LyX
 | |
 | |
| Developer(s) | The LyX Team |
|---|---|
| Initial release | 1995 |
| Stable release | 2.0.7 / 24 January 2014 |
| Preview release | 2.1.0 beta 2 / 24 November 2013 |
| Development status | Active |
| Written in | C++, Qt 4 |
| Operating system | Cross-platform |
| Available in | Multilingual (23) |
| Type | Document processor |
| License | GNU General Public License |
| Website | www.lyx.org |
LyX (styled as 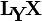 ) is an open source document processor based on top of the LaTeX typesetting system. Unlike most word processors, which follow the WYSIWYG ("what you see is what you get") paradigm, LyX has a WYSIWYM ("what you see is what you mean") approach, where what shows up on the screen is only an approximation of what will show up on the page.
) is an open source document processor based on top of the LaTeX typesetting system. Unlike most word processors, which follow the WYSIWYG ("what you see is what you get") paradigm, LyX has a WYSIWYM ("what you see is what you mean") approach, where what shows up on the screen is only an approximation of what will show up on the page.
Since LyX largely functions as a front-end to the LaTeX typesetting system, it has the power and flexibility of LaTeX, and can handle documents including books, notes, theses, to academic papers, letters, etc. Knowledge of the LaTeX markup language is not necessary for basic usage, although a variety of specialized formatting is only possible by adding LaTeX directives directly into the page.
LyX is popular among technical authors and scientists for its advanced mathematical modes, though it is increasingly used by social scientists and humanities scholars as well[1][2] for its bibliographic database integration[3] and ability to manage multiple files.[3] LyX has also become popular among self-publishers.[4][5]
LyX is available for various operating systems, including Windows, Mac OS X, Linux, UNIX, OS/2 and Haiku. LyX can be redistributed and modified under the terms of the GNU General Public License and is thus free software.
Features
- GUI with menus
- Automatically numbered headings, titles, and paragraphs, with table of contents
- Text is laid out according to standard typographic rules, including indents, spacing, and hyphenation
- Support for right-to-left languages like Arabic,[6] Persian,[7] and Hebrew,[8] including support for bi-directional text
- Support for Chinese, Japanese, and Korean languages
- Basic support, as of LyX 2.0, for the XeTeX and LuaTeX typesetting systems[9]
- Standard operations like cut/paste, spell-checking
- Notes
- Textclasses and templates similar to the \documentclass[arguments]{theclass} command in LaTeX
- BibTeX Support
- Table Editor (WYSIWYG)
- Math Editor (WYSIWYG)
- Ability to import various common text formats
 Screenshot of PDF document created with LyX
Screenshot of PDF document created with LyX - Ability to natively export the document to DocBook SGML, XHTML and plain text
- SVN-support for collaboration
- And others – see detailed list
History
Matthias Ettrich started developing a shareware program called Lyrix in 1995. It was then announced on USENET, where it received a great deal of attention in the following years.
Shortly after the initial release, Lyrix was renamed to LyX due to a name-clash with a word processor produced by the company Santa Cruz Operation.[10] The name LyX was chosen because of the file-suffix '.lyx' for Lyrix files.[11]
Versions
- LyX 0.7.0 was released on October 24, 1995.
- LyX 1.0.0 was released on February 1, 1999.
- LyX 1.2.0 was released on May 29, 2002.
- LyX 1.3.0 was released on February 7, 2003.
- LyX 1.4.0 was released on March 8, 2006.
- LyX 1.5.0 was released on July 27, 2007.
- LyX 1.6.0 was released on November 10, 2008.
- LyX 2.0.0 was released on May 8, 2011.[12]
- LyX 2.0.1 was released on September 5, 2011.
- LyX 2.0.2 was released on November 30, 2011.
- LyX 2.0.3 was released on March 1, 2012.
- LyX 2.0.4 was released on July 2, 2012.
- LyX 2.0.5 was released on November 11, 2012.
- LyX 2.0.6 was released on May 9, 2013.
- LyX 2.0.7 was released on December 18, 2013.
Besides the main distribution of LyX which requires installation, there is also an unofficial portable version integrated with TeXLive called LyTeX.[13]
Pronunciation
According to the project's wiki, the developers pronounce LyX as [ˈlɪks], like the English word "licks", or [ˈlʏks].[14]
See also
- List of word processors
- Comparison of word processors
- Document processor
- Comparison of TeX editors
- Scientific WorkPlace – A proprietary software (non-free) counterpart of LyX
- Qt 4 toolkit, which is used for the user interface in LyX.[15]
References
- ↑ "Lyx for Linguistics".
- ↑ "Lyx for Humanities".
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 "Lyx features".
- ↑ "LyX and Lulu".
- ↑ "LyX produced publications".
- ↑ "Arabic support for LyX".
- ↑ "Farsi support for LyX".
- ↑ "Hebrew support for LyX".
- ↑ "New in LyX 2.0". Retrieved 2010-11-19.
- ↑ "WANTED: Name for Wordprocessor (comp.os.linux.development.apps)". Retrieved 2010-10-15.
- ↑ LyX Archaeology
- ↑ "ANNOUNCE: LyX version 2.0.0 is released". Retrieved 2011-05-08.
- ↑ LyTeX
- ↑ FAQ/Pronunciation, LyX Wiki. Retrieved 4 April 2008.
- ↑ http://wiki.lyx.org/LyX/NewInLyX15#toc13
External links
- Official LyX Website
- LyX Wiki
- A comparative review of Scientific WorkPlace and LyX in Journal of Statistical Software
- Collection of thesis and dissertation LyX-templates
| ||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||