Low Coniscliffe
| Low Coniscliffe | |
 West end of village |
|
 Low Coniscliffe | |
| OS grid reference | NZ247137 |
|---|---|
| Unitary authority | Darlington |
| Ceremonial county | County Durham |
| Region | North East |
| Country | England |
| Sovereign state | United Kingdom |
| Post town | DARLINGTON |
| Postcode district | DL2 |
| Dialling code | 01325 |
| Police | Durham |
| Fire | County Durham and Darlington |
| Ambulance | North East |
| EU Parliament | North East England |
| UK Parliament | Sedgefield |
| |
Low Coniscliffe is a village in the civil parish of Low Coniscliffe and Merrybent, in County Durham, England. It is situated 3 miles (4.8 km) west of Darlington. Its present built-up area is confined in practice between the A1, the A67 and the Tees, but its old boundaries probably extend much further. Its most obvious landmark on the A67 is the Baydale Beck Inn. The village contains a couple of listed buildings and the probable site of a medieval manor house. There was once a gallows in the village.[1] A rare fungus Rhodotus palmatus was found nearby.[2][3]
Geographical and political

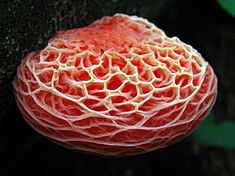
In 1762 the village had a turnpike gate.[8] In the 1891 census Low Coniscliffe included Coniscliffe Grange, Dublar Castle and East Farm,[9] and there was a Badle Beck Inn which is probably the current Baydale Beck Inn.[10] The village was not affected by the flooding of 2007, but lost power for one morning.[11] Chenopodium glaucum, or oak−leaved goosefoot, was found here in 1930, and Yellow Star of Bethlehem was found in 1942.[12] The rare fungus Rhodotus palmatus was found in the area in 1993.[2][3]
History

A foundling was abandoned on 31 January 1602 on the window ledge of a house in Nether Cunsley which was occupied by Cuthbert Smith. The child, who lived for 69 years until 21 December 1671, was baptised Tychicus, with no surname.[13] The inhabitants of Thornton Hall were associated with Lowe Coniscliffe.[6] Sir Francis Bowes, who was born in 1648 and became High Sheriff of Northumberland, lost most of his family during his lifetime and left a memorial to them in the parish church at High Coniscliffe.[14] In 1848 the village had 134 inhabitants.[6] Arthur Pease of Darlington gave instructions in 1877 for the building of the British School for 105 pupils.[13] Scouts and Cubs used to come to the banks of the Tees near here in the 1920s for picnics.[15]
Archaeological sites and finds


A Palaeolithic axehead was found somewhere in the area.[16] Roman coins were found in 1856 and 1978 in Cocker Beck, and the later finds were dated 308–346 AD.[17] Bishop Bek ordered a tower to be built in Low Coniscliffe in the 13th century; the site is unknown, but it may be the site of the manor house.[18] There is an unknown site of a gallows, pre−1293 AD, south of the Tees, and west of Howden Hill Farm.[1] The extreme south−west end of the present built−up area of the village is probably the site of the old medieval manor house, 1066–1540. The site includes earthwork enclosures, and a 1960s excavation revealed a 15th–16th century round dovecote.[19] There is supposed to be another dovecote here; location unknown.[20] The house at the south−west end of the village, numbers 55–57, is a 17th-century listed building: a roughcast brick and rubble structure with a pantiled roof. This is a pair of houses; once a farmhouse with a cottage on the right.[21] Well Bank House, number 20 near the south−east corner of the village, is a listed building dated around the late 18th to early 19th century. Like numbers 55–57 it is built of roughcast rubble with a pantiled roof, and this building contains a 19th-century iron range.[22]
Low Coniscliffe today
It is now a dormitory village for Darlington, and there is no school; the nearest post office is at Mowden Park in Darlington. The Baydale Beck Inn serves real ale and permits dogs in the bar.[23][24]
Just to the east of the village is Tees Cottage Pumping Station, a Victorian pumping station now opened as a museum containing a 1904-built rotative beam engine, and a 1914 gas engine, believed to be the largest working preserved example in Europe.
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 "Keys to the past". Low Coniscliffe; Gallows (Low Coniscliffe). 2010. Retrieved 6 April 2010.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Downie, S.; Coulson, J. C.; Bauer, L J.; Butterfield, J. E. L; Davies, L; Goodyer, S. A. (1993). "The-vasculum.com". New and significant records of fungi, ISSN 004g-6891. Retrieved 6 April 2010.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Coles, A.; Jessop, L. (October 1994). "The Vasculum, Vol.79, No.3". RUSSULALESBASIDIOMYCOTINA: AGARICALES, BOLETALES, CORTINARIALES. Sunderland Museum and Art Gallery. Retrieved 6 April 2010.
- ↑ "British Geological Survey". Caves, subsidence and soluble rocks. BGS. 2010. Retrieved 6 April 2010.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 "Streetmap.co.uk". Low Coniscliffe. 2010. Retrieved 6 April 2010.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 Lewis, Samuel, ed. (1848). 'Conhope – Cooknoe', A Topographical Dictionary of England: Low Coniscliffe. Institute of Historical Research. pp. 679–682. Retrieved 6 April 2010.
- ↑ "My Wainwrights". The Coniscliffes. 25 May 2009. Retrieved 6 April 2010.
- ↑ Raine, Jo (1 July 2007). "Raine genealogy". Other Raine info: Burials and Memorial Inscriptions. Retrieved 6 April 2010.
- ↑ "Your Archives". Place:Darlington Registration District, 1891 Census Street Index C-F. 2010. Retrieved 6 April 2010.
- ↑ "Your Archives". Place:Darlington Registration District, 1891 Census Street Index P-R. 2010. Retrieved 6 April 2010.
- ↑ "The Northern Echo". Emergency teams on standby for flooding. 30 June 2007. Retrieved 6 April 2010.
- ↑ Simpson, N.D. (1960). "bsbi.org.uk". Bibliographic index to the British Flora. p. 122. Retrieved 6 April 2010.
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 "High Coniscliffe CE Primary School". About Us. 2010. Retrieved 2 April 2010.
- ↑ Peile, John. "Google books". Biographical Register of Christ's College, 1505–1905. p. 608. Retrieved 6 April 2010.
- ↑ "DBC Leisure and Culture". Low Coniscliffe, Darlington Boy Scouts and cubs. 2007. Retrieved 6 April 2010.
- ↑ "Keys to the past". Low Coniscliffe; Axehead (Low Coniscliffe). DCC. 2010. Retrieved 6 April 2010.
- ↑ "Keys to the past". Low Coniscliffe, Cocker Beck; Roman coins found. (Low Coniscliffe). DCC. 2010. Retrieved 6 April 2010.
- ↑ "Keys to the past". Low Coniscliffe; site of tower. (Low Coniscliffe). DCC. 2010. Retrieved 6 April 2010.
- ↑ "Keys to the past". Low Coniscliffe; site of manor house. (Low Coniscliffe). DCC. 2010. Retrieved 6 April 2010.
- ↑ "Keys to the past". High Conniscliffe; Dovecote (Low Coniscliffe). DCC. 2010. Retrieved 6 April 2010.
- ↑ "Keys to the past". Low Coniscliffe, 55–57; Listed building (Low Coniscliffe). DCC. 2010. Retrieved 6 April 2010.
- ↑ "Keys to the past". Well bank house; Listed building (Low Coniscliffe). DCC. 2010. Retrieved 6 April 2010.
- ↑ Crosby, E.K. (2001–2007). "Doggie pubs". England: Low Coniscliffe: The Baydale Beck. Retrieved 6 April 2010.
- ↑ "Beer in the evening". The Baydale Beck Inn, Low Coniscliffe. 2010. Retrieved 6 April 2010.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Low Coniscliffe. |
 |
Merrybent | Archdeacon Newton | Hummersknott Darlington |
 |
| Greystones Manfield |
|
Darlington | ||
| ||||
| | ||||
| River Tees / Howden Hill Cleasby |
River Tees / Cleasby | River Tees / Blackwell Darlington |