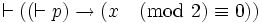Logical assertion
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
In mathematical logic, logical assertion is a statement that asserts that a certain premise is true, and is useful for statements in proof. It is equivalent to a sequent with an empty antecedent.
For example, if p = "x is even", the implication
is thus true. We can also write this using the logical assertion symbol, as
In computer programming and programming language semantics, these are used in the form of assertions; one example is a loop invariant.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike; additional terms may apply for the media files.