vastly outnumbered. Driven into the citadel, they collected all their property, dependents and slaves into a central building, and burned them up. Then, after taking an oath not to surrender, they died to a man fighting the Persians, foreshadowing and perhaps setting an example for Spartan conduct at the Battle of Thermopylae a few generations later. Coincidentally archaeology has turned up a major fire on the acropolis of Xanthus in the mid-6th century BC, but as Antony Keen points out, there is no way to connect that fire with the event presented by Herodotus. It might have been another fire.[8] The Caunians, says Herodotus, followed a similar example immediately after.[9] If there was an attempt by any of the states of Lycia to join forces, as happened in Greece 50 years later, there is no record of it, suggesting that no central government existed. Each state awaited its own fate alone.
Herodotus also says or implies that 80 Xanthian families were away at the time, perhaps with the herd animals in alpine summer pastures (pure speculation), but helped repopulate the place. However, he reports, the Xanthians of his time were mainly descended from non-Xanthians. Looking for any nuance that might shed light on the repopulation of Xanthus, Keen interprets Herodotus' "those Lycians who now say that they are Xanthians" to mean that Xanthus was repopulated by other Lycians (and not by Iranians or other foreigners).[10] Herodotus says nothing of the remainder of Lycia; presumably, that is true because they submitted without further incident. Lycia was well populated and flourished as a Persian satrapy; moreover, they spoke mainly Lycian.
The Harpagid theory
The Harpagid Theory was initiated by Charles Fellows, discoverer of the Xanthian Obelisk, and person responsible for the transportation of the Xanthian Marbles from Lycia to the British Museum. Fellows could not read the Lycian inscription, except for one line identifying a person of illegible name, to whom the monument was erected, termed the son of Arppakhu in Lycian, equivalent to Greek Harpagos. Concluding that this person was the conqueror of Lycia in 546, Fellows conjectured that Harpagos had been made permanent satrap of Lycia for his services; moreover, the position was hereditary, creating a Harpagid Dynasty. This view prevailed nearly without question for several generations.
To the inscriptions of the Xanthian Obelisk were added those of the Letoon trilingual, which gave a sequel, as it were, to the names on the obelisk. Studies of coin legends, initiated by Fellows, went on. Currently most, but not all, of the Harpagid Theory, has been rejected. The Achaemenids utilized no permanent satrapies; the political circumstances changed too often. The conqueror of new lands was seldom made their satrap; he went on to other conquests. It was not the Persian custom to grant hereditary satrapies; satrap was only a step in the cursus honorum. And finally, a destitute mountain country would have been a poor reward for Cyrus' best general.[10] The main evidence against the Harpagid Theory (as Keen calls it) is the reconstruction of the name of the Xanthian Obelisk's deceased as Lycian Kheriga, Greek Gergis (Nereid Monument), a king reigning approximately 440-410 BC, over a century later than the conqueror of Lycia.
The next logical possibility is that Kheriga's father, Arppakhu, was a descendant of the conqueror. In opposition, Keen reconstructs the dynastic sequence from coin inscriptions as follows.[11] Kheriga had two grandfathers, Kuprlli and Kheriga. The younger Kheriga was the successor of Kuprlli. The latter's son, therefore, Kheziga, who was Kheriga's uncle, must have predeceased Kuprlli. Arppakhu is listed as regnant on two other inscriptions, but he did not succeed Kuprlli. He must therefore have married a daughter of Kuprlli, and have also predeceased the long-lived Kuprlli. The latter then was too old to reign de facto. On the contemporaneous deaths of both him and his son-in-law, Kheriga, named after his paternal grandfather, acquired the throne.
Kuprlli was the first king recorded for certain (there was an earlier possible) in the coin legends. He reigned approximately 480-440. Harpagos was not related by blood. The conqueror, therefore, was not the founder of the line, which was not Harpagid. An Iranian family, however, producing some other Harpagids, did live in Lycia and was of sufficient rank to marry the king's daughter. As to whether the Iranian family were related to any satrap, probably not. Herodotus says[12] that Satrapy 1 (the satrapies were numbered) consisted of Ionia, Magnesia, Aeolia, Caria, Lycia, Milya, and Pamphylia, who together paid a tax of 400 silver talents. This satrapy was later broken up and recombined. Keen hypothesizes[13] that since Caria had responsibility for the King's Highway through Lycia, Lycia and Caria were a satrapy.
The Lycian monarchy
The Achaemenid policy toward Lycia was hands-off.[13] There was not even a satrap stationed in the country. The reason for this tolerance after such a determined initial resistance is that the Iranians were utilizing another method of control: the placement of aristocratic Persian families in a region to exercise putative home rule. There is some evidence that the Lycian population was not as docile as the Persian hand-off policy would suggest. A section of the Persepolis Administrative Archives called the Persepolis Fortification Tablets, regarding the redistribution of goods and services in the Persepolis palace economy, mentions some redistributed prisoners of war, among whom were the Turmirla or Turmirliya, Lycian Trm̃mili, "Lycians." They lived during the reign of Darius I (522-486), the tablets dating from 509.[14]
For closer attention to their conquered, the Persian government preferred to establish a client state, setting up a monarchy under their control. The term "dynast" has come into use among English-speaking scholars, but that is not a native term. The Lycian inscriptions indicate the monarch was titled xñtawati, more phonetically khñtawati. The holders of this title can be traced in coin legends, having been given the right to coin. Lycia had a single monarch, who ruled the entire country from a palace at Xanthos. The monarchy was hereditary, hence the term "dynast." It was utilized by Persia as a means of transmitting Persian policy. It must have been they who put down local resistance and transported the prisoners to Persepolis, or ordered them transported. Some members of the dynasty were Iranian, but mainly it was native Lycian. If the survivors of 546 were in fact herdsmen (speculation), then all the Xanthian nobility had perished, and the Persians must have designated some other Lycian noble, whom they could trust.[15]
The first dynast is believed to be the person mentioned in the last line of the Greek epigram inscribed on the Xanthian Obelisk, which says "this monument has brought glory to the family (genos) of ka[]ika," which has a letter missing. It is probably not *karikas, for Kherika, as the latter is translated in the Letoon trilingual as Gergis. A more likely possibility is *kasikas for Kheziga, the same as Kheriga's uncle, the successor to Kuprlli, who predeceased him.[16]
Herodotus[17] mentions that the leader of the Lycian fleet under Xerxes in the Second Persian War of 480 BC was Kuberniskos Sika, previously interpreted as "Cyberniscus, the son of Sicas," two non-Lycian names. A slight regrouping of the letters obtains kubernis kosika, "Cybernis, son of Cosicas," where Cosicas is for Kheziga.[15] Cybernis went to the bottom of the Straits of Salamis with the entire Lycian fleet in the Battle of Salamis, but he may be commemorated by the Harpy Tomb. In this view, he was the KUB of the first coin legends, dated to the window, 520-500.[18] The date would have been more towards 500.[19]
There is a gap, however, between him and Kuprlli, who should have had a father named the same as his son, Kheziga. The name Kubernis does not appear again. Keen suggests that Darius I created the kingship on reorganizing the satrapies in 525, and that on the intestate death of Kubernis in battle, the Persians chose another relative named Kheziga, who was the father of Kuprlli. The Lycian dynasty may therefore be summarized as follows:
| Greek Name | Lycian Name | Status | Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| Kosikas | Kheziga | First of the line. | 525 – ? |
| Kubernis | KUB | Second in succession, son of the former. | ? – 480 |
| Kosikas | Kheziga | Third in succession, unknown relative. | 480 – ? |
| ? | Kuprlli (ΚΟ𐊓, pronounced kop) | Fourth in succession, son of the former. | ? – 440 |
| Kosikas | Kheziga | Regent, son of the former. | ? – ? |
| Harpagus (Iranian name) | Arppakhu | Regent, son-in-law of Kuprlli. | ? – 440 |
| Gergis | Kheriga | Fifth in succession, son of the former. | 440-410 |
| ? | Kherei | Sixth in succession, brother of the former. | 410-390 |
| Arbinas (Iranian name) | Erbina | Seventh in succession, son of the former. The last known of the line. | 390-380 |
| Artembares (Iranian name, *Rtambura, self-identified as "the Mede.") | Arttum̃para | Ruler of western Lycia from Telmessos. | 380 – ? |
| Pericles (Greek name) | Perikle | Ruler of eastern Lycia from Limyra, victor over Arttum̃para, rebel in the Revolt of the Satraps, last Lycian king. | ? - 360 |
Classical period
Following the ousting of the Persians, as Athens and Sparta fought the Peloponnesian wars, the majority of Lycian cities defaulted from the Delian League, with the exception of Telmessos and Phaselis.
In 429 BC, Athens sent an expedition against Lycia to try to force it to rejoin the league. This failed when Lycia's leader Gergis of Xanthos defeated General Melasander. The Lycians once again fell under Persian domination, and were ruled by men such as Mithrapata (late 4th century BC), whose name was Persian, and by 412 BC, Lycia is documented as fighting on the winning side of Persia. The Persian satraps were re-installed, but (as the coinage of the time attests) they allowed local dynasts the freedom to rule.[20] Persia held Lycia until it was conquered by Alexander III (the Great) of Macedon during 334–333 BC.[21]
Hellenistic period
After the death of Alexander the Great in 324 BC, his generals fought amongst themselves over the succession. Lycia fell into the hands of the general Antigonus by 304 BC. In 301 BC Antigonus was killed by an alliance of the other successors of Alexander, and Lycia became a part of the kingdom of Lysimachus, who ruled until he was killed in battle in 281 BC.[22] By 240 BC Lycia was part of the Ptolemaic Kingdom, centred on Egypt,[23] and remained in their control through 200 BC.[24] It had apparently come under Seleucid control by 190 BC, when the Seleucids' defeat in the Battle of Magnesia resulted in Lycia being awarded to Rhodes in the Peace of Apamea in 188 BC. It was then granted autonomy as a protectorate of Rome in 168 BC and remained so until becoming a Roman province in 43 AD under Claudius.[25]
Lycian League
| City | Votes |
|---|---|
| Xanthos | 3 |
| Patara | 3 |
| Myra | 3 |
| Pinara | 3 |
| Tlos | 3 |
| Olympos | 3 |
| Sympolity of Aperlae, Simena, Isinda, Apollonia | 1 |
| Amelas | ? |
| Antiphellus | ? |
| Arycanda | ? |
| Balbura, Lycia | ? |
| Bubon, Lycia | ? |
| Cyaneae | ? |
| Dias | ? |
| Gagae | ? |
| Idebessos | ? |
| Limyra | ? |
| Oenoanda | ? |
| Phaselis | ? |
| Phellus | ? |
| Podalia | ? |
| Rhodiapolis | ? |
| Sidyma | ? |
| Telmessus | ? |
| Trebenna | ? |
Formation
The Lycian League (Lukiakou systema in Strabo's Greek transliterated, a "standing together") is first known from two inscriptions of the early 2nd century BC in which it honors two citizens.[26] Bryce hypothesizes that it was formed as an agent to convince Rome to rescind the annexation of Lycia to Rhodes. Lycia had been under Rhodian control since the Peace of Apamea in 188 BC. A fragment from Livy[27] records a "pitiful embassy" in 178 BC from Lycia to the Roman Senate complaining that the Lycians were being treated as slaves. Whipping had been instituted as corporeal punishment and the women and children were being abused. The Romans sent back a stern warning with the Lycians to Rhodes saying that they had not intended the Lycians or any other people born in freedom to be enslaved by Rhodes, and that the assignment was only a protectorate. A fragment from Polybius[28] tells a slightly different version of the story, which has the Romans sending legates to Rhodes to say that "the Lycians had not been handed over to Rhodes as a gift, but to be treated like friends and allies." The Rhodians sent an embassy in return claiming that the Lycians had made the story up for reasons of their own and that in fact they were a financial burden on Rhodes.
The continuation of the story did not survive, but in 168 BC, Rome took Lycia away from Rhodes and turned over home rule to the League. There was no question of independence. Lycia was not to be sovereign, only self-governing under republican principles. It could neither negotiate with foreign powers nor disobey the Roman Senate. It was not independent. It could govern its own people and for a time mint its own coins as a right granted by Rome. It did not determine its own borders. Land and people could be assigned or taken away by the Senate. Remarking on this protectorate Strabo says of the government:"Formerly they deliberated about war and peace, and alliances, but this is not now permitted, as these things are under the control of the Romans. It is only done by their consent, or when it may be for their own advantage."
Exactly what such a statement might imply is uncertain. Lycia had not been a sovereign state for some time. Whether the Lycian League as such is meant, implying that it existed anciently, or some other similar government is meant, is not clear. The statement does not say also whether there was a gap between the former sovereign state and the new Lycian League, or whether they are to be conceived as chronologically continuous.
Composition
According to Strabo, the league comprised some 23 known city-states as members.[29] Lucius Licinius Murena (elder), Roman consul, added three more in 81 BC:[30] Balbura, Bubon and Oenoanda, which he had stripped from another systema to the north, the Tetrapolis, Cibyratis, or Cabalian League. It was dominated by the city of Cibyra (Kibyra), which formed a league approximately contemporaneously with the Lycian League. Cibyra ruled the Turkish Lakes Region. It was called Cibyra Megale, "Greater Cibyra," to distinguish it from Cibyra Mikra or "Little Cibyra" (today near Okurcalar) near Side. The lakes region is a string of alpine valleys in the folds of the Taurus Mountains, which have no natural exits. Instead they have collected lakes. Cibyra was on a low hill to the west of Gölhisar Valley and Gölhisar Lake, just north of Gölhisar.
Cibyra dominated an ancient region, Cabalis, which was divided between the later states of Lycia, Pisidia and Lydia, subsequently incorporated in Phrygia. According to Strabo, it spoke four languages, Lydian, even though Lydian had disappeared elsewhere, Greek, Pisidian and "that of the Solymi."[31] Cabalis, which was later divided into Lycian and Asian Cabalis, was the putative home of the Solymi. It included the Milyas District of Lycia, putatively the home of the first Lycians. It is possible that they spoke a form of Anatolian earlier than the attested Lycian, which some have dubbed "Milyan." A further connection of this "Milyan" with Lycian B of the Xanthian Obelisk is pure fantasy.
Unlike the Lycian League, the Cibyratis was ruled by a succession of deliberately ostentatious and high-handed tyrants. Having become a thorn in the side of Rome, they attracted the attention of Gnaeus Manlius Vulso, commander of the Roman armies successfully fighting the Galatian War of 189 BC. Manlius turned toward Cibyratis with the intent of removing the thorn. The tyrant, Moagetes, barely escaped with his life and his position by entering the Roman camp dressed in humble clothing, with a handful of similarly dressed assistants, claiming destitution and begging for mercy. He offered a payment of 15 talents. Manlius set the payment at 500 talents, a huge sum, impossible of payment. Finally moved to mercy, he allowed Moagetes to bargain him down to 100 and a substantial payment of grain, necessary to the Roman commissary.
When the Romans had departed Moagetes dropped the pretense, and Cibyratis resumed its arrogance. Consequently, when Murena did finally deal with Cibyratis, he had no political mercy. Strabo says that Bubon and Balbura were transferred to the Lycian League forthwith. He does not mention Oenoanda, but it had been a city of the Lycians anyway. It minted coinage of the League subsequently. There is no evidence that Cibyra was ever admitted to the League, although that assumption sometimes is made. It was in Asian Cabalia and as such was joined to Phrygia later, an event supported by their coin issues. The last tyrant of the Tetrapolis was also named Moagetes, a different one, unless the term was a title, or Strabo made a mistake.
The 23 at first and then 26 city states joined together in a federal-style government that shared political and economic resources. A “Lyciarch” was elected by a senate (συνέδριον, synedrion, "sitting together") that convened by agreement beforehand at "what city they please." Each member had one, two or three votes (presumably by different representatives), depending on the city's size. The diminishment of some cities over time caused them to join with the major state in their vicinity to form a sympolity. In that case they lost their vote (if they had one) assuming an influence in the vote of the major city. After election of the Lyciarch the Senate voted for the other public officials and the magistrates. The League's government took precedence, but, as in many federal systems, the issue was not entirely settled, and the resulting civil conflict led to the dissolution of the union.
Strabo identified the major cities of the League; that is, the three-vote cities, as Xanthos, Patara, Pinara, Olympos, Myra, and Tlos, with Patara as the capital. The full complement has been identified by a study of the coins and mention in other texts.[32] The coins recognize two districts, termed, for want of a better term, "monetary districts:" Masicytus and Cragus, both named after mountain ranges, in the shadow of which, presumably, the communities lived and conducted business.[33] Where coinage before the Lycian League had often been stamped LY for Lycia, it was now stamped KP (kr) or MA.
Treaty with Rome
An inscription from Tyberissos records the treaty between Rome and Lycian League, which is of a type the Romans called a foedus. It was much used between Italian cities and Rome, except that their treaties provided for contributions to Rome, but this one does not. There is a general statement and four clauses.[34] The general statement establishes "peace, friendship, and loyal alliance ... by land and sea for all time." The four clauses provide for neutrality of Rome to the enemies of the Lycian League, neutrality of the Lycian League to the enemies of Rome, mutual assistance in the case of first aggression by an enemy against either, and alteration of the treaty only by joint agreement. The treaty is written as though between independent and co-equal states, but all parties knew that this was conventional hypocrisy. The Lycian League was subject to the decisions of the Roman Senate and the decrees of the Roman emperors, but not vice versa. Only the Roman state was powerful.
Roman period
In 43 AD, the emperor Claudius annexed Lycia to the Roman Empire as a province and by the time of Vespasian, it was united with Pamphylia as a Roman province.[35] The heir of Augustus, Gaius Caesar, was killed there in 4 AD.
Byzantine era
It subsequently was a part of the Byzantine Empire.

Turkish era
It was incorporated into the Ottoman Empire and eventually became part of Turkey. A substantial Christian community of Greeks lived in Lycia until the 1920s when they were forced to migrate to Greece after the population exchange between Greece and Turkey following the Greco-Turkish War in the early 20th century.[36] The abandoned Greek villages in the region are a striking reminder of this exodus. Abandoned Greek houses can still be seen at in the towns of Demre, Kalkan and Kas, and Kaya is a Greek ghost town.[36] A small population of Turkish farmers moved into the region when the Lycian Greeks migrated to Greece.[36] The region is now one of the key centres of domestic and foreign tourism in Turkey.
Episcopal sees
Ancient episcopal sees of Lycia that are listed in the Annuario Pontificio as titular sees include:[37]
- Acalissus
- Acarassus
- Antiphellus
- Aperlae (ruins at Kakamo)
- Araxa (Örenhan)
- Arycanda (Aruf)
- Arneae (Irnesi, Ernes)
- Balbura (Katara)
- Bubon (ruins near Elbacik)
- Calynda
- Candyba (Gendova)
- Caunus
- Choma (Hôma?)
- Comba (Gömile kalesi)
- Corydala (ruins at Hacivela)
- Cyanae (Yarvu)
- Eudocia (near Makri)
- Idebessus
- Lebessus
- Limyra
- Marciana
- Mastaura in Lycia
- Meloë in Lycia (near the promontory of Kilidonia)
See also
- Lycian script
- Tomb of Amyntas
References
- ↑ Bernstein, Richard (September 19, 2005). "A Congress, Buried in Turkey's Sand". The New York Time. Archived from the original on 13 October 2010.
- ↑ Harrison, Martin; Young, Wendy (2001). Mountain and plain: from the Lycian coast to the Phrygian plateau in the late Roman and early Byzantine period. Ann Arbor: The University of Michigan Press. pp. 48–50.
- ↑ "Tahtali Dagi (2366 m.)". Antalya Website. antalyaonline.net. 1996-2011.
- ↑ "Xanthos-Letoon". World Heritage – The List. UNESCO. Retrieved 13 October 2010.
- ↑ Keen 1998, p. 11.
- ↑ Keen 1998, p. 49.
- ↑ Book, Section 173.
- ↑ Keen 1998, p. 73.
- ↑ Histories, Book I, Section 176.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 Keen 1998, p. 76.
- ↑ Keen 1998, pp. 78, 116–117.
- ↑ Book 3, Chapter 90.
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 Keen 1998, p. 84.
- ↑ Keen 1998, p. 86.
- ↑ 15.0 15.1 Keen 1998, p. 87.
- ↑ Keen 1998, p. 81.
- ↑ Book 7, Chapter 98.
- ↑ Keen 1998, p. 89.
- ↑ Hill 1897, p. xxvi. Coin Series I of the British Museum, bearing the KUB, is dated by Hill to the window 520-480, somewhat less precisely than the 520-500.
- ↑ "Lycian Dynasts". www.AsiaMinorCoins.com.
- ↑ Haywood, John, et al. Historical Atlas of the Classical World: 500 BC – AD 600. Barnes & Noble Books: New York, New York, 2002, Plate 2.09.
- ↑ Haywood
- ↑ Barraclough, Geoffrey, ed. Collins Atlas of World History. Borders Press: Ann Arbor, Michigan, 2003, p. 77.
- ↑ Black, Jeremy, ed. World History Atlas. Dorling Kindersley: London, 2000, p. 179.
- ↑ Barraclough
- ↑ Bryce & Zahle 1986, p. 102.
- ↑ History of Rome, Book 41.6.
- ↑ History, Book XXV.3.
- ↑ Strabo. "Book XIV, Chapter 3". Geography.
- ↑ Hill 1897, p. xxiii.
- ↑ Strabo. "Book XIII, Chapter 4, Sections 15-17". Geography.
- ↑ "Lycian League cities and coins". www.AsiaMinorCoins.com.
- ↑ Hill 1897, p. xxii.
- ↑ Derow, Peter; Christopher John Smith; Liv Mariah Yarrow (2012). Imperialism, cultural politics, and polybius. Oxford: Oxford University Press. p. 136.
- ↑ Şahin, S. and M. Adak, Stadiasmus Patarensis. Itinera Romana Provinciae Lyciae. İstanbul 2007; F. Onur, Two Procuratorian Inscriptions from Perge, Gephyra 5 (2008), 53–66.
- ↑ 36.0 36.1 36.2 Darke, Diana (1986). Guide to Aegean and Mediterranean Turkey. M. Haag. p. 160. ISBN 9780902743342. "The Lycians were essentially Greeks so they went to Greece, leaving a small population of Turkish farmers to move in behind them. The Greek ghost town of Kaya in the hills behind Fethiye is the most dramatic reminder of this exodus, but derelict Greek houses can also be seen at Kalkan, Kas and Demre."
- ↑ Annuario Pontificio 2013 (Libreria Editrice Vaticana 2013 ISBN 978-88-209-9070-1), "Sedi titolari", pp. 819-1013
Sources
Primary sources
- “Poem on the Battle of Kadesh” 305–313, Ramesses II
- “Great Karnak Inscription” 572–592, Merneptah
- Breasted, J. H. 1906. Ancient Records of Egypt. Vol. III. Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
- “Plague Prayers of Mursilis” A1–11, b, Mursilis
- Pritchard, J. B. 1969. Ancient Near Eastern Texts. Princeton: Princeton University Press.
Secondary sources
- Barnett, R. D. (1975). "The Sea Peoples". In J. B. Bury; S. A. Cook,; F. E. Adcock. The Cambridge Ancient History. II, part 2. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. pp. 362–366. – Refers to many different sea peoples and their contact with Egypt and Anatolia. Also tells about the Philistines during the reign of Ramesses III.
- Bryce, T. (1993). "Lukka Revisited". Journal of Near Eastern Studies 51 (2): 121–130. doi:10.1086/373535. – Discusses Lukka's relations to other regions (like Miletus) and where they inhabited.
- Bryce, T.; Zahle, J. (1986). The Lycians 1. Copenhagen: Museum Tusculanum Press. – Covers the Lycians and where they lived, their history, language, culture, cults, and their language.
- Drews, R. (1995). The End of the Bronze Age: Changes in Warfare and the Catastrophe ca. 1200 B.C. Princeton: Princeton University Press. – A description of the Egyptian evidence on the Sea Peoples.
- Hill, George Francis (1897). "Catalogue of the Greek Coins of Lycia, Pamphylia, and Pisidia". A Catalogue of the Greek Coins in the British Museum. London: Trustees of the British Museum. – A presentation of the history of Lycia during the time of its minting coins, and the coins.
- Keen, Antony G. (1998) [1992]. Dynastic Lycia: A Political History of the Lycians & Their Relations with Foreign Powers, c. 545 - 362 BC. Mnemosyne: bibliotheca classica Batavia. Supplementum. Leiden; Boston; Köln: Brill.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Lycia. |
- Satyurek, Patty; Satyurek, Kemal. "Lycian Turkey". lycianturkey.com. Retrieved 14 February 2012.
- Walker, Christopher; Anderson, Thorne (Photographer) (September/October 2007). "Splendid Ruins for an 'Excellent Republic'". Saudi Aramco World.
- Kamiya, Takeo. "Lycian Influence to the Indian Cave Temples". Retrieved 20 February 2012.
- Foss, Pedar W. "Lycia". Encyclopedia of the Roman Provinces (ERP).
- "Virtual Tours / Myra, Mahmutlar, Lara (Turkey)". EDS Systems. Fullscreen panoramas of the rock-cut tombs of the ancient Lycian necropolis at Myra
- "Virtual Tour—Demre. Myra (Lycia)". Alexander Peskov Photography. 2011.
Coordinates: 36°44′N 29°54′E / 36.733°N 29.900°E
| |||||
| |||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||

